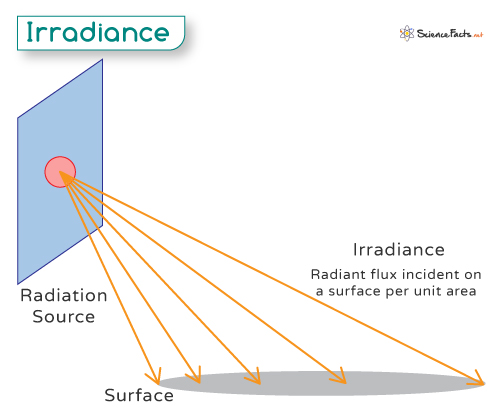
For example, when we stand outside in the sun, we feel its warmth due to the Sun’s energy reaching us. To measure how much of this solar energy is hitting a specific area, like a square meter of ground, we use irradiance.
Formula
Solar Irradiance
How to Measure Solar Irradiance
To measure irradiance, scientists use instruments called pyranometers or radiometers. These devices are designed to capture and measure the amount of sunlight (or other electromagnetic radiation) falling on a given area Where: – I is the irradiance – P is the power of the electromagnetic radiation hitting the surface – A is the area over which the power is distributed Among its various forms, solar irradiance is a specific type that focuses on sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface.
Types of Solar Irradiance
Solar irradiance can be categorized into different components to understand its characteristics better.
Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) represents the total solar power received on a horizontal surface, accounting for direct sunlight, diffuse radiation from the sky, and ground-reflected radiation.Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI) focuses on the direct beam of sunlight that reaches a surface perpendicular to the Sun’s rays, excluding diffuse and reflected radiation.Diffuse Horizontal Irradiance (DHI) quantifies the scattered sunlight in the sky, omitting direct and ground-reflected radiation.
Applications of Irradiance
Here are some applications of solar irradiance: Here are some applications in various other fields: