Igneous rocks are generally formed by the process of cooling and solidification of hot molten magma. When hot, molten magma at 600 to 1,300 °C (1,100 to 2,400 °F) cools and crystallizes at the earth’s surface or inside the crust, they solidify into igneous rock. The magma develops underground, either in the lower crust or the upper mantle, due to the extreme heat and pressure. When magma gushes out to the surface through cracks or volcanoes, it is called lava. Igneous rocks are formed either at volcanoes on the earth’s surface or deep inside the crust when it is in melted form.
What are Igneous Rock Made of
Types: Where and How are they Formed
Igneous Rocks Examples
Uses and Benefits of Igneous Rocks
Fun Facts for Kids
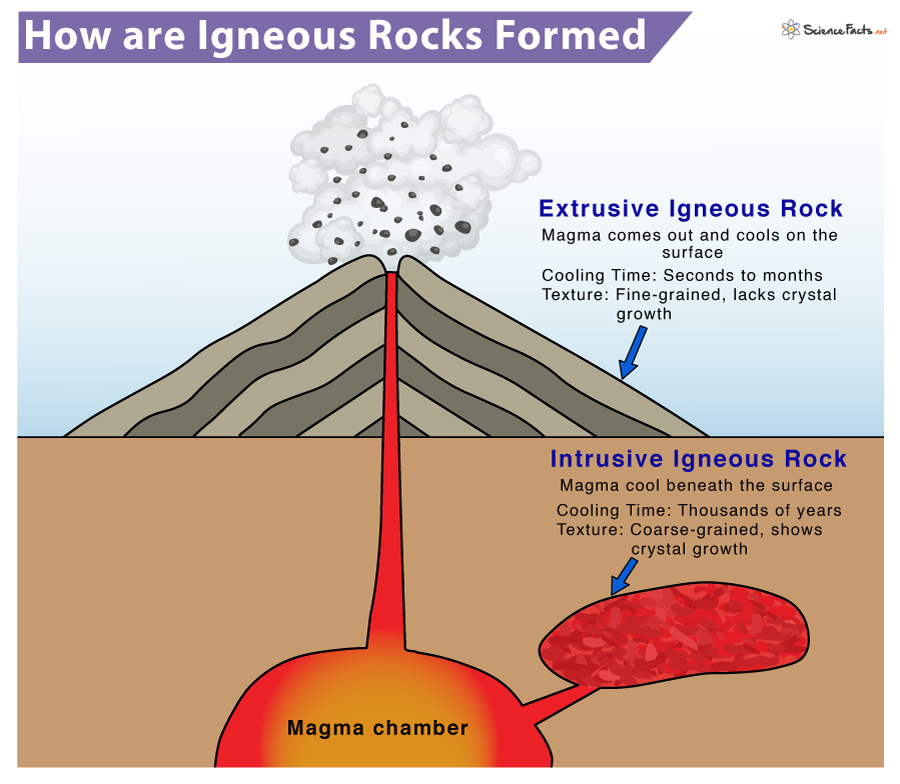
1) Extrusive Igneous Rocks
Extrusive or volcanic igneous rocks are formed on the earth’s surface when lava exists and cools almost instantly when exposed to a relatively cool temperature in the atmosphere. The quick cooling of the lava prevents the mineral crystals from growing and forms a fine-grained or even glassy texture. These fine-grained rocks are known as aphanitic, from a Greek word meaning ‘invisible’. Hot gas bubbles are trapped in the quenched lava, forming a vesicular texture. Extrusive igneous rocks are found in:
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, HawaiiSunset Crater Volcano National Monument, ArizonaCrater Lake National Park, Oregon
Properties and Characteristics
2) Intrusive Igneous Rocks
Intrusive or plutonic igneous rocks develop when magma is trapped deep inside the earth and solidifies without ever reaching the surface. The magma cools and solidifies very slowly over thousands or millions of years in chambers of pre-existing rocks. Slow cooling allows individual mineral grains to grow very long, forming rock with visible, large crystals. Intrusive igneous rocks are found in:
Acadia National Park, MaineJoshua Tree National Park, CaliforniaYosemite National Park, California
Properties and Characteristics
Basalt is a hard, black-colored extrusive igneous rock composed mainly of plagioclase and pyroxene minerals. Pumice is a light-colored vesicular extrusive igneous rock. It is composed primarily of silica and A1-oxide but may contain metal oxides, calcite, or salts. Obsidian is a dark-colored, extrusive igneous rock that forms due to the rapid cooling of molten rock and thus does not form crystals. Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in lighter elements such as silicon and oxygen. Rhyolite is a light-colored, fine-grained extrusive igneous rock typically consisting of quartz and feldspar minerals. Scoria is a dark-colored vesicular extrusive igneous rock formed due to trapped gas at the time of solidification. It is composed of almost 50% silica and 10% calcium oxide with lesser contents of potash and soda. Dacite is a light-colored (white to light gray), extrusive igneous rock consisting primarily of plagioclase and quartz. Granite is a light-colored, course-grained intrusive igneous rock consisting of quartz, feldspar, and mica minerals. It is the most common intrusive igneous rock. Gabbro is a dark-colored, coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock that contains feldspar, pyroxene, and sometimes olivine. Diabase is a dark grey to the black-colored, course-grained intrusive igneous rock consisting primarily of plagioclase feldspar and pyroxene minerals. The grains in diabase are more extensive than those in basalt but smaller than those in gabbro. Diorite is a coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock with a contrasting mix of black and white mineral grains. It consists of a mixture of feldspar, pyroxene, hornblende, and sometimes quartz. Pegmatite is a light-colored, course-grained intrusive igneous rock consisting of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic composition as granite. Peridotite is a dark-colored, coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock consisting of small amounts of amphibole, feldspar, quartz, or pyroxene. Granite
Construction of buildings and statuesBuilding kitchen countertops
Basalt
Rich source of ironCommonly used as an ingredient of concrete
Pumice
Abrasive – removing dead skin from the bottom of feetMaking of lightweight materials such as toothpaste and cosmetic products
Gabbro
Polishing surfacesThe raw material of gold and silver