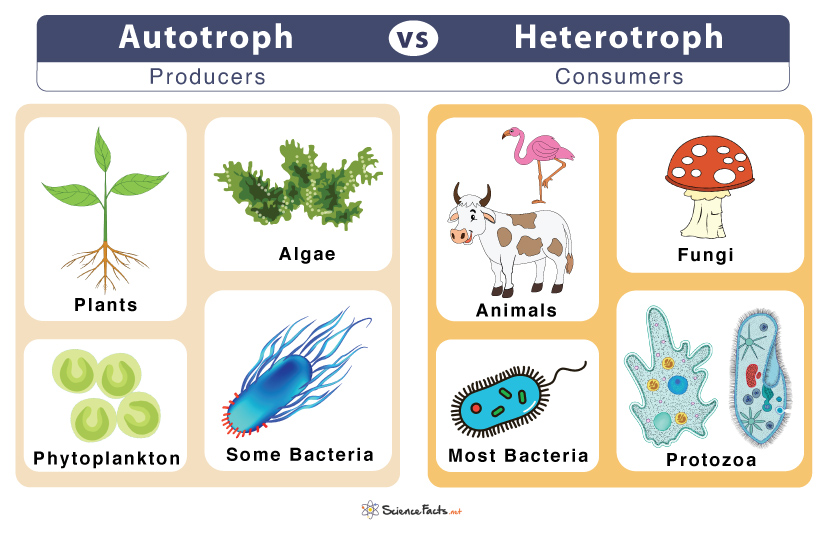
All members of kingdom Animalia are heterotrophs, including dogs, cats, squirrels, rabbits, mice, lions, and leopards. Some plants, such as Venus flytrap and pitcher plants, are also heterotrophs as they feed on insects for their food. Also, many microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, and some protists, exhibit a heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Heterotrophs occupy the second and third trophic levels in a food chain after the first level consisting of autotrophs.
Types of Heterotrophs
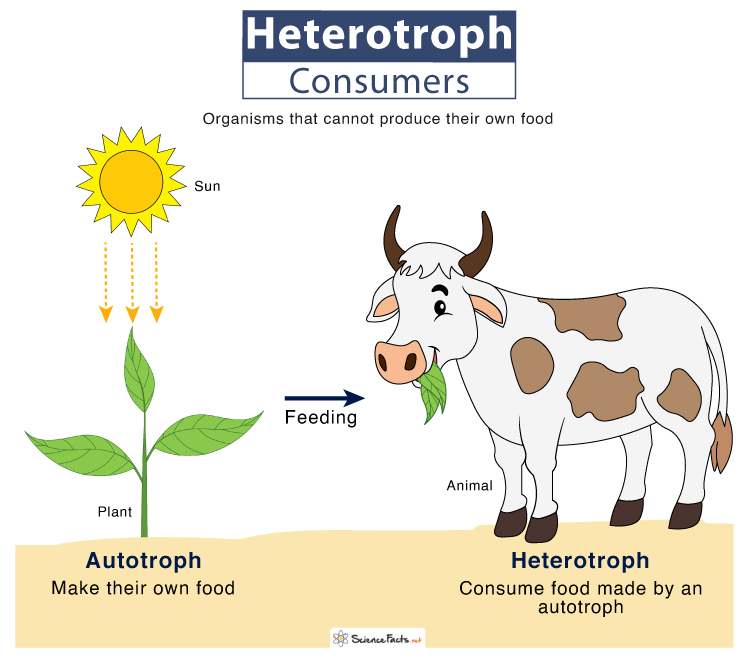
Autotroph vs. Heterotroph
- Herbivores feed on autotrophs like plants and algae for food. Herbivores occupy the second trophic level of the food chain. Examples: Deer, cow, and buffalo
- Carnivores eat meat and feed on herbivores, thus called primary consumers. Carnivores inhabit the third trophic level of the food chain. Examples: Tiger, wolf, and crocodile
- Omnivores: They eat both plants (autotrophs) and meat (herbivores and carnivores) and are thus called secondary consumers. Similar to carnivores, omnivores also occupy the third trophic level of the food chain. Examples: Humans, bears, and foxes
- Detritivores (Decomposers) feed on the remains of plants and animals and fecal matter. Detritivores help to clean the ecosystem and keep them healthy. Examples: Bacteria, fungi, worms, and insects
Based on Energy Source
Heterotrophs are also sometimes classified based on their energy source into two types. They are photoheterotrophs and chemoheterotrophs. a. Photoheterotrophs get their energy from light. They, however, obtain carbon from other organisms as they cannot utilize carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere. Examples: Purple non-sulfur bacteria, green non-sulfur bacteria, and heliobacteria b. Chemoheterotrophs get both light and carbon from other organisms. They cannot utilize light and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Examples: Bacteria and archaebacteria in deep-sea vents and volcanoes
Differences
Similarities
Both are:
Living things and thus need food and energy to surviveCan reproduceRespond to the environment and maintain homeostasisIn need of carbon source (inorganic or organic)Made of cellsPart of the ecosystem and food chain of the biosphere
The key differences and similarities between an autotroph and a heterotroph are shown using a Venn diagram.