Why Does the Earth have Different Layers and How Are They Formed
How Many Layers Does the Earth Have, and What Are They Called
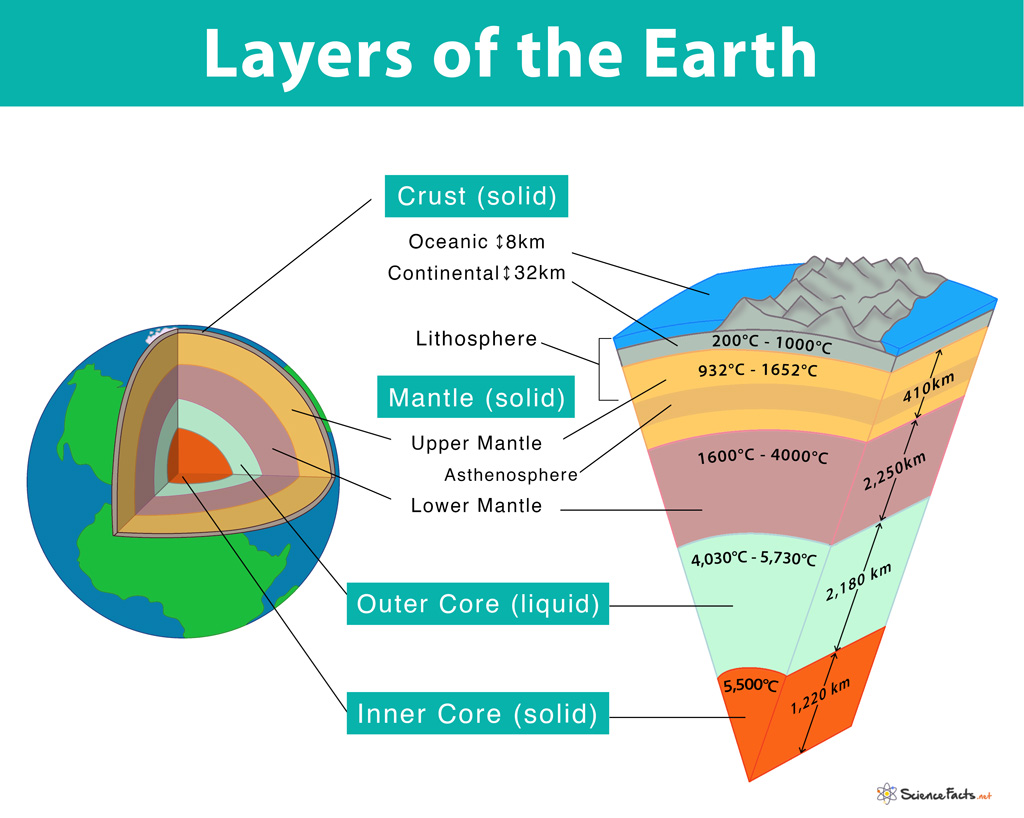
All the Earth’s Layers, Their Structure and Composition
- Crust
- Upper Mantle
- Lower Mantle
- Outer Core
- Inner Core Thickness: 25 miles (32 km) for continental crust and 3-5 miles (8 km) for oceanic crust Density: ∼ 2830 kg/m3 at the continental crust and ∼ 3000 kg/m3 at the oceanic crust It is the outermost and thinnest layer of our planet and is least dense among all other layers. Based on its thickness and location, the crust is of two types, the continental crust that consists of granite rocks and found near the mountain ranges, and the oceanic crust that consists of basalt and found under the oceans. The most abundant elements found in the earth’s crust include oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, and calcium. The temperature within the earth’s crust is high enough to melt rocks and form the lower layer called the upper mantle.
2. Upper Mantle
Temperature: 1200 K (∼ 932°C) at the upper boundary with the crust to 1900 K (∼1652 °C) at the boundary with the lower mantle Thickness: 255 miles (410 km) Density: ∼ 3400 kg/m3 It is the largest and thickest layer of earth. The upper mantle, along with the crust, makes up the lithosphere of earth, which is physically distinct from the layers lying below due to its low temperature high thickness. Below the lithosphere is found a much hotter and malleable portion of the upper mantle called the asthenosphere layer that begins at the bottom of the lithosphere and extends up to 450 miles (700 km) deep inside.The composition of the upper mantle is not found to be in a steady-state but always in constant motion. The upper mantle moves large areas of crust, called tectonic plates, resulting in the formation of volcanoes, mountains, or earthquakes. Between the upper and lower mantle, there is the presence of the transition zone, which ranges in depth from 250 – 410 miles (410 – 660 km).
3. Lower Mantle
Temperature: 1900 K (∼ 1600°C) in the outer regions which can reach up to 4300 K (∼4000°C) at the bottom Thickness: 1,400 miles (2,250 km) Density: ∼ 4400 kg/m3 It is found below the upper mantle from a depth of about 400 miles (650 km) down to 1,800 miles (2,900 km) and is thus incredibly large and takes up most of the earth’s volume. Being so deep inside the earth, the temperature and pressure of the lower mantle are extremely high. Here in the lower mantle, the convection currents allow heat from the interior of the earth to rise to the surface.
4. Outer Core
Temperature: 4,300 K (4,030°C) in the outer regions to 6,000 K (5,730°C) closest to the inner core Thickness: 1,355 miles (2,180 km) Density: 9,900 – 12,200 kg/m3 Found below the mantle and having a composition similar to the inner core with 80% iron, along with nickel and some other lighter elements. The outer core has a very high density and thus always found to exist in the viscous-liquid state due to not having enough pressure to be compressed to a solid.
5. Inner Core
Temperature: 5,700 K (∼5,500°C) Thickness: 760 miles (∼1,220 km) Density: 12,600 – 13,000 kg/m3 It is the center, and the hottest part of the earth. Similar to the outer core, the inner core is composed primarily of iron and nickel and has the highest density among all other layers. The inner core is made mostly metals such as gold, platinum, palladium, silver, and tungsten. Due to extremely high temperature and pressure, the metals present in the inner core change their structural conformation and are found to exist in solid state. Recent discoveries also suggest that the solid inner core itself is composed of two layers, separated by a transition zone of about 150 – 250 miles (250 – 400 km) thickness.