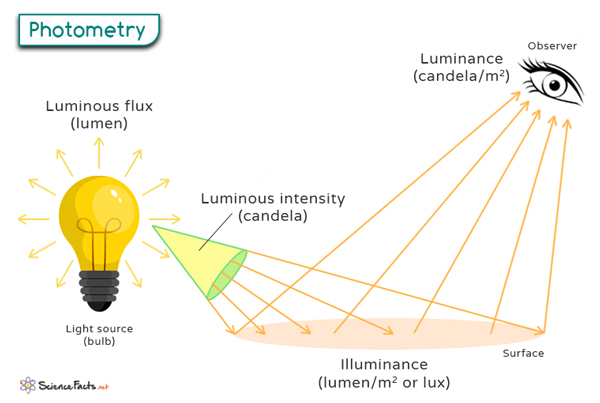
Photometric Quantities and Units
Photometer
Applications of Photometry in Various Fields
Types of Photometer
Working Principle of a Photometer
Photometers function by observing how various wavelengths of light are either reflected or absorbed by these materials. Their primary operation is the conversion of light into an electric current, allowing the intensity of the light to be measured based on the resulting electric current. When light passes through a colored solution, specific wavelengths are absorbed, producing an absorption spectrum. The point at which maximum light absorption occurs is identified as the absorption maximum. Conversely, the wavelengths that are not absorbed are transmitted through the solution, giving it its characteristic color. The transmittance (T) can be calculated by taking the ratio of emergent light’s intensity (IE) to that of incident light’s (Io). T = IE /Io x 100% Some photometers operate by directing a beam of white light at a surface and measuring the amount of light reflected back. This method helps determine the surface’s reflective properties.