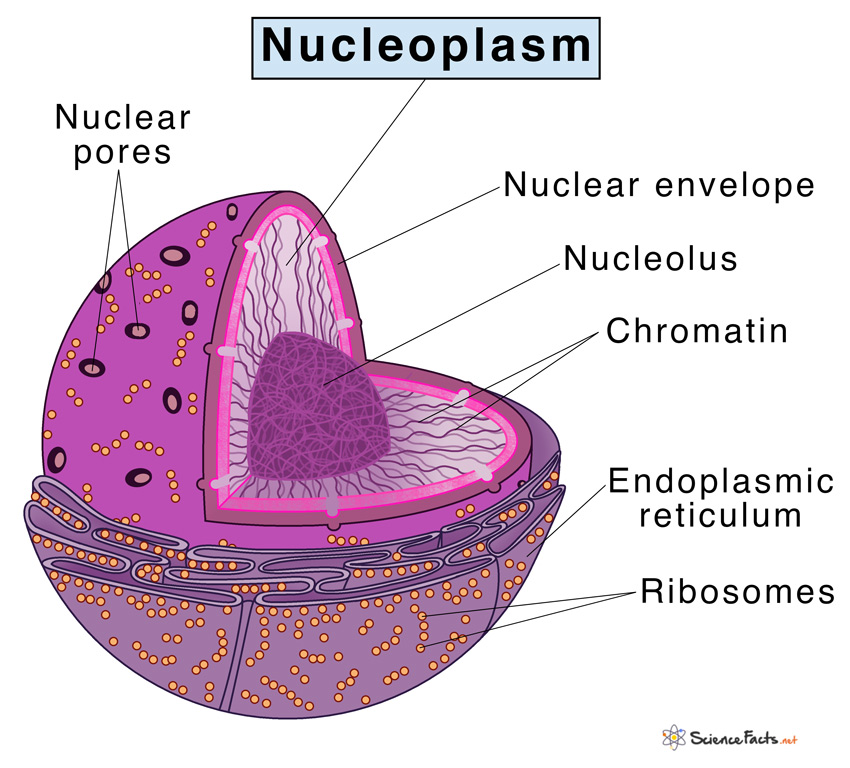
Now, let us discuss its detailed structure:
Structure
Function
Difference between Nucleoplasm and Cytoplasm
Chemical composition It is mainly made up of water, nuclear proteins, and other inorganic and organic substances such as nucleic acids, proteins, enzymes, and minerals. The soluble, fluid portion of the nucleoplasm is called the nucleosol or nuclear hyaloplasm. The nucleoplasm contains two types of nuclear proteins, histone or basic proteins and non-histone or acidic proteins. The common nucleic acids found here are DNA and RNA. It also contains critical enzymes that are necessary to catalyze reactions occurring in the nucleus. The most vital enzyme found here is DNA polymerase, as it helps produce DNA from nucleotide bases. Some other enzymes found in it are hexokinase, 6-P-gluconic dehydrogenase, TPN-linked isocitric dehydrogenase, P-fructokinase, glucose-6-P dehydrogenase, and glutamic dehydrogenase. Parts of the Nucleoplasm i) Nucleolus It is the major ribosome manufacturing center within the nucleus. Specially designed proteins enter the nucleolus through nuclear pores to create ribosomal RNA, which in turn produces ribosomal subunits. These subunits are then pushed out of the nucleolus, i.e. into the nucleoplasm. There these subunits are processed into fully functional ribosomes. The ribosomes can then attach to the nuclear membrane. Ribosomes are also found throughout the cytosol and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). ii) Nucleotides Nucleoplasm also houses nucleotides, the fundamental building blocks of DNA and RNA. All the nucleotides consist of a base (double-ringed purine or a single-ringed pyrimidine), a phosphate group, and deoxyribose (for DNA) or ribose (for RNA) sugar. The five most common nucleotide bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil. These bases can be combined and methylated to form a wider variety of complex bases that form the fundamental genetic material. iii) Chromatin It is a molecular complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins that help them in folding. Chromatin specifically works to shrink long strings of DNA so that it can better fit inside a cell. It also prevents the entangling of the strings during DNA folding and improves the efficiency of replication. Chromatin is also closely linked to gene repression, DNA transcription, and gene expression. iv) Nuclear Matrix It can be found throughout the nucleus and plays an essential role in maintaining the structure of the nucleus. It also aids in organizing the genetic material of the cells.
Every part of nucleoplasm aids in several essential cellular activities. Let us discuss some of those: