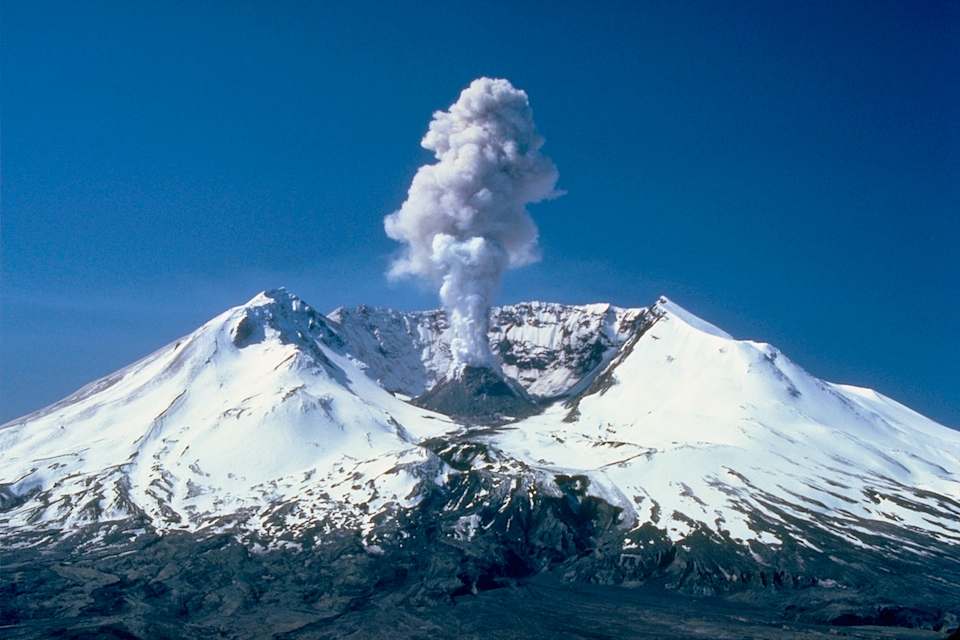
Earth’s crust is broken into 17 major tectonic plates, which float on its mantle (the layer beneath the earth’s surface). Since these plates are always converging or diverging, sometimes they collide or pull apart, and volcanoes may erupt in these active zones. During a volcanic eruption, molten rock or lava come out through vents in Earth’s crust. When the lava is beneath the earth’s surface, it is called magma. Mount St. Helens (USA), Mauna Loa (Hawaii), Mount Cotopaxi (South America), Mount Pinatubo (Philippines) are some famous volcanoes in the world.
How Many Types of Volcanoes Are There
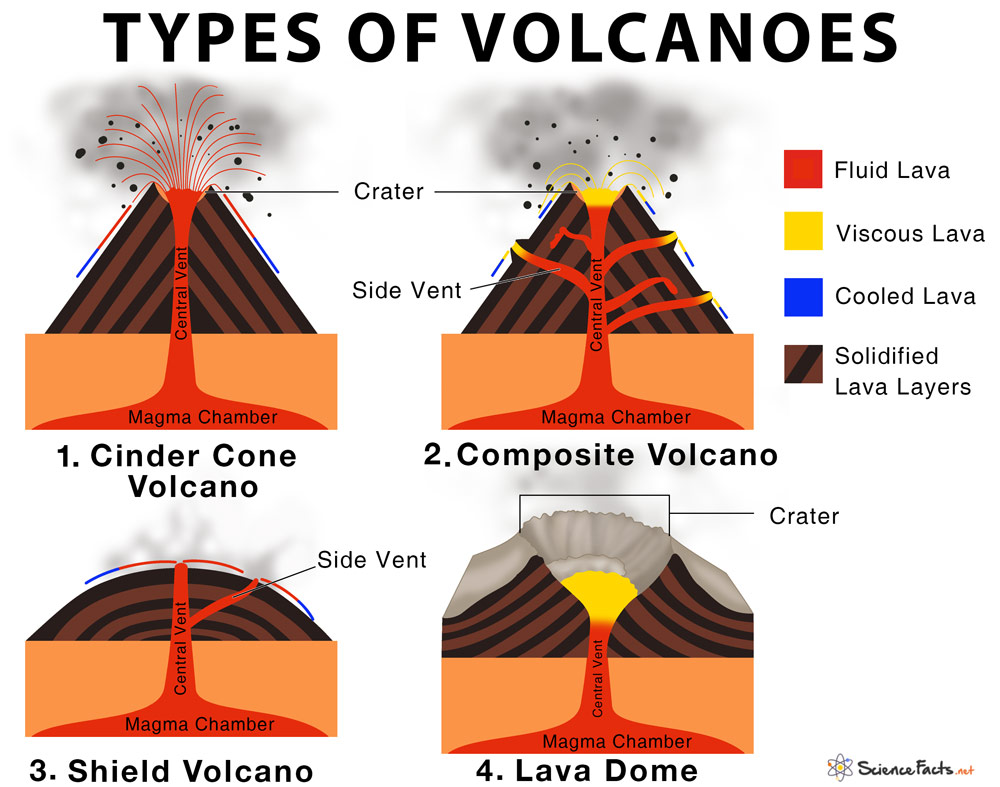
What are the Different Types of Volcanoes Based on Their Eruption Characteristics
What are the Different Types of Volcanoes Based on Their Frequency of Eruptions
Based on their frequency of eruption, volcanoes can be of three types – active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes. Lava Type: Less viscous, quite fluid basaltic lava (enriched in iron and magnesium and depleted in silica) Examples: Lava Butte in Oregon (USA), Cerro Negro in Nicaragua (Central America), Parícutin in Mexico.
