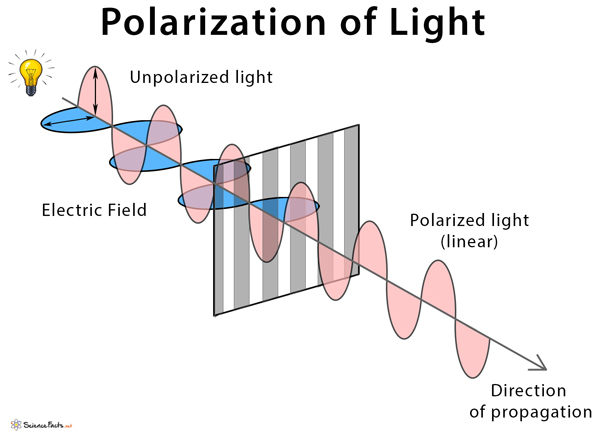
The history of light polarization began with the Danish physicist, physician, and mathematician, Erasmus Bartholinus, who, in 1669, discovered the phenomenon of double refraction of calc-spar.
Examples of Polarization of Light
The light reflected from the water surface forms glare making it difficult to see through.The view of the surroundings through polaroid sunglasses.
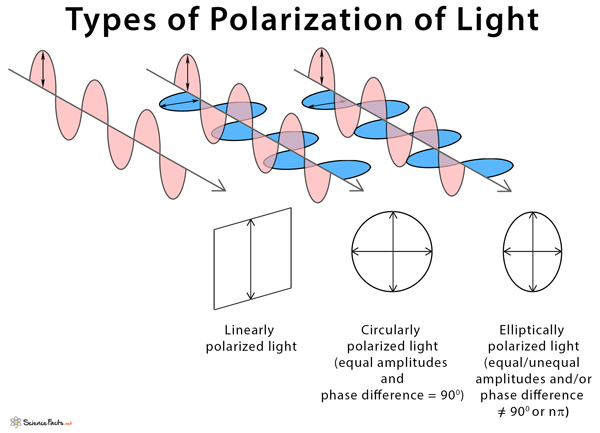
Linear Polarization
In linear polarization, the electric field of light is restricted to a single plane along the direction of propagation.
Circular Polarization
In circular polarization, the electric field has two linear components that are perpendicular to each other such that their amplitudes are equal, but the phase difference is 90 °. The resulting electric field rotates in a circle around the direction of propagation. Depending on the rotation direction, it is called left- or right-hand circularly polarized light
Elliptical Polarization
In elliptical polarization, the electric field has two linear components that are perpendicular to each other. However, either their amplitudes are not equal, or their phase difference is not 90°.