The presence of pigment ‘chlorophyll’ makes the leaf green in color that helps to prepare food in plants through photosynthesis. Collectively, green leaves are called foliage.
What are the Different Parts of a Leaf
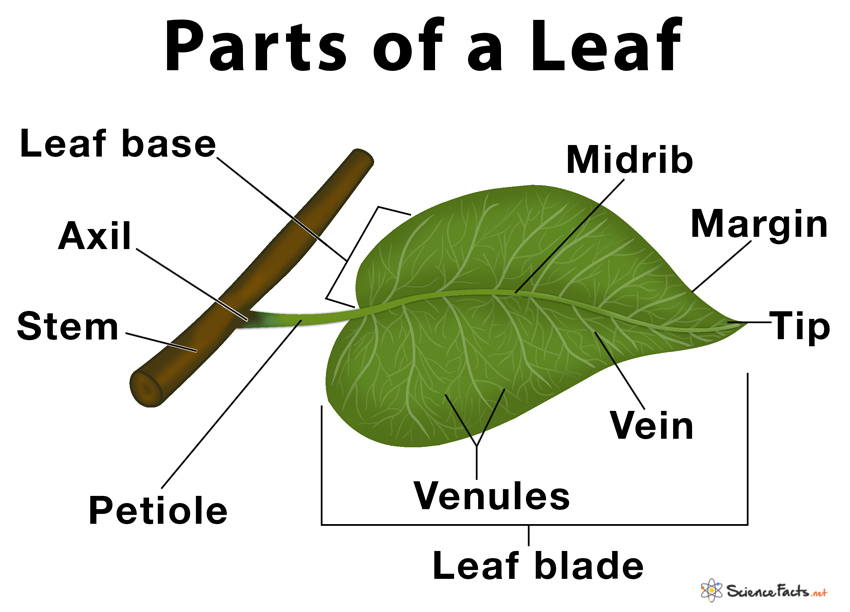
1. Petiole
2. Leaf Base
3. Leaf-blade or Lamina
Functions
Providing support to the leaf and keeps it erect Transporting water and nutrients absorbed by the roots to the leaves Transporting photosynthetic products from the leaves to the rest of the plant
Functions
Helping in the attachment of the leaf to the stem It protects the young axillary bud
Functions
Helping plants to prepare their food using raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and minerals through photosynthesis Performing evaporation from the aerial parts of a plant by a process known as transpiration Veins and venues help in transporting water and nutrients throughout the leaf
Ans. Petiole, leaf base, lamina, leaf apex, and leaf margin are the external parts of a leaf. Q.2. What are the internal parts of a leaf? Ans. Stomata, guard cells, epidermal cells, mesophyll cells, and vascular bundles (xylem, phloem, veins) are the internal parts of a leaf. Q.3. What part of a leaf helps in gas exchange? Ans. The gas exchange which involves the absorption of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen occurs through tiny pores present in the leaves called stomata. Q4. What is a sessile leaf? Ans. Leaves that are attached directly to the stem without the petioles are called sessile leaves. Saffron and Achyranthus plants have sessile leaves.