2. Composite Volcano
Also referred to as strato-volcanoes, it includes some of the world’s grandest mountains. It is a tall conical mountain composed of an alternating layer of lava-flow, which justifies the name composite volcano. It can have a cluster of vents, with lava breaking through walls or issuing from fissures on the sides of the mountain. The eruptions are extremely explosive and dangerous. Pressure builds in the magma chamber as gases under immense heat and pressure are dissolved within the magma. When the magma reaches the vents, the pressure is released, and the gases explode violently. These can be up to 100 to 3500 meters high. Lava Type: Highly viscous rhyolitic lava that hardens before it can spread far (high content of silica and low iron and magnesium contents) Examples: Mount St. Helen and Mount Rainier in the USA, Mount Etna and Stromboli in Italy, Mount Fuji in Japan, Cotopaxi in Ecuador, Mount Vesuvius in Italy, Mount Pinatubo and Mayon in the Philippines, Volcan de Colima in Mexico, Eyjafjallajokull in Iceland, Popocatepetl in Mexico, Arenal Volcano in Costa Rica, Mount Shasta (White Mountain) in USA.
3. Shield Volcano
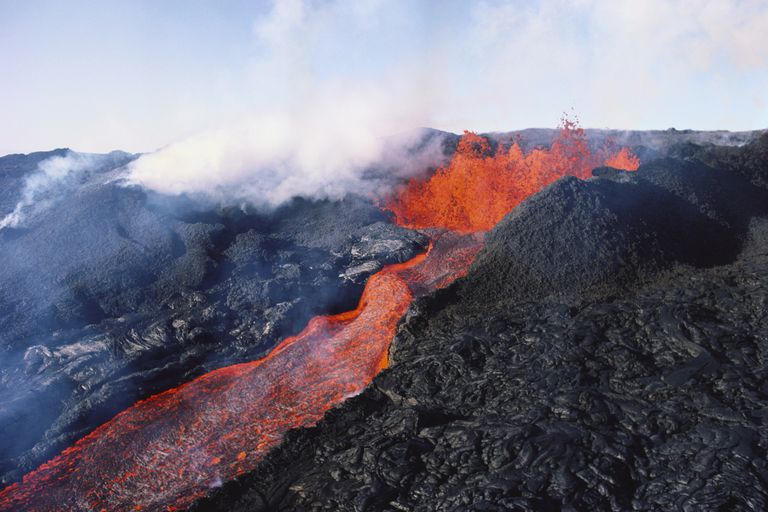
Shield volcanoes are huge, gently sloped volcanoes that almost exclusively erupts basaltic lava and include some of the largest volcanoes in the world. The eruptions are not explosive; the lava oozes out from the central vent or a group of vents and spreads far, building a dome shape profile like a warrior’s shield. They can be as high as 9000 meters from the base. Lava Type: Less viscous, quite fluid basaltic lava Examples: The volcanoes in the Hawaiian Island, including Kilauea, Diamond Head, Mauna Loa, and Mauna Kea
4. Lava Dome
These are relatively small, circular mounds formed as the lava is too viscous to flow, which makes it piles over and around the vents. As the lava oozes out, its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, spilling loose fragments down its side. Lava domes are found within the crater or on the sides of large composite volcanoes. Their height depends on the size of the composite volcanoes they appear around. Lava Type: Highly viscous, less fluid rhyolitic lava Examples: Lassen Peak and Mono domes in California (USA), Novarupta lava dome in Alaska (USA) Examples: Mount Etna in Italy and Mauna Loa in Hawaii.
2. Dormant Volcanoes
Those that have not erupted in the last 10,000 years, but are likely to erupt after remaining inactive for a long period. Examples: Mt. Kilimanjaro in Africa and Mt. Fuji in Japan.
3. Extinct Volcanoes
Those that were active in the past, but have not erupted in the last 10,000 years and are not likely to erupt in the present or the future. Examples: Mt. Kenya in Africa and Mt. Aconcagua in South America. Ans. Caldera is a bowl-shaped depression formed when a volcano collapses shortly after emptying the magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. Though sometimes considered a separate type of volcano, it is actually formed as an after-effect of an eruption. Yellowstone Caldera in the USA is one such example. Q 2. What are pyroclasts or pyroclastic materials? Ans. Pyroclasts refer to the rocks, lava fragments, ash, vapor expelled during volcanic eruptions. Q 3. What is the world’s largest active shield volcano? Ans. Mauna Loa (Hawaii).