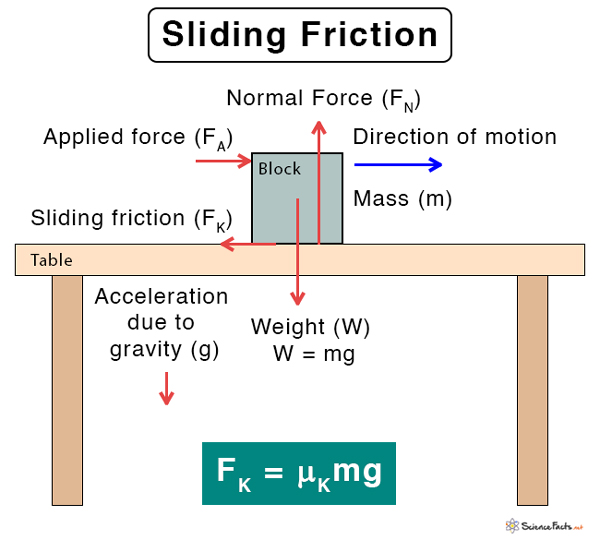
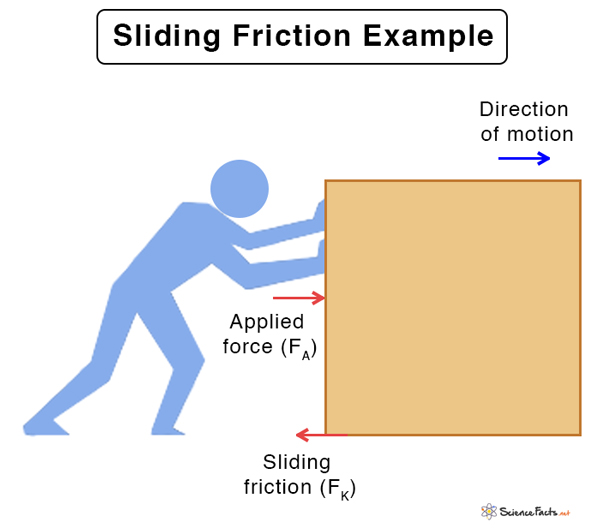
Surfaces are not always perfectly smooth. Friction arises due to tiny bumps and hills that are present on surfaces. As a result, when one surface comes in contact with another, these bumps interlock and hinder the motion. Because there is no liquid between the surfaces, the phenomenon is also called dry sliding friction.
Examples of Sliding Friction
Characteristics of Sliding Friction
Laws of Sliding Friction
How to Calculate Sliding Friction
How to Reduce Sliding Friction
Sliding and Rolling Friction
Rubbing the hands together generates heat due to frictionDifficulty in pushing a fridge on a floorSkidding of a car when trying to brakeSlowing of motion during sledding and skiing
Contact forceOpposes the motion of an objectThe direction is opposite to the force applied to the object
Proportional to the normal force or loadIndependent of the area of contactIndependent of the sliding speed
Sliding Friction Formula
Suppose a force is acting on an object of mass m that displaces it on a surface. According to Newton’s third law of motion, the surface will apply an equal and opposite force on the object, which is the force of sliding friction FK. According to friction laws, the frictional force is proportional to the normal load FN. Therefore, FK ∝ FL Or, FK = μK FL Where μK is known as the coefficient of sliding friction. Its value is a constant depending on the surfaces in contact. It is unitless and dimensionless. The unit of friction is Newton or N. Again, according to Newton’s third law of motion, the normal force is equal to the object’s weight mg. FN = mg Therefore, the magnitude of sliding friction is given by FK = μK mg From the above equation, it is clear that the weight influences sliding friction. As the weight increases, the friction increases proportionately. Now, suppose the object is moving with an acceleration a. According to Newton’s second law, it experiences a force ma given by ma = FA – FK ma = FA – μK mg Therefore, the acceleration is given by a = FA/m – μK g
Introducing a lubricant between the two surfaces such that the dry friction is converted into lubricationUsing rollers, like a ball bearing, that changes sliding friction into rolling friction easilyReducing the normal load since the frictional force is proportional to the normal force
Why is Sliding Friction More Than Rolling Friction
The cause of sliding friction is the interlocking of the bumps and hills present on surfaces. When the contact area is large, then the friction force will be high. In the case of rolling friction, there is a layer of rollers between two surfaces. As a result, the contact between the flat surfaces and the curved rollers is minimum. Hence, the friction is reduced. Below are some differences between sliding and rolling friction.
Sliding Friction vs. Rolling Friction