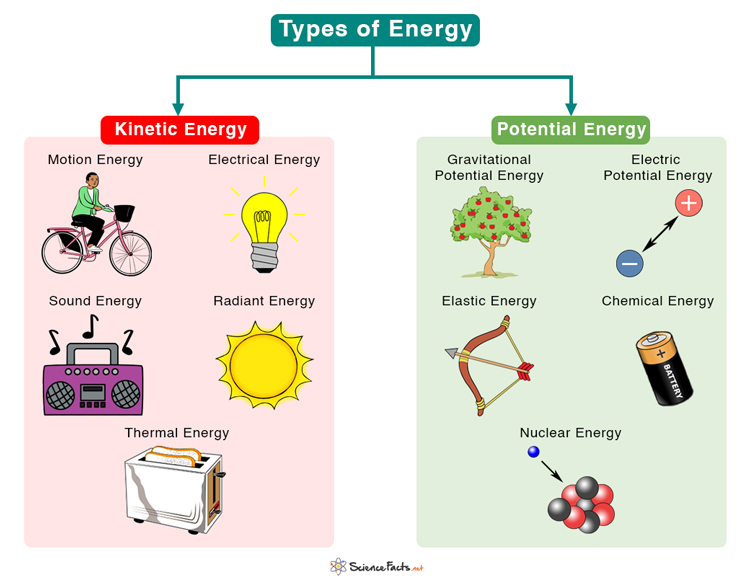
Kinetic Energy
Potential Energy
1. Motion Energy
Motion energy is the energy due to the movement of an object. The faster the object moves, the higher its energy is. Also, a heavier object has more energy than a lighter one. Examples
A person cyclingA bullet moving through the airWind howling
2. Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is due to the flow of electrons in a wire that results in current. It is used at home to power electrical appliances. Examples
Powering a televisionTurning on the lightsLightning
3. Sound Energy
Sound energy is due to the vibration of air particles. When these vibrations reach the ears, the brain perceives them as sound. Examples
Drumming of drumsA balloon poppingA plane flying
4. Radiant Energy
Radiant energy is due to oscillating electric and magnetic fields. It propagates in a direction perpendicular to the planes of oscillations. Particles or waves carry the energy. Examples
Light and heat from the SunRadiation emitted by an X-ray machineMicrowave emitted by a microwave oven
5. Thermal Energy
Thermal energy is because of the random motion of atoms and molecules in a substance. It is transferred as heat, which alters the temperature of the substance. The thermal energy present underneath the Earth’s surface is called Geothermal energy. Examples
Baking a pie in an ovenA hot cup of coffeeThe heat from an electric heater
1. Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is due to the Earth’s gravitational force. It is the energy stored in an object due to its height from Earth’s surface. The greater the height, the higher the gravitational potential energy. Examples
An object suspended in the airA car on top of a hillAn apple on a tree
2. Electric Potential Energy
Electric potential energy is due to the interaction between charged particles. A point charge in an electric field has potential energy. Examples
Capacitor
3. Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is stored in an elastic material when compressed or stretched. When the energy is stored in the spring, it is called spring energy. Examples
A stretched rubber bandAn archer stretching a bowA person jumping on a trampoline
4. Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is the energy stored in the bonds of a chemical compound. It is released during a chemical reaction when the bond breaks. Examples
A battery powering a flashlightGasoline fueling a vehicleDigesting food
5. Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is the energy inside the atoms that make up matter. It is released when atoms combine (nuclear fusion) or split (nuclear fission). Examples
The fusion reaction in the SunFission reaction in nuclear power plants to produce electricityFission reaction in a nuclear bomb