Climate scientists have recently spoken about how humans have dramatically changed the Earth’s environment over the past two centuries, increasing its average temperature.
What is the Greenhouse Effect and Why is it Important
Which Gases Contribute to the Greenhouse Effect
What Causes the Greenhouse Effect
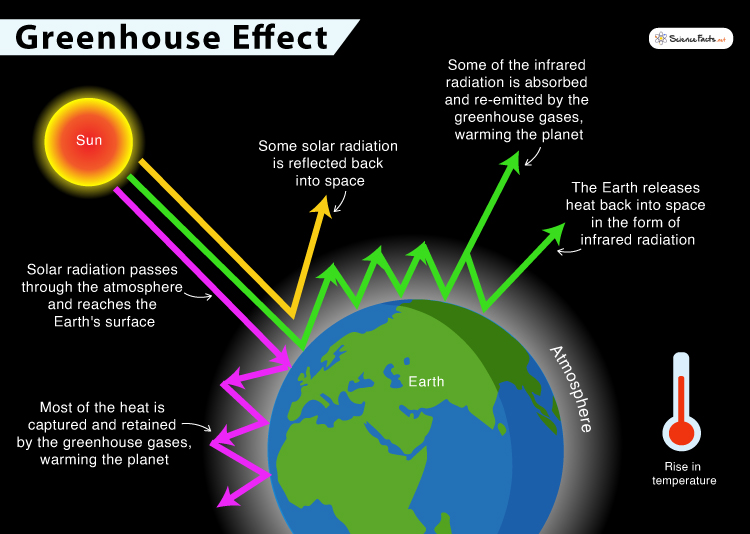
How does the Greenhouse Effect Work
Consequences of Greenhouse Effect
What is the Runaway Greenhouse Effect
Is the Greenhouse Effect Good or Bad
The existence of greenhouse gases was first proposed by French mathematician and physicist Joseph Fourier in 1824. The term ‘greenhouse effect’ was given by Swedish physicist and physical chemist Svante Arrhenius in 1896.
Burning of Fossil Fuels: It is the primary artificial source of greenhouse gas emissions on Earth. Fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas are widely used in transportation and for producing electricity. With the increasing population, fossil fuels’ utilization has also increased, leading to an increase in the greenhouse effect.Deforestation: Since plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis, cutting trees affects this process, causing an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Agricultural Activities: Nitrous oxide used in chemical fertilizers and pesticides contributes to about 30 percent of greenhouse gas emissions. This rate is rising with each passing day due to an increase in food demand. Industrial Wastes and Landfills: The factories and industries release toxic greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Landfills release carbon dioxide and methane that further adds to the greenhouse effect.
How is the Greenhouse Effect Related to Global Warming and Climate Change
Due to the excessive release of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, there is a gradual increase in the Earth’s average temperature in the last two centuries, known as global warming. Global warming has led to changes in the Earth’s climate, causing an alteration in many ecosystems and living organisms’ natural habitat. It also raises the sea level due to the melting of glaciers, producing extreme weather events such as floods, drought, hurricanes, and heatwaves.
Other Harmful Effects
Ozone Layer Depletion: Accumulation of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere depletes the ozone layer present in the upper stratosphere. As a result, the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays reach the