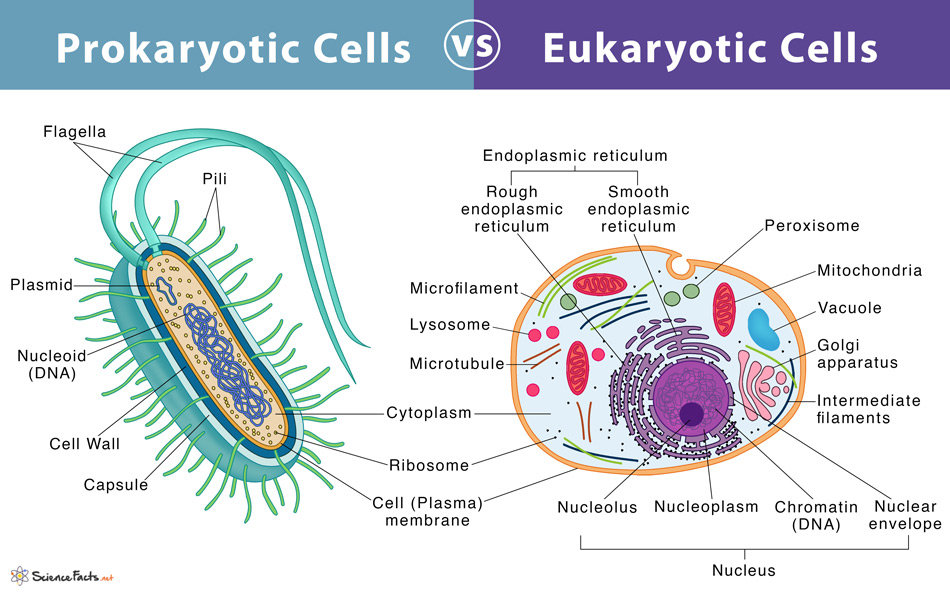
Prokaryotes are primitive organisms lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The term ‘prokaryote’ is derived from the Greek words ‘pro’, meaning ‘before’ and ‘karyon’, meaning ‘kernel’. Together it means ‘before nuclei’. In contrast, eukaryotes are advanced organisms with a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The term ‘eukaryotes’ is derived from the Greek words ‘eu’, meaning ‘good’ and ‘karyon’, meaning ‘kernel’, meaning ‘true nuclei’. The eukaryotes are thought to have originated from the prokaryotes about 2.7 billion years ago.
Compare and Contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
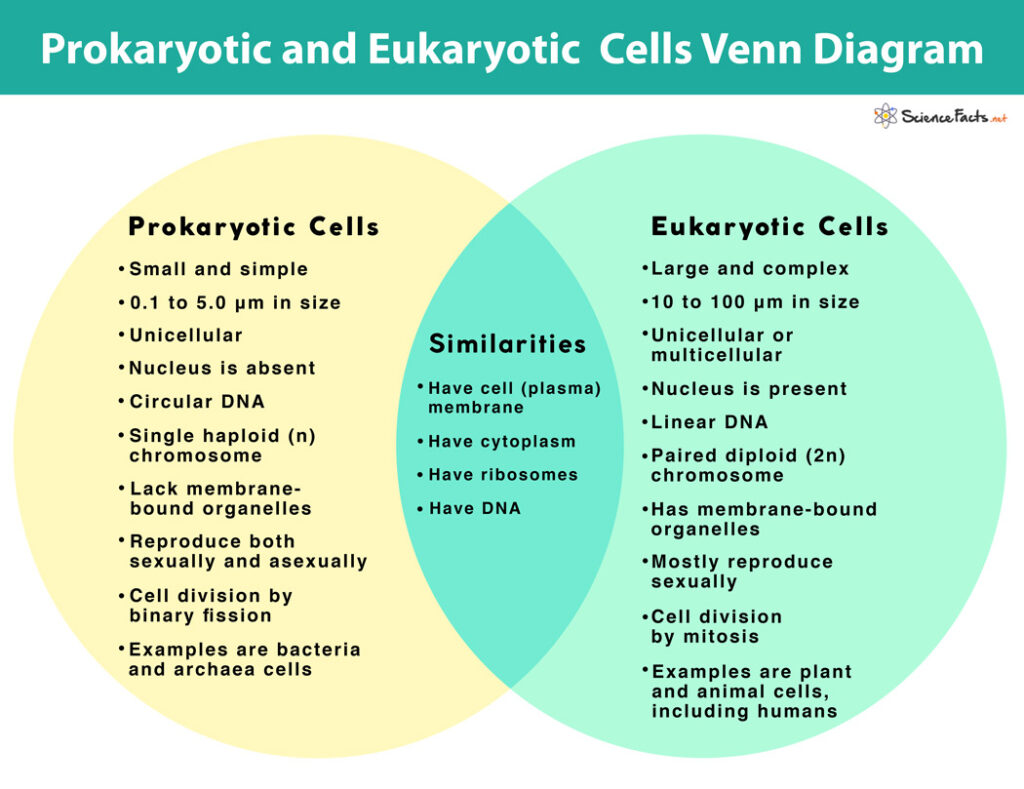
What is the Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
What do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in Common
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are alike in some ways and share some common features that are given below:
Plasma Membrane, an outer covering that allows selective entry and exit of substances in and out of the cell, is found in both cell types. Their fundamental composition in forming a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins is also the same.Both contain cytoplasm, a jelly-like fluid that fills the cell’s entire interior, where all other cellular components are found.DNA is the genetic material in both cell types.In both, ribosomes help in protein synthesis.