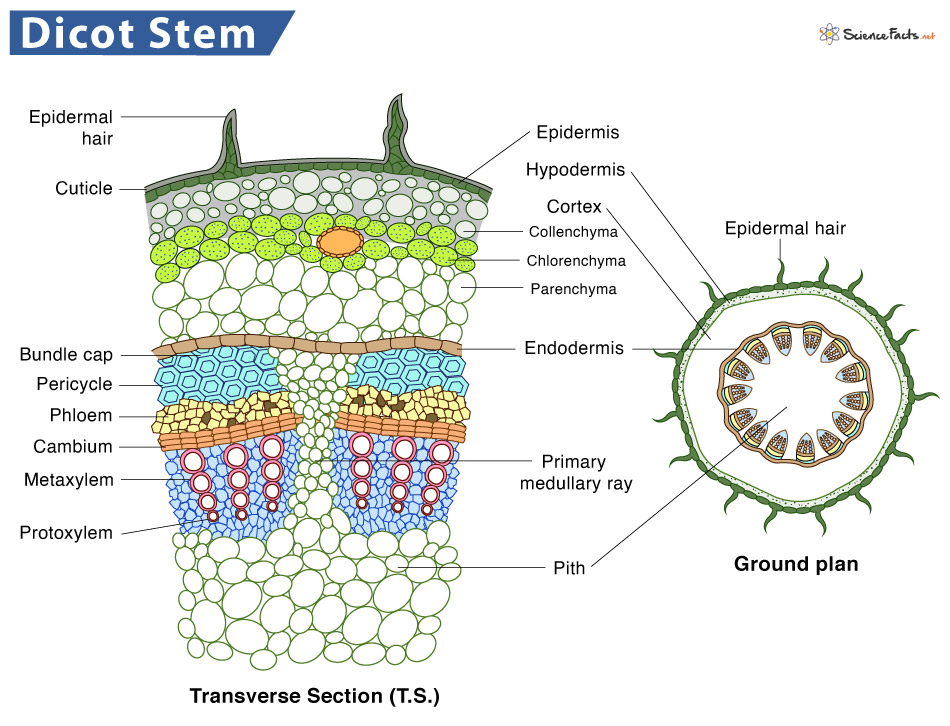
The dicot stems are stems of dicot plants. They are arranged concentrically, one above the other. The vascular bundles of dicot stems are arranged in a ring without a bundle sheath. However, parenchyma cells surround each vascular bundle in the dicot stem. The hypodermis of dicot stems is made of collenchymas cells. They have other significant features such as trichomes in the epidermis, prominent cortex, and stele. In addition, dicot stems show secondary thickening, which leads to secondary growth. Let us discuss the structural and functional similarities in monocot and dicot plants.
Similarities
Functions
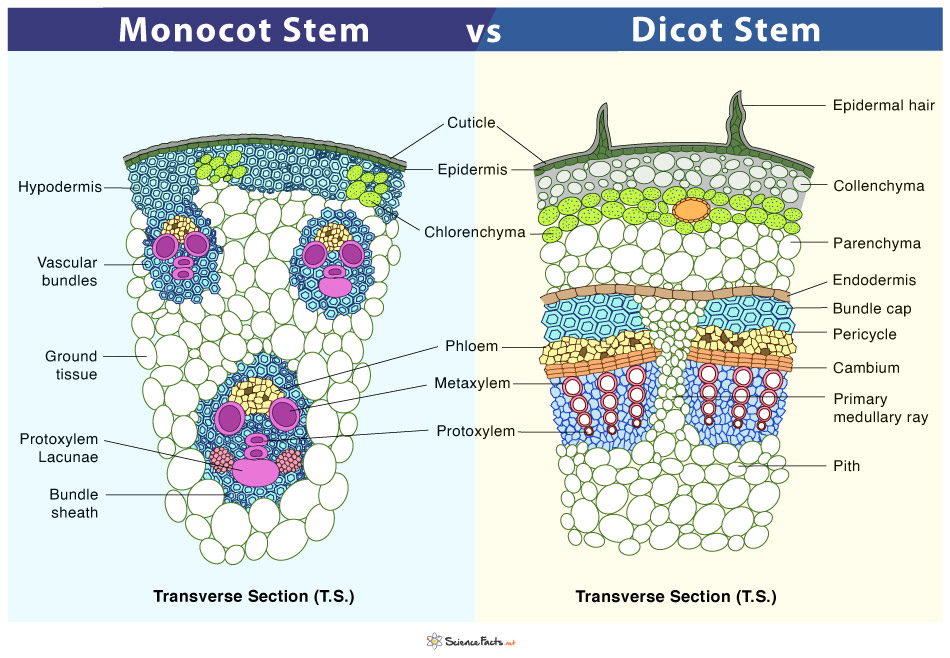
Difference between Monocot and Dicot Stem
Epidermis
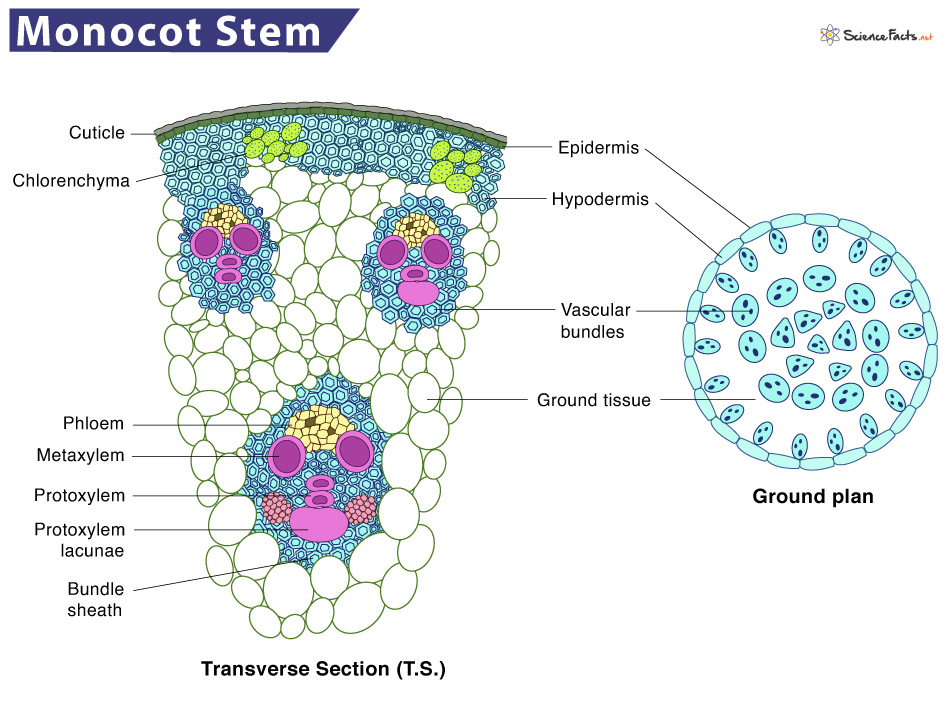
It is the single, outermost layer arranged compactly without intercellular spaces.The epidermis cells lack chlorophyllOutside the epidermis is a layer of the cuticle that protects the epidermis and tissues lying underneathIt contains stomata for the gas exchange
Cortex
It is divided into different sections, but the region covered differs widely between monocot and dicots stems.The hypodermis is present immediately below the epidermis, which provides additional support to the epidermis. It is a thick multicellular layer composed of collenchyma tissue. The cells of this region contain chlorophyll and thus can prepare food for the plant.
Ground Tissue
It is a mass of parenchymatous cells extending to the hypodermis center.The cells are spherical, thin-walled, and loosely organized with intercellular spaces.
Pericycle
It is the tissue found between the endodermis and the vascular bundles.The cells are sclerenchymatous, which has the shape of semilunar patches above the vascular bundles.
Vascular Bundles
They are of conjoint and collateral type surrounded by parenchyma cellsThey are limited in number and have a uniform size. Each bundle consists of a patch of xylem and phloemXylem consists of both protoxylem and metaxylemThe quantity, arrangement, and components of vascular bundles vary widely between monocot and dicots stems
Pith
The cells are parenchymatous and appear like medullary rays around the arterial bundles.The cells might be spherical or polygonal, with or without any intercellular spaces.They store food and aid in transporting food and water between the bundles.
It is the central axis of the plant that supports other parts such as leaves, branches, flowers, and fruitsTransports food, water, and minerals throughout the plant bodyYoung, green stem having pigments chlorophyll prepares food by photosynthesisStores a large number of food particles like starch and other nutrientsThe meristem tissue of the stem divides to form new tissues, thus helping the plant to growThe stomata in the stem helps in transpirationModified stems like cactus help to store water and food, prevent water loss, and thus in their survival in the desert
Although monocot and dicot stems have the following structures in common, there are several differences. They are discussed below.