Rainforest is home to diverse plants and animal species. They are home to almost 150 species of butterflies, 125 species of mammals, 100 species of reptiles, 1500 species of unique flowering plants, 60 amphibian species, and almost 400 bird species.
Tropical Rainforest Food Chain Examples
Decomposers
Competition and Interdependence within the Rainforest
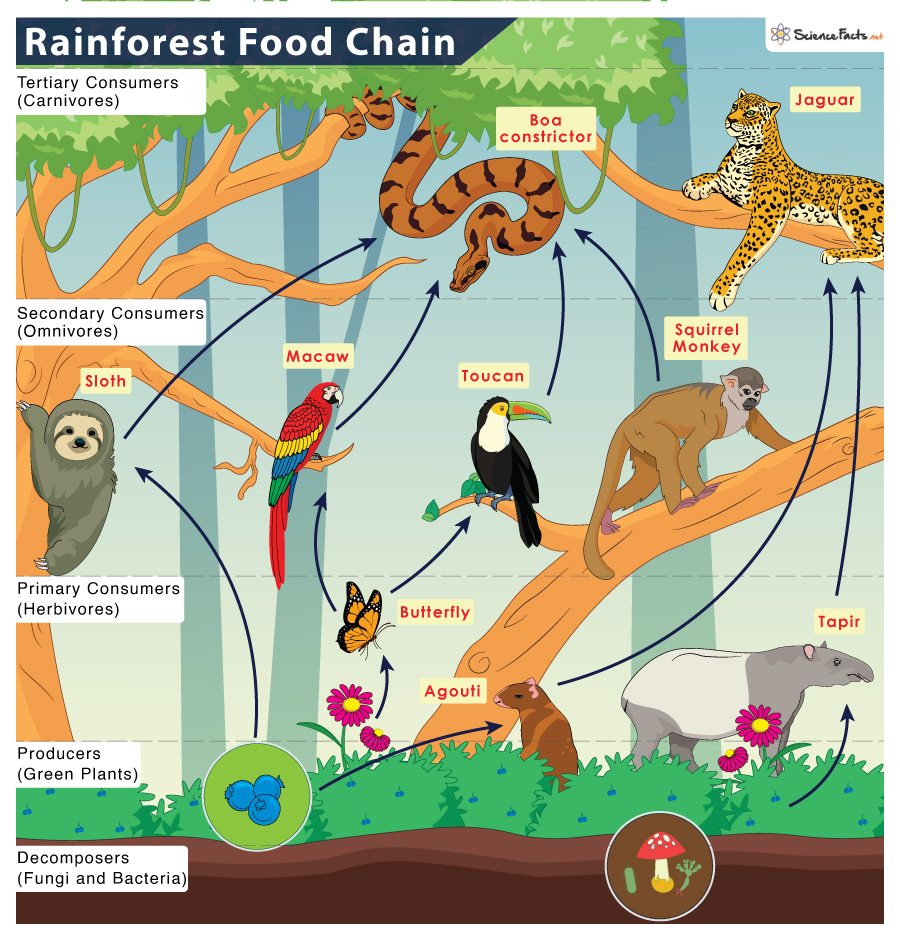
Producers
These organisms are found at the bottom of the food chain. With over 40,000 plant species in the tropical rainforest, this trophic level is the most diverse and extensive food chain. They are the primary food source for organisms that feed on them for survival. Trees such as bananas, bamboo, coconut, orchids, bromeliads, epiphytes, microscopic algae, ferns, and mosses make up the ecosystem’s flora.
Primary Consumers
Next to producers in the food chain are the primary consumers. They are herbivorous animals that feed on green plants for their food. Fishes, kangaroos, birds, macaws, monkeys, agouti, and sloths are some examples of primary consumers in the rainforest food chain.
Secondary Consumers
Above the primary consumers are the secondary consumers that feed on primary consumers (non-plant eaters) and producers (plant eaters). Secondary consumers are thus primarily omnivores. Small animals and birds like snakes (boa constrictors), lemurs, deer, woodpeckers, bats, owls, and kookaburras are all secondary consumers in the rainforest food chain. Scavengers like toucans are opportunists and prey on insects, smaller birds, and small lizards.
Tertiary Consumers
They are top-order consumers found at the apex position of the food chain. Based on their participation in the food chain, the same animal can assume the role of a tertiary consumer or the highest-level predator, the apex consumer. Large carnivores include tigers, dogs, cats, jaguars, cougars, leopards, crocodiles, alligators, green anacondas, pythons, Philippine eagles, black eagles, and crowned eagles are examples of tertiary and apex consumers. Even sometimes, larger animals prey on smaller animals compared to their usual prey. Birds in the rainforest usually eat snakes, but sometimes the reverse is also true. The largest carnivores, the alligators, usually feed on smaller animals and a few larger ones. However, sometimes it catches a giant carnivore. Even a snake kills an alligator baby for its food. Even decomposers will also not survive if plants and animals do not die. Also, like any rainforest creature, the top predators, like the big cats, face threats from human predation. Thus, every species in the rainforest is connected to another either directly or indirectly, keeping the food chain active. Let us suppose organisms in any particular food chain level become extinct or are endangered. In that case, the balance of interdependence will become disrupted, and the ecosystem and its food chain will be in danger.