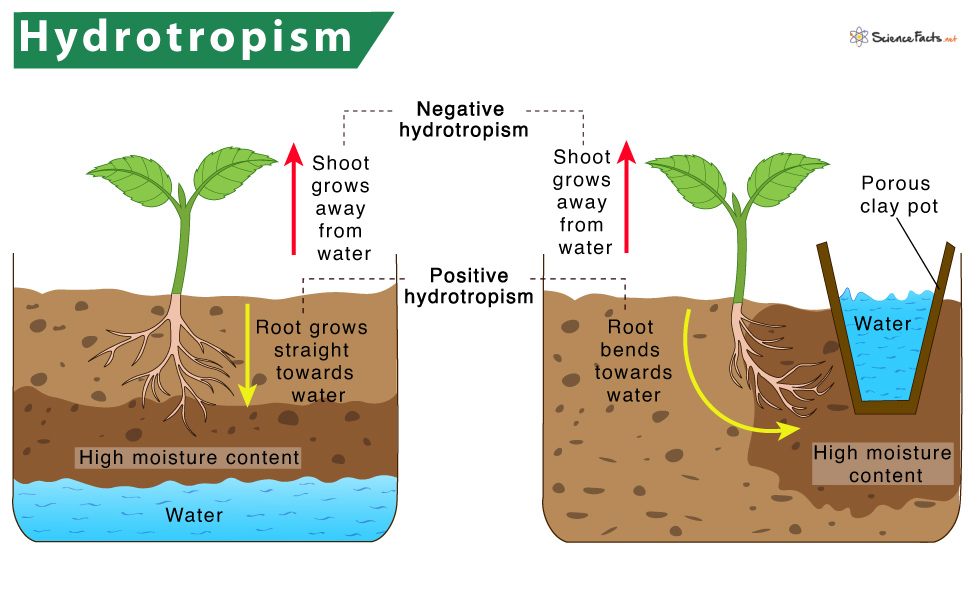
The term ‘hydrotropism’ is a combination of two words, ‘hydro’ and ‘tropism’. Here, ‘hydro ‘means ‘water’, and ‘tropism’ stands for ‘tropic movement’. Tropic movement is a directional movement displayed by a plant in response to any external stimuli, such as light, gravity, chemical, touch, temperature, and water. In this case, the external stimulus is water or moisture. Example: The movement of plant roots towards water.
Its Types
Based on whether the plant part moves towards or away from the water stimulus, hydrotropism can be of two types:
- Positive hydrotropism: Here, the plant part tends to grow towards moisture or water stimulus. Example: Growth of plant roots towards relatively higher humidity or moisture content.
- Negative hydrotropism: In this type, the plant part grows away from the water stimulus. Example: Growth of stem away from the moisture content.
How does Hydrotropism Work in Plants
Why is Hydrotropism Important