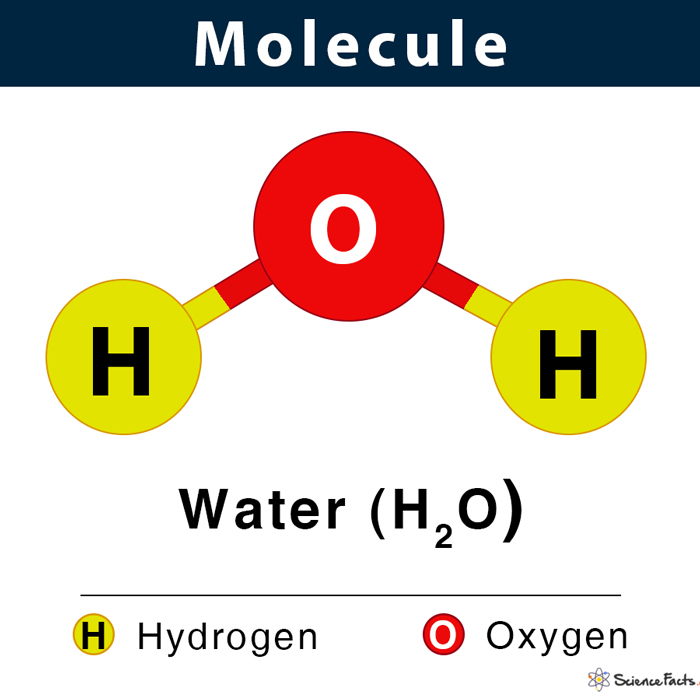
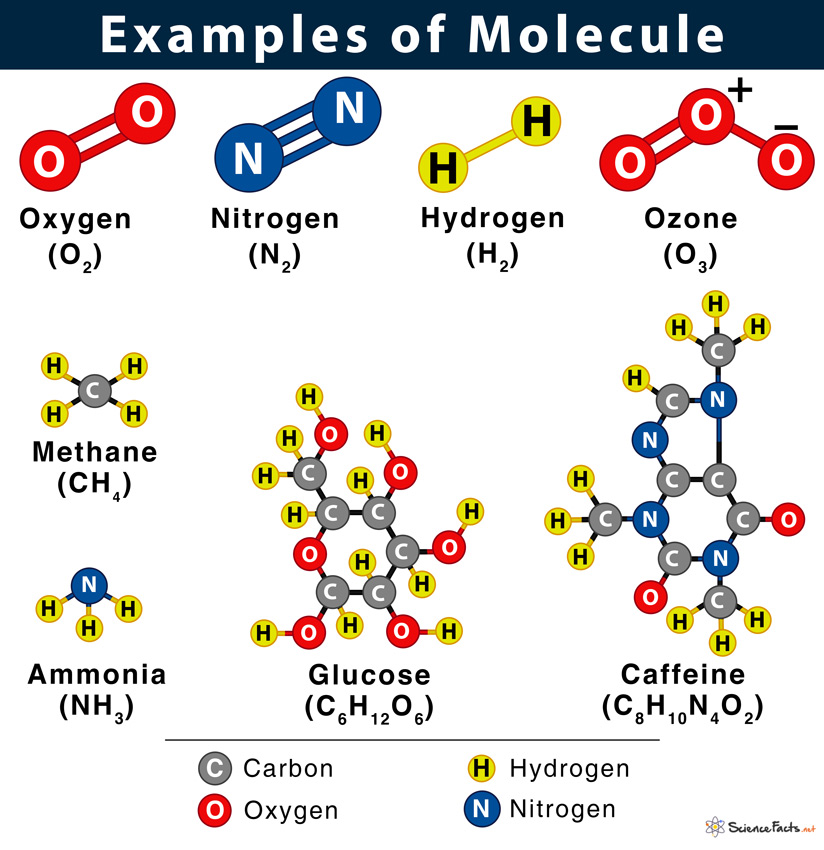
Shown below is the water molecule (H2O). All objects that we see around us are made of molecules. From living objects such as a plant or an animal, including humans, inanimate objects like a chair, table, wall, door, windows, books, computer, and mobile phones are all made of molecules. Examples Oxygen (O2), ozone (O3), methane (CH4), sodium chloride (NaCl), and glucose (C6H12O6) are some other common examples of molecules.
Molecules and Elements
Molecules and Compounds
What is Molecular Formula
How Are Molecules Formed
Some Fun Facts
It is possible because each substance is made of different types of atoms, and atoms uniquely combine to form molecules. For example, when two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom combine, they form a carbon dioxide molecule written as CO2. Again, a sugar or a glucose molecule with formula C6H12O6 is made of six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms. Some other examples are ammonia (NH3: one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms), methane (CH4: one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms), and sucrose (C12H22O11: twelve carbon atoms, twenty-two hydrogen atoms, and eleven oxygen atoms). Thus, the only way a specific substance is formed is by bonding the precise number and kind of atoms in proper order or orientation. Both types of bonds involve electrons that are negatively charged particles revolving around the nucleus in a fixed path or shell. The shells in an atom follow a specific rule of filling up electrons, known as the octet rule. The outermost shell plays a crucial role in forming a chemical bond. When this shell is partially-filled, the atoms will bond to complete the shell with electrons and form the chemical bond.
- Ionic Bonds: Occurs when one participating atom gives up an electron to another atom. In other words, one atom receives an electron from another atom to form a stable molecule or compound.
- Covalent Bonds: Occurs when two or more participating atoms share their electrons between them to form a stable molecule or compound.