It is widely used nowadays to produce disease-free plants, including ornamental plants, food plants, and orchids, rapidly on a large scale and with desirable qualities. The process is known as micropropagation, when tissue culture is used to develop identical plants from a single parent.
History of Plant Tissue Culture
Principles of Plant Tissue Culture
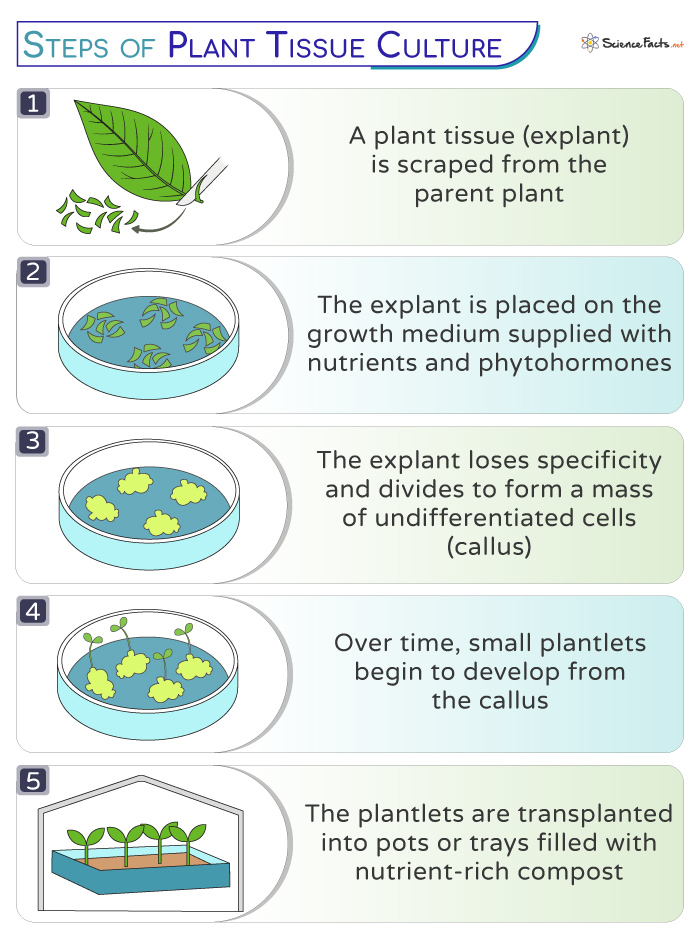
Procedure of Plant Tissue Culture
Types of Plant Tissue Culture
Applications of Plant Tissue Culture
Embryo Culture
In embryo culture, the embryo of a plant seed is first isolated and then cultivated under in-vitro conditions. It is crucial for rescuing embryos from seeds that may not germinate under natural conditions. Embryo culture propagates plants with low seed viability or for breeding purposes.
Seed Culture
In this technique, the seeds of a plant are grown under in-vitro conditions. Seed culture is valuable for mass propagation, especially when seeds are scarce or exhibit low germination rates. It allows the production of many plants from a limited seed resource.
Protoplast Culture
Protoplasts are cells with their cell walls removed, which allows them to be cultured as individual cells. Protoplast culture is employed in genetic modification and the creation of hybrid plants. Protoplasts can be fused to form hybrid cells with combined genetic traits.
Organ Culture
Organ culture involves cultivating entire plant organs, such as roots, shoots, or leaves. This technique helps study organ-specific responses to various stimuli. It also plays a role in the micropropagation of plants with intact organs.
Other Types
Some other types of plant tissue culture less commonly used are:
Single-cell culture involves isolating and culturing individual plant cells. It is used to study cellular responses and behaviors in plants.Suspension culture consists of cultivating plant cells in a liquid medium, allowing cells to float freely. It is valuable for the large-scale production of plant metabolites.Anther culture deals with cultivating anthers, the male reproductive organs, in a nutrient medium. It is employed in the production of haploid plants.Pollen culture involves the cultivation of pollen grains that give rise to plants with desired characteristics.
Clonal Propagation
Plant tissue culture allows for the propagation of plants with specific and desirable traits. Clonal propagation ensures the preservation of unique characteristics, such as disease resistance, high yield, or enhanced nutritional content.
Rapid Multiplication
The micropropagation technique enables the rapid multiplication of plants from a single source. This efficiency is particularly valuable for massively producing elite plant varieties on a large scale. Techniques like anther and pollen culture facilitate the rapid generation of haploid plants. It expedites breeding programs, allowing new plant varieties with desired traits to be developed quickly.
Preservation of Desirable Traits
Plant tissue culture allows for the propagation of plants with specific and desirable traits. This clonal propagation ensures the preservation of unique features, such as disease resistance, high yield, or enhanced nutritional content.
Genetic Modification
Plant tissue culture provides a controlled environment for introducing and expressing specific genes in plant cells. This precision in genetic modification allows for breeding crops with improved traits, such as resistance to pests or tolerance to environmental stress.
Disease-Free Plants
Through the process of surface sterilization and aseptic conditions, plant tissue culture helps in producing disease-free plants. It is crucial for maintaining the health and vigor of plant materials, especially when propagating from valuable or endangered species.
Seasonal Independence
Plant tissue culture enables the production of plants independent of seasonal constraints. This year-round availability benefits continuous research, crop production, and conservation efforts.
Conservation of Germplasm
In the face of biodiversity threats, plant tissue culture provides a means to conserve and propagate endangered plant species. This germplasm preservation contributes significantly to biodiversity conservation and ecosystem restoration.
Fundamental Research
Plant tissue culture provides a controlled environment for studying fundamental aspects of plant physiology and biochemistry at the cellular and molecular levels. It also serves as a valuable tool for advancing our understanding of plant biology.