Characteristics of Laminar flow
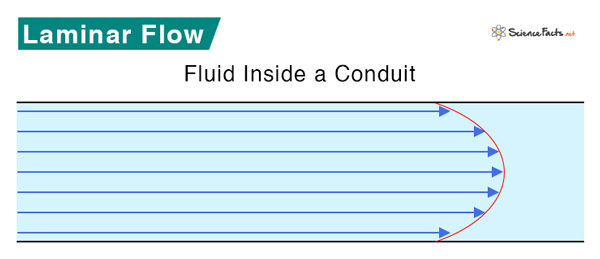
Laminar Flow Velocity Profile
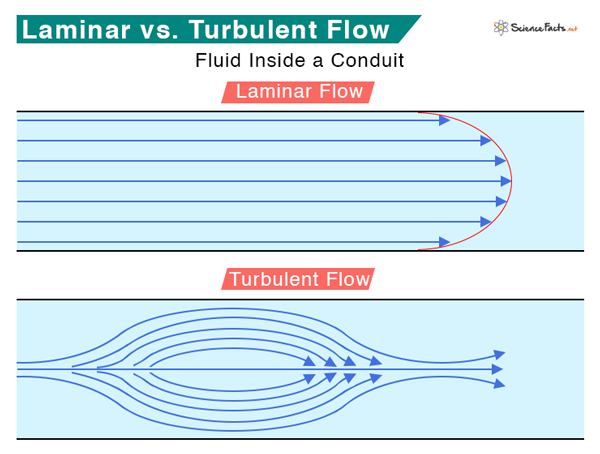
Laminar vs. Turbulent Flow
Transition Regime
Applications
In many fluid dynamics problems, it is a challenging task to determine the instantaneous velocities at different points on the same cross-section. Therefore, an average value is used in fluid flow equations. This average value of the velocity is obtained by applying integral calculus. Laminar flow occurs at low velocity and high viscosity. It is prominent when the diameter of the pipe is small. On the other hand, turbulent flow is characterized by irregular flow with eddies and wakes. Generally, turbulent flow happens at high flow rates and in wide pipes. There is a threshold value beyond which the flow changes from laminar to turbulent. This value is determined by the Reynolds number, named after British physicist Osborne Reynolds after he popularized its use in 1883. The flow is laminar if the calculated Reynolds number is less than 500. If it is between 500 and 1999, the flow transitions from laminar to turbulent. If it is 2000 and above, the flow is fully turbulent. Table Courtesy: Simscale.com