History and Discovery of the Strong Nuclear Force The first theory of the strong nuclear force was discovered in 1935 by Japanese physicist Hideki Yukawa, who discovered the force-carrying particles known as mesons. He suggested that nucleons exchanging particles create a force field.
Strength and Range of Strong Nuclear Force
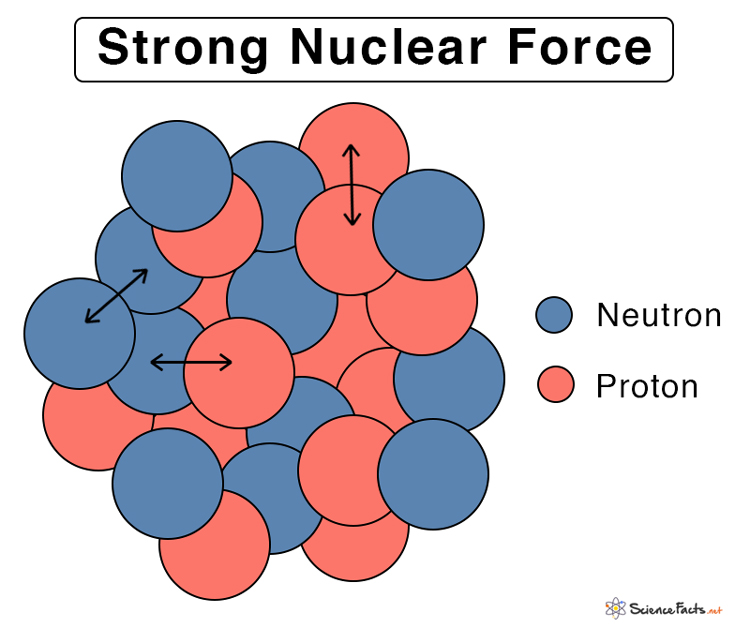
How does the Strong Nuclear Force Work
Properties of Strong Nuclear Force
Examples of Strong Nuclear Force
Relative Strength and Range of Fundamental Forces The particles responsible for carrying the strong nuclear force are known as gluons. It is so-called because the particles are like ‘glue,’ that holds the protons, neutrons, and quarks together. An exchange of gluons causes the strong nuclear force. The theory that describes the strong force is called quantum chromodynamics (QCD).
The most potent force in natureExchange forceShort-range (~10-15 m)Non-central and non-conservativeSpin-dependent and charge-independentDoes not follow product law and the inverse-square law137 times stronger than the electromagnetic force, 106 times stronger than the weak nuclear force, and 1.67 x 1038 times stronger than the gravitational force.