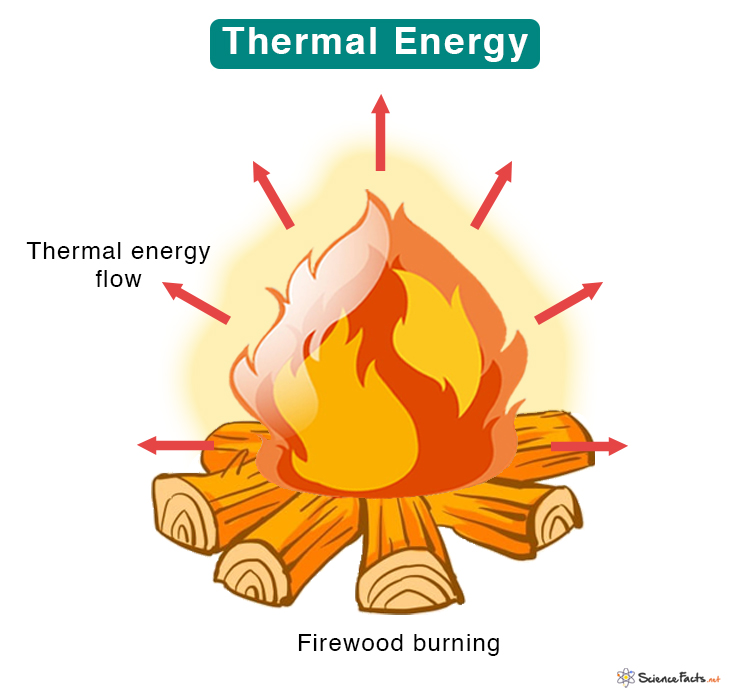
English physicist and mathematician James Prescott Joule discovered thermal energy in 1847.
How is Thermal Energy Produced
What is the Difference Between Thermal Energy and Heat
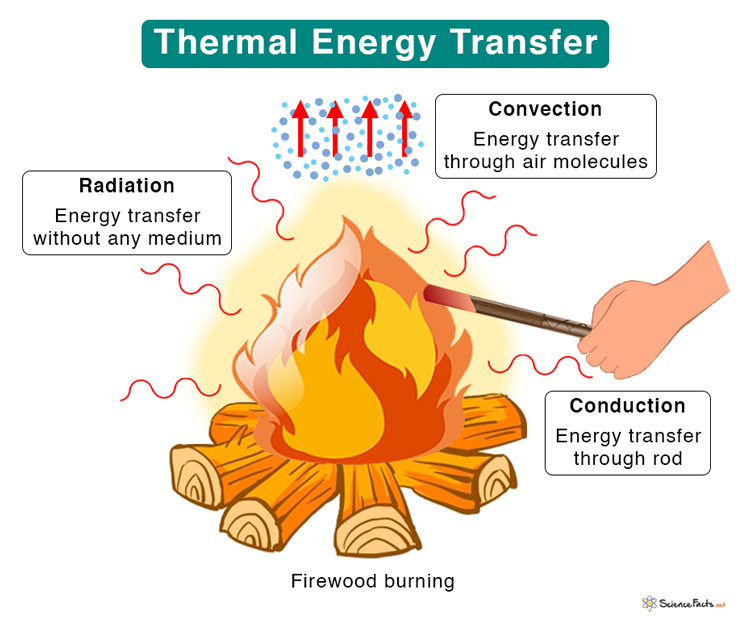
Thermal Energy Transfer
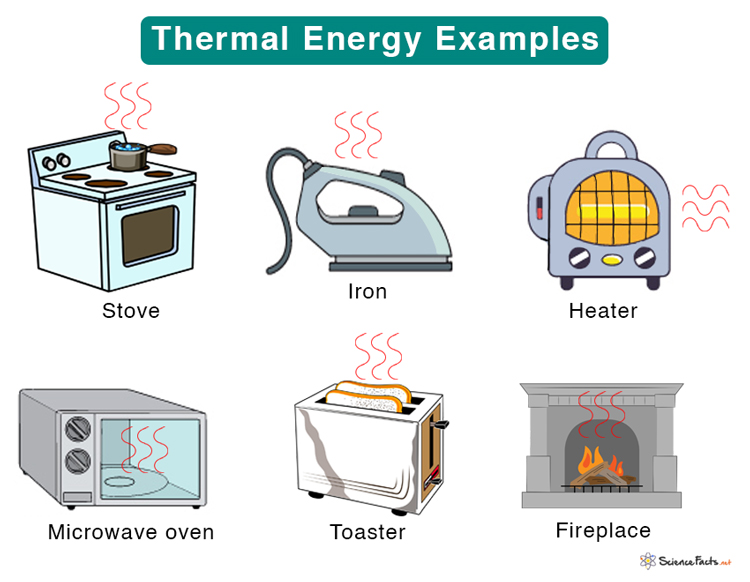
Examples of Thermal Energy
How to Calculate Thermal Energy
Applications of Thermal Energy
- Conduction: A process through which thermal energy is transferred between two molecules in contact. The transfer occurs when molecules strike one another, resulting in collisions. Conduction takes place in solid, liquid, and gas. For example, when we heat one end of a metal rod, thermal energy quickly transfers to the other end.
- Convection: It occurs when thermal energy is transferred through a medium like liquid or gas. Molecules carry the energy from a hot region to a cold region. For example, when we boil water in a pan, the molecules at the bottom get heated first and carry the energy to the top.
- Radiation: It is the process by which energy is transferred without contact between the molecules. No medium is necessary for the energy to travel as electromagnetic waves carry it. An example of radiation is sunlight which is essential for all living beings on Earth. The energy received from the sun is known as solar thermal energy. It is renewable.
Stove, microwave oven, toaster, and heater are sources of thermal energyA cup of hot tea or a slice of hot pizza radiates thermal energyA glass of water transfers thermal energy to an ice floating on itA bathtub filled with hot water, a hot water pool, and a spa conducts thermal energyConvection currents carry thermal energy in the atmosphere
Conversion of Chemical Energy into Thermal Energy
Burning of coal, natural gas, and gasolineAn explosionCombustion and exothermic reactionsHand warmersButane torch
Conversion of Electrical Energy into Thermal Energy
HeaterMicrowave ovenHeat pumpToasterCoffee making machine
An example of a device that converts thermal energy into electrical energy is a thermoelectric generator. W = F · d Or, W = f · d Where W : Work done F: Applied force d : Displacement of the box f : Friction force From the law of conservation of energy, work done by the man is converted into thermal energy. Heat is generated in the region between the box and the floor, which increases the temperature. The equation can be written as follows. Change in thermal energy = Work done Or, ΔET = f · d Where ΔET : Change in thermal energy SI Unit: Joule or J (1 J = 1 kg m2/s2) The friction force is given by f = μKFN Where μK : Coefficient of kinetic friction FN : Normal force The normal force can be written in terms of the box’s mass. FN = mg Where m : Mass of the box g : Acceleration due to gravity Therefore ΔET = μKmg The example above shows how mechanical energy (man pushing a box) can be converted into thermal energy. It is also possible to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy by using a heat engine.