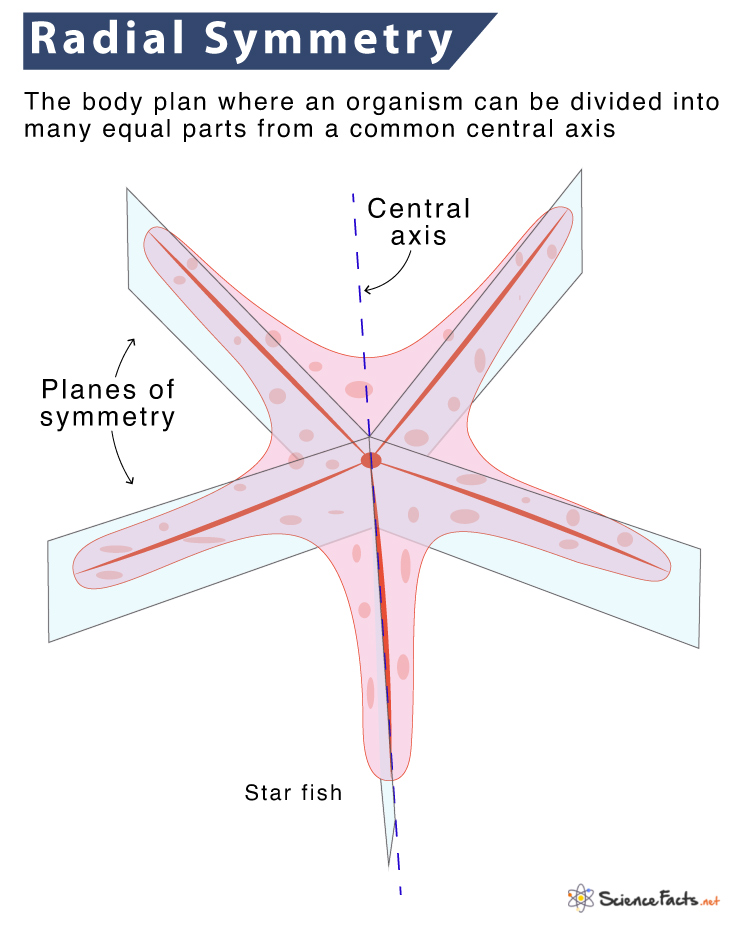
What is Radial Symmetry
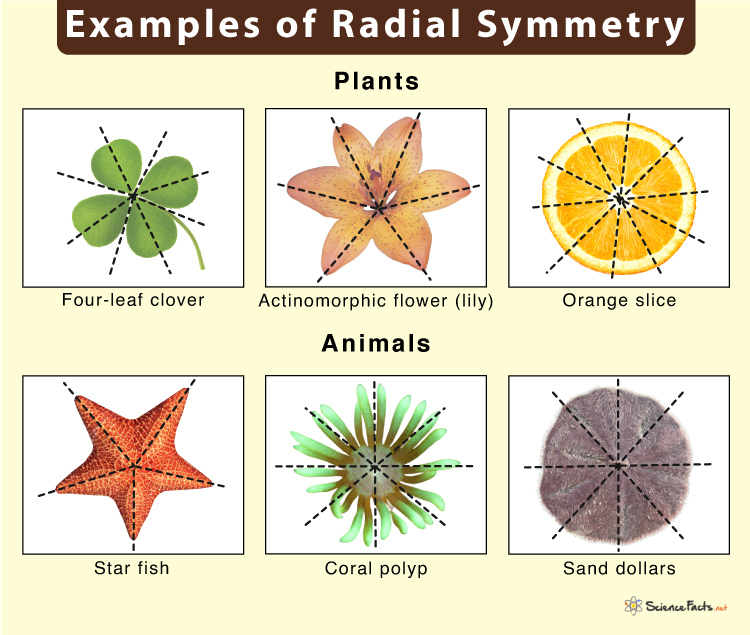
Examples of Radial Symmetry
Characteristics of Animals
Advantages and Disadvantages
In animals, two phyla – cnidarians and echinoderms exhibit radial symmetry. Cnidarians include jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals. Specifically, jellyfish has radial symmetry in four points around its center. Again, starfish, sea urchins, and sand dollars are echinoderms. Sea stars have radial symmetry in five points around their center.
have many lines of symmetryhave a top and a bottom region but do not have a front, back, or distinctive left and right sideshave a side with a mouth – the oral side. And, without the mouth – the aboral sidecan move in all directionsmove slowly, if at all, compared to bilaterally symmetrical organisms. For example, jellyfish primarily drift with waves and currents, sea stars move very slowly, and sea anemones barely move.are primarily sessile – organisms that are more or less permanently attached to a surface and cannot move on their ownand have sensory structures scattered around their body. For example, sea stars have eyespots at the end of their arms
It is easier for organisms to regenerate their lost body parts. For example, a starfish can completely regenerate its lost arm or even an entirely new body as long as its central disk is present.It is best for sessile animals as they can obtain food or detect enemies easily from all directions.
However, it offers some disadvantages as well.
Organisms are very slow and not compatible with a coordinated and quick movement.Have a restricted vision that is primarily two-dimensional. It makes catching prey and evading predators difficult.