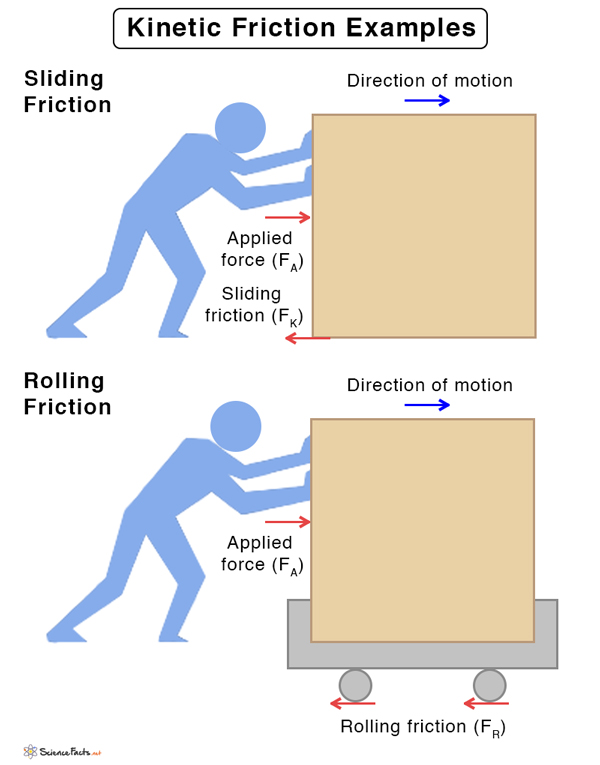
Types of Kinetic Friction
Laws of Kinetic Friction
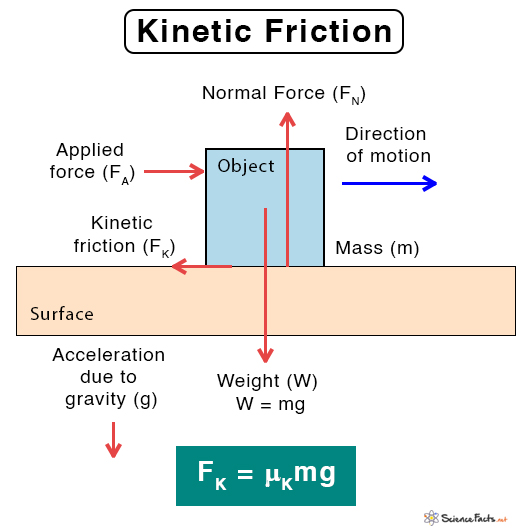
Kinetic Friction Equation
Sliding Friction
In this type of friction, the object slides over the surface. Examples
A vehicle skidding on the road after applying brakesAn ice skater or a skier coming to a stopA box being pushed on a floorGeneration of heat due to rubbing of hands
Rolling Friction
In this type of friction, the object rolls over the surface
A soccer ball coming to a stop after kicking itA golf ball coming to a stop after rolling over the greenA roller skater coming to a stopA roller coaster slowing down before coming to a stop
Acts in a direction opposite to the object’s motionProportional to the normal forceIndependent of the area of contact between the surfacesIndependent of the sliding speed as long as the speed is not too high
FK ∝ FL Or, FK = μL FL Symbol of kinetic friction: FK Unit of kinetic friction: Newton or N Dimension of kinetic friction: MLT-2 The constant of proportionality μL is called the coefficient of kinetic friction. It is unitless and dimensionless. Its value depends upon the pair of surfaces. The coefficient of kinetic friction is less than that of static friction. The work done by a force is the product of the force and displacement d. Therefore, the work done W by the kinetic friction force is W = FK x d The kinetic friction remains constant over time as long as the normal load remains unchanged.
How to Find the Coefficient of Kinetic Friction
The coefficient of kinetic friction can be determined through experiments, such as measuring the force needed to overcome friction or measuring the angle at which an object will start to slide off an incline.