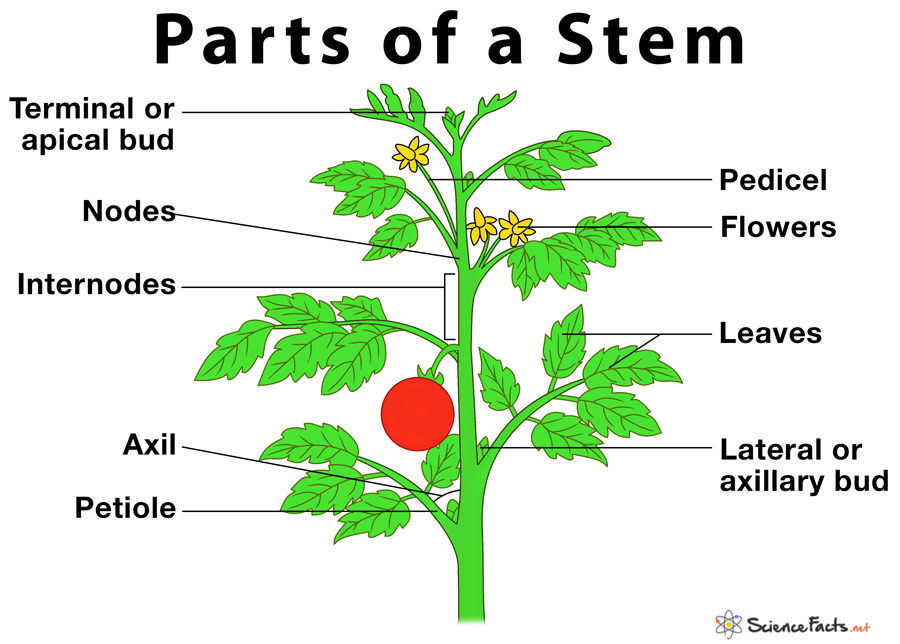
The stem is the connecting medium between the roots, the leaves, and the flowers, whose primary function is to provide mechanical support to the plant. The main woody stem of a plant is called the ‘trunk’.
What Are the Different Parts of a Stem
1) Nodes
2) Internodes
3) Terminal or Apical Bud
4) Lateral Bud or Axillary Bud
6) Pedicel
7) Leaves
8) Flowers
Functions
Helping the plant to form buds, leaves, and branching twigs Helping plants to heal from injury Providing additional structural support to the plant Reproducing new plant parts or even a complete plant by the process of stem cutting, like rose, salvia, dahlia, boxwood, etc.
Functions
Acting like blood vessels that carry and distributes food, water, and minerals from one node to another Providing height to the plant, greater the inter-nodal space more the height of the plant
Functions
Acting as the primary growing point in the stem Producing growth hormones that inhibit the growth of other buds in the stem (apical dominance), thus helping the plant to grow vertically upwards
Functions
Helping the plant to develop its lateral branches and leaves, the vegetative parts of a plant Helping the plant to develop flowers, the reproductive part of a plant
5) Petiole
The thin stalk of the leaf that connects the leaf to the node of the stem is called a petiole. A leaf with a petiole is called a petiolate leaf, whereas leaves without them are called sessile. Functions
Attaching the leaf to the stem and thus providing strength and support to the leaf Transporting water and minerals from the stem to enter the leaf and photosynthetic products to be distributed from the leaf to the rest of the plant
Functions
Exposing flowers to the sun and wind so that they can attract pollinators like bees and insects for the purpose of sexual reproduction in plants
Functions
Helping plants to produce food with the help of sunlight, carbon dioxide and water by a process called photosynthesis Helping the plant to cool down by losing water in the form of water vapor by a process known as transpiration Helping in exchange of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide in plants Helping in the reproduction of a specific group of sprout plants known as Bryophyllum
Functions
Helping in the sexual reproduction of plants Attracting pollinators like bees and other animals that help to transfer pollen grains from the male to the female reproductive part of the flower, a process known as pollination