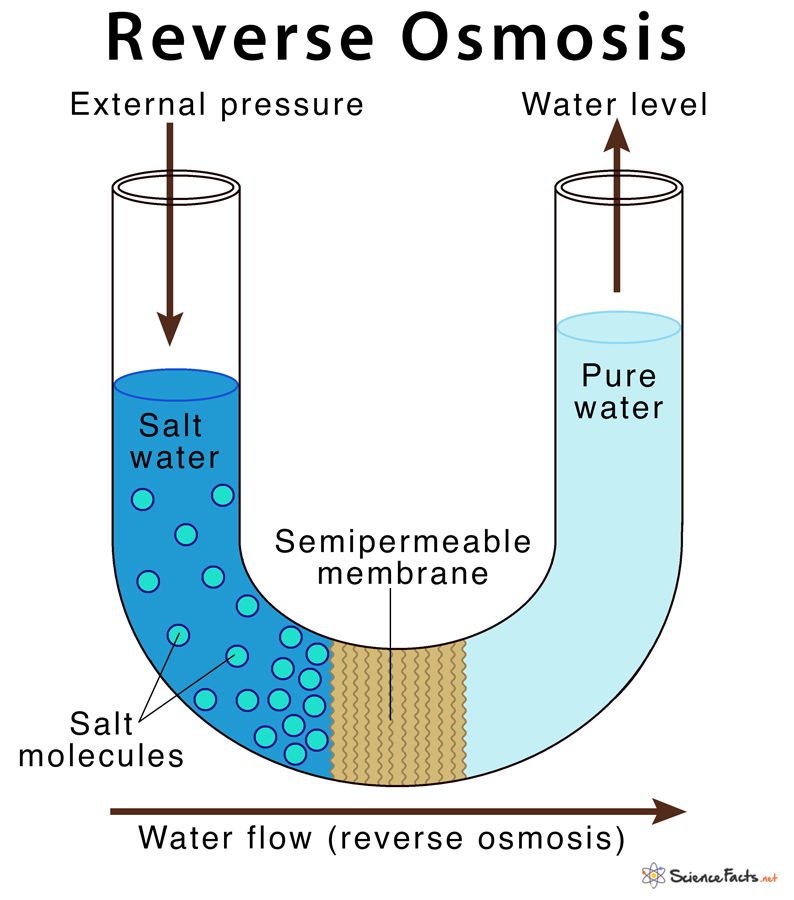
In the RO system, external pressure is applied to overcome the normal osmotic pressure of the solution that allows separation of pure water from their impurities. The impurities are removed based on the size and charge of the particle. Thus in RO, the solvent moves from the region of low to high solute concentration in the solution.
All dissolved and suspended impurities such as salt particles, colloids as well as bacteria and pyrogens are eliminated from drinking waterSalts and excess minerals are removed from seawater (desalination) to make it fit for use in agriculture and drinking purposesKeeps the environment clean because of its eco-friendly nature
Disadvantages
Smaller charged impurities such as sodium and calcium ions cannot be filtered through the RO membrane Dissolved gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen are not filtered out by RO membraneSome essential ions and minerals are unnecessarily removed from drinking water