Pollution is primarily human-made, but nature can have an adverse effect also sometimes acts as a source of pollution.
What are the Different Types of Pollution: Causes and Effects
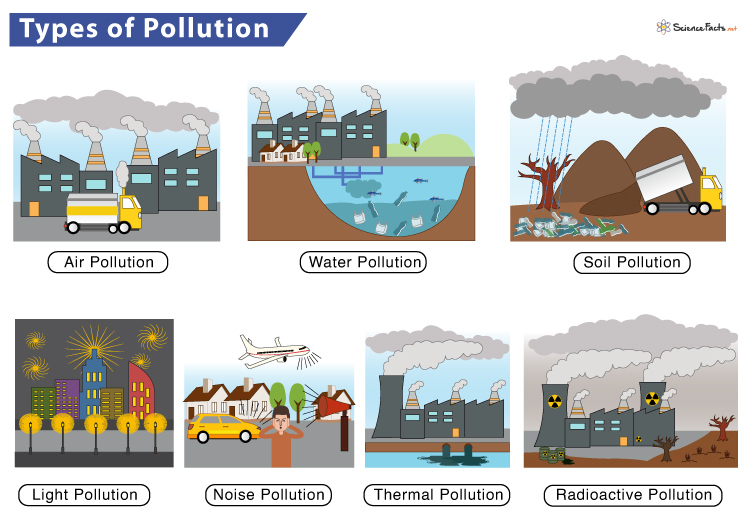
1. Air Pollution
The air in our atmosphere has a roughly stable chemical composition consisting of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases. Any change in the air composition due to the addition of unwanted gases such as sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides, chemicals, particulate matter, and biological molecules is called air pollution. Among all other types of pollution, air pollution is found to have the most diverse impact on Earth. Sources/Causes Air pollution can happen from both human-made (anthropogenic) and natural sources. Some of the significant sources of air pollution are given below:
Burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gasExhaust from automobiles and industriesIndiscriminate cutting of trees (deforestation)Wildfires resulting from burning stubble and farm residuesRelease of methane from microbial decayExcessive discharge of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and nitrous oxideChlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) released from aerosols sprays, refrigerants, and air conditionersRelease volcanic ash and gases
Effects
Respiratory disorders in humans such as asthma, lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, and other lung problemsFormation of smog that reduces visibilityFormation of acid rainDepletion of the ozone layerGlobal warmingHazards to wildlife
Prevention
Planting of trees (afforestation) purifies the airUse of renewable energy such as sunlight and wind energy and reducing dependence on nonrenewable sources such as coal, petroleum, and natural gasIncreasing efficiency in energy usageUse of eco-friendly vehiclesCleaning of industry emissions before their release into the atmosphereReducing dependence on vehicles
2. Water Pollution
Water pollution occurs when toxic pollutants and particulate matter are introduced into water bodies such as oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds, and aquifers, making them impure and toxic. These contaminants are primarily generated by human activities and sometimes by natural disasters. Among all other types of pollution, water pollution is found to have the maximum adverse consequences on the ecosystem. Sources/Causes
Industrial and domestic sewage dischargeOil spills and natural gas leakage into water bodies from underground sites called petroleum seepsSocial practices such as washing, bathing, and littering in water bodies and religious practicesAcid rainAgricultural runoff containing pesticides, fertilizers, herbicides, slurry, debris, and manuresMining and drilling sometimes make underground water contaminatedFloods and storm carrying dust and debris to the water bodies
Effects
Algal bloom (eutrophication) caused due to an increase in nutrients of the water bodiesReducing dissolved oxygen in the water bodies thus disrupting aquatic lifeDisturbing the pH and salinity of the water bodies leading to loss of aquatic lifeIncreasing the risk of water-borne diseases such as hepatitis, cholera, diarrhea, and typhoid in humansIncreasing the level of toxins and pollutants at each successive level of the food chain (biomagnification)
Prevention
Proper disposing of domestic, agricultural, and industrial wastes before releasing them into water bodiesUsing sewage treatment methods such as precipitation, ion exchange, reverse osmosis, and coagulationReducing reusing, and recycling of waterUsing plants such as water hyacinth that absorbs heavy metals in areas contaminated with radioactive pollutants
3. Soil Pollution
Sometimes called land pollution, it refers to the degradation of land quality due to unwanted chemicals and other factors in the soil. Such chemicals change the soil’s chemical and biological properties, thus affecting plant growth. Green plants, being the primary producer, absorb those pollutants, which are then passed through the food chain, affecting the whole ecosystem. Soil pollution can seep into groundwater or run off to the nearest streams and lakes, creating a vicious pollution cycle. Sources/Causes
Intensive farming leading to the overuse of agrochemicals such as pesticides, fertilizers, herbicides, slurry, debris, and manuresImproper disposal of wastes from paper mills, sugar factories, petroleum, and chemical industriesDust particles such as silica dustUrban wastes consisting of garbage and rubbish materials, dried sludge, and sewage from households and commercial bodiesAccidental oil spills from oil refineriesRadioactive pollutants such as radium, thorium, and uranium from power plantsAcid rain, increasing the acidity of the soilDeforestation that increases soil erosion causing low soil fertility
