The union of the male and female reproductive cells inside the ripened ovule of a flower helps in the formation of seeds in a plant. Different seeds have different sizes, shapes, and colors that participate in the reproduction of flowering plants.
Parts and Structure of a Seed
1) Seed Coat
2) Endosperm
3) Embryo
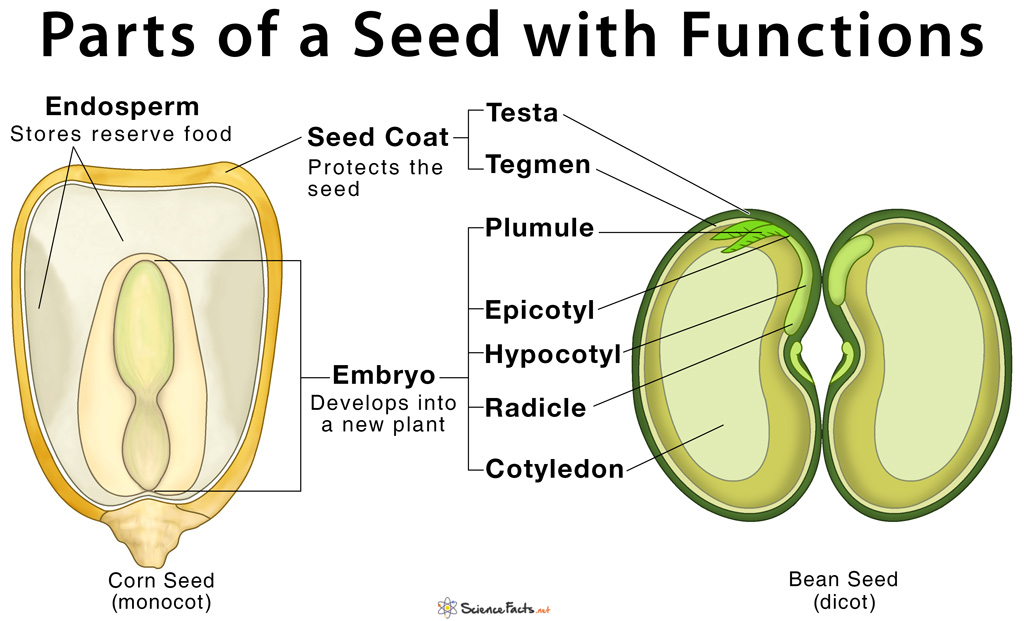
A typical seed consists of three main parts: 1) seed coat, 2) endosperm, and 3) embryo. A seed coat has the following four parts: a) Micropyle – the small opening present at one end of the seed coat, b) Funiculus – the seed stalk with which the seed is attached to the fruit body, the integument, c) Hilum – the region from which the seed breaks off from the fruit, leaving a scar, and d) Raphe – the base of the funiculus that is fused with the integument. Functions
Protecting the seed from physical and mechanical damage Preventing the seed from germination even under favorable conditions of growth (seed dormancy) Preventing the excessive loss of water from the seeds Acting as a physical barrier against the entry of parasites
i) Non-endospermic or exalbuminous seeds – Characterized by the complete absence of the endosperm, such as the seeds of the pea plant, groundnut, and gram. ii) Endospermic or albuminous seeds – Characterized by the presence of the endosperm, such as the seeds of millets, palms, and lilies. Functions
Storing of reserve foods that provide nourishment to the developing plant Protecting the embryo, the next part of the seed, by acting as the mechanical barrier
What are the Parts of an Embryo of a Seed
Epicotyl – The tiny shoot of an embryo, from which the entire shoot system develops. The tip of the epicotyl is called plumule. Hypocotyl – The stage of transition for the growing shoot and root of the embryo Radicle – The tiny root of the embryo Cotyledons – They are the leaves of the embryo that provide nourishment to the developing plant. There are two types of cotyledons present in flowering plants: i) monocotyledonous or monocots – embryo with one cotyledon and ii) dicotyledonous or dicots – embryo with two cotyledons.
Functions
Giving rise to a new complete new plant Storing food and nourishing the baby plant