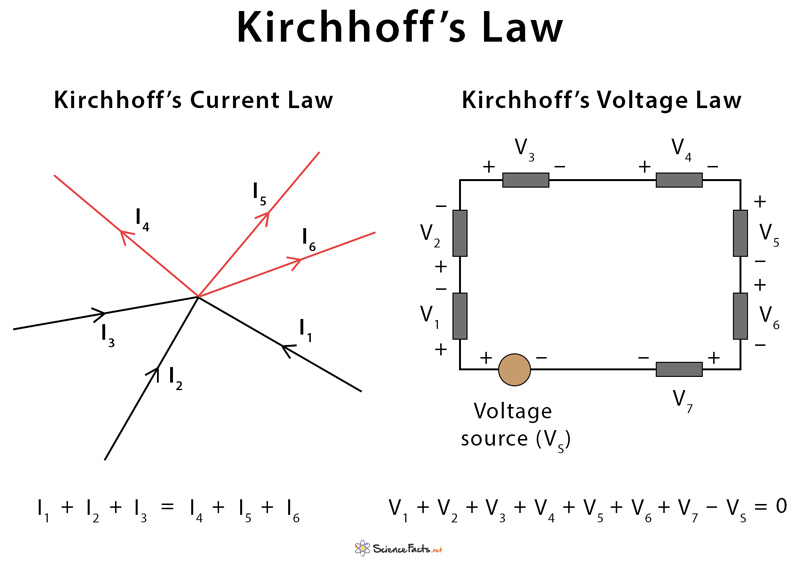
Σ Iin = Σ Iout Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that “in any closed-loop network, the sum of voltage drops around the loop is equal to zero.” This law is known as the conservation of energy. The formula is given by Σ Vtotal = 0 The term node in an electrical circuit generally refers to a connection or junction of two or more current-carrying paths. Also, for current to flow either in or out of a node, a closed-circuit path must exist.
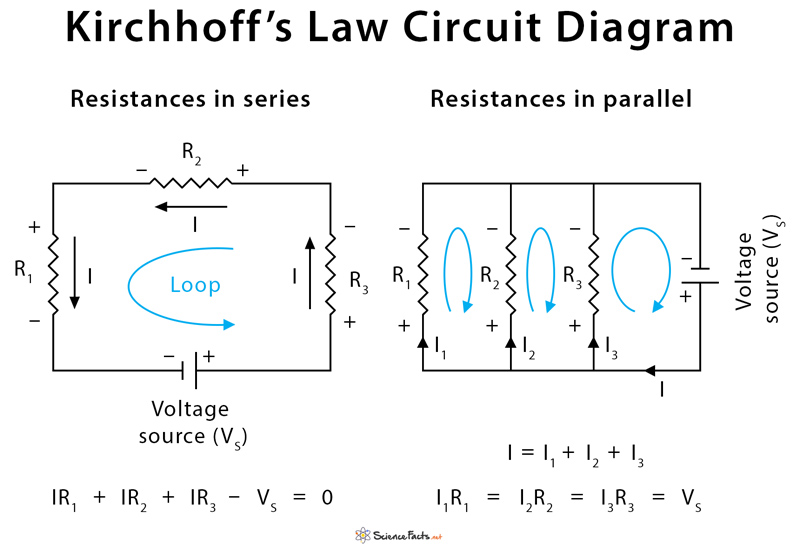
Resistances in Series
Resistances are said to be in series when they are connected in a single path. The current from a source flows through all the resistances in a closed loop.
Resistances in Parallel
Resistances are said to be in parallel when the path branches and each branch consists of one resistance. The current from the source splits into different paths. The equation for replacing resistances in parallel is a bit more complicated.
Sign Convention
The sign convention for applying signs to the voltage polarities in KVL equations is as follows. When traversing the loop, if the positive terminal of a voltage difference is encountered before the negative terminal, the voltage difference will be interpreted as positive. If the negative terminal is encountered first, the voltage difference will be interpreted as negative.
To find the unknown resistances, impedances, voltages, and currents (direction as well as value).In a branched circuit, currents passing each branch are determined by applying KCL at every junction and KVL in every loop.In a looped circuit, the current passing each independent loop is determined by applying KVL for each loop and calculating the currents in any resistance of the circuit.
Another limitation is that it works under the assumption that there is no fluctuating magnetic field in the closed-loop. Electric fields and emf could be induced, which causes Kirchhoff’s laws to break in the presence of a variable magnetic field.