Effects
Loss of soil fertility making it unfit for agricultureAdverse effect on the growth of flora and fauna in the soilGroundwater pollutionIncreasing the salinity of the soil, making it unfit for agricultureCausing respiratory problems, neuromuscular blockage, and various forms of cancer, especially lung cancerCausing nausea, headache, eye irritation, skin rash, and depression
Prevention
Use of organic matures instead of artificial fertilizers in agriculturePlanting of trees (Afforestation)Treating solid wastes such as garbage, domestic refuse, and industrial materials before dumping them in landfillsRecovering and recycling of materials such as plastics, cloth, and glass before dumping
4. Other Types of Pollution
- Light Pollution Light pollution refers to the excessive amount of light in the night sky. It occurs due to excessive, misdirected, and inefficient lighting systems by humans. It is also called photo pollution that disrupts the ecosystem by reducing the distinction between night and day. Although light pollution seems to have a lesser impact than any other form, it is expected to have consequences similar to air or water pollution. Sources/Causes
Increased energy consumption through over-illumination from artificial light sources such as street lighting, domestic lighting, and garagePoor planning by engineers while placing street lights and signageOverpopulation increases electricity consumption, which increases glareSmog and fog due to air pollution reflect light emitted by cities, making the surrounding look much brighter
Effects
Produce behavioral changes in animals. Nocturnal animals, who are active at night, venture out during the daytime. In contrast, diurnal animals, which are active during the day, remain active at nightAffecting migration pattern in seasonal birdsDifficulty for astronomers to see the stars properlyAffecting newly hatched turtles that rely on starlight to guide them from the beach to the ocean. They often head in the wrong direction.Causing flowering and developmental patterns in plantsInducing smog by destroying nitrate radicals, helping in the dispersion of smog, and causing air pollutionInducing a delay in melatonin secretion in humans, which delays sleep at night
Prevention
Reducing the use of decorative lightings that produce more light and consumes more energyUse of covered bulbs or light that face downwardsSwitching to an LED light that reduces luminance without compromising visibilityProper planning during installation of street lights and signageSwitching off street lights during daytimeUsing glare-free lighting in the outdoorsStopping light-trespass
- Noise Pollution It refers to the excessive amount of sound in the surroundings disrupting the natural balance. The acceptable amount of sound is about 60 to 65 decibels, which is the same as our everyday conversation. Sound levels above 85 decibels are harmful depending on the duration of exposure. Noise above 140 decibels can cause permanent hearing loss. Also, the duration of exposure to the sound is found to have negative health impacts. Sources/Causes
Noise from heavy machines in factories, mills, and industriesTraffic noise from vehicles (trains and buses) and airplanesConstruction noises from boring and drilling machinesNoise from firecrackers and loudspeakers in social eventsHousehold noises from television, mixer grinders, and music systems
Effects
Loss of hearing and behavioral disordersLoss of focus on work leading to low work outputStress and Hypertension (high blood pressure)Lack of sleep and fatigueDifficulty in speech and impairment
Hearing disorders like tinnitusSongbirds, such as robins, fail to communicate and find foodDisrupting sonar, used by marine animals to communicate and locate food
Prevention
Honking in public places like hospitals, academic institutions such as schools and colleges should be bannedInstalling adequate soundproof systems in commercial buildings and hospitalsAfforestation as trees can absorb soundRestricting the use of firecrackers during festivities and doing open public rallies
Apart from the types of pollution discussed, there are other forms of pollution called thermal or heat pollution and radioactive pollution. Thermal pollution is caused due to excessive heat in the environment released from industrial power plants, deforestation, urban sprawl, and air pollution. It increases the Earth’s atmosphere causing drastic climate change and extinction of wildlife. In contrast, radioactive pollution results from accidental leakage from nuclear power plants and improper disposal of nuclear wastes. It can cause massive, long-lasting impacts such as cancer, infertility, blindness, and congenital disabilities.