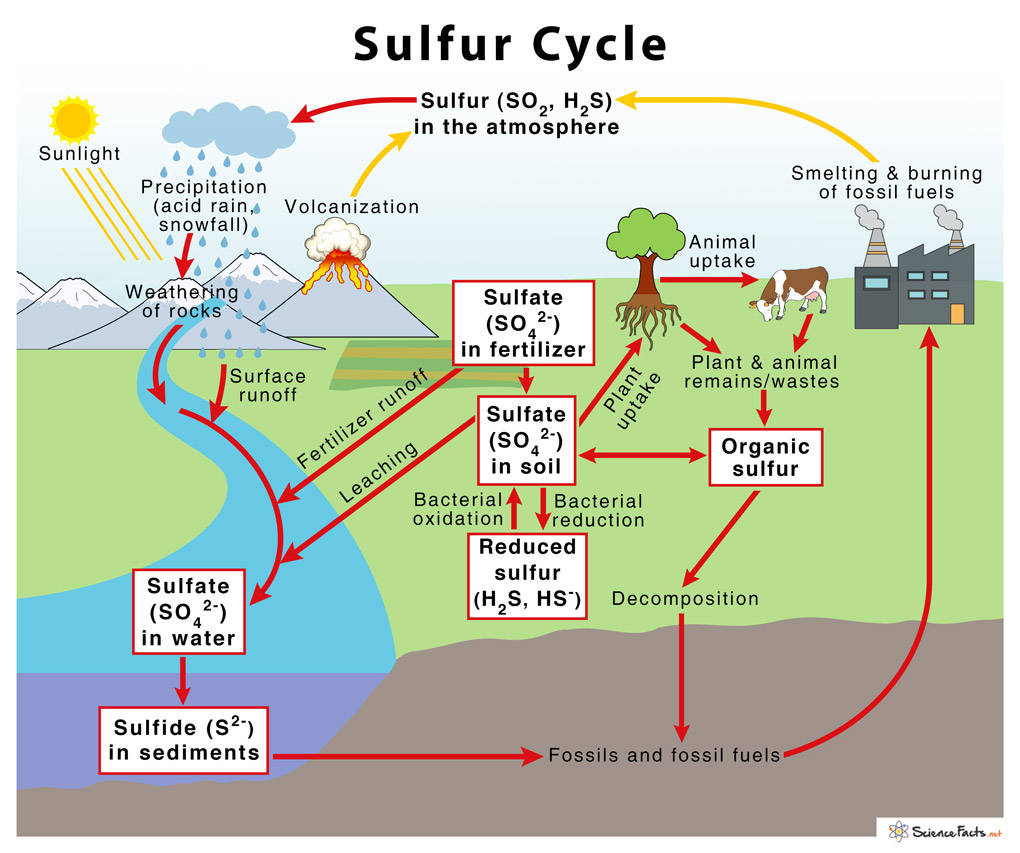
It occurs through two different processes – 2) Oxidation of Inorganic Sulfur to Sulfate (SO42−) It involves two steps – 3) Assimilative Reduction of Sulfate to Sulfide (S2−) Also known as sulfur reduction, it is performed by plants, fungi and various microorganisms such as Desulfovibrio and Desulfobulbus species in two steps – 4) Incorporation of Sulfide into Organic Compounds The sulfide assimilated is converted into an organic form which the animals consume and fix through the foods they eat. Once these plants and animals die, decomposers release the fixed organic sulfur back into its free form as elemental sulfur.
Releasing sulfur from oil and coal-based power plantsProcessing of sulfur-containing metalsUsing sulfur-containing fertilizers
The sulfur emitted through all the above human activities reacts with water, oxygen, and other chemicals in the atmosphere and precipitates down in the form of rain, known as acid rain that reduces agricultural yield, affects marine life, and damages buildings and monuments