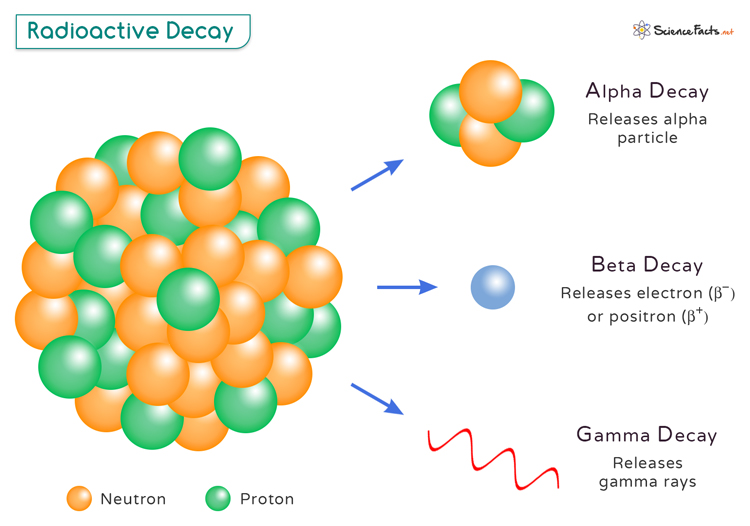
What Happens During Radioactive Decay
Types of Radioactive Decay
Radioactive Decay Equation
Applications of Radioactive Decay
The radioactive decay formula is expressed as: N(t) = N₀ × e-λt Where:
N(t) is the number of radioactive atoms remaining at time tN₀ is the initial number of radioactive atomse is the base of the natural logarithm (approximately 2.718)λ is the decay constant, which is a characteristic of the particular radioactive isotopet is the time elapsed
The decay constant (λ) is related to the half-life (t½) of the radioactive isotope, which is the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms to decay. This relationship is: Using the radioactive decay formula and a radioactive isotope’s half-life, scientists can accurately predict the amount of radioactive material remaining after a given period of time.