The nuclear force is spin-dependent. However, it is charge-independent, which means that the forces between two protons, two neutrons, and a proton and a neutron are approximately the same when the electromagnetic forces are ignored.
Properties of Nuclear Force
Types: Strong and Weak Nuclear Forces
Applications of Nuclear Force
Classified into strong nuclear force and weak nuclear forceOccurs between nucleons, like protons and neutronsShort-range and finite (of the order of proton dimension)Strong nuclear force that is powerful than the electric force by 137 timesIt does not affect the physical and chemical properties of a substanceDetected through nuclear reactions and radioactivityDependent on the spin of the particles
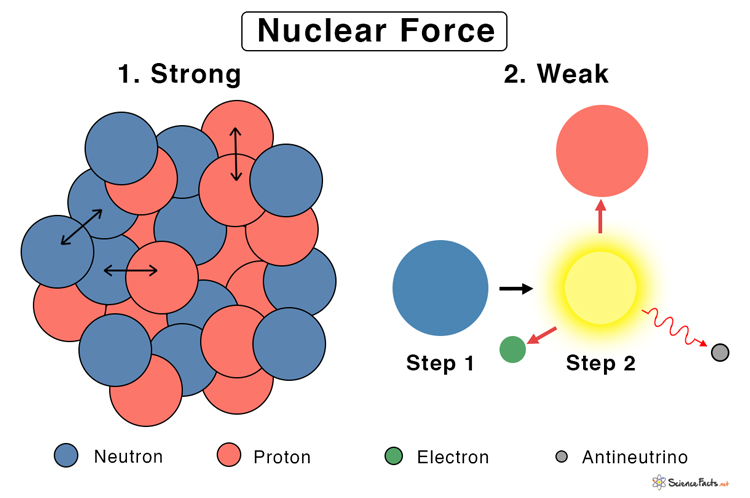
- Strong Nuclear Force: The attractive force ensures the nucleus’s unity by holding all fundamental particles like protons, neutrons, and quarks together. The force is responsible for alpha radiation.
- Weak Nuclear Force: The force that acts inside the individual nucleons and occasionally leads to a neutron transforming into a proton and vice versa. This force is commonly observed during beta decay. How are the strong and weak nuclear forces alike? Both the strong and the weak nuclear forces are present inside the nucleus of an atom. Both of them act on the quarks that make up the protons and neutrons. They have a short, finite range and are more powerful than gravity. Strong vs. Weak Nuclear Force The following table lists the differences between the strong and weak forces.
Nuclear power plantNuclear weaponsAdvanced medical diagnosis and treatmentRadiocarbon dating (determines the age of the organic materials from carbon isotope abundances)Determine the age of the EarthResponsible for the existence of the Sun
Difference between Gravitational Force and Nuclear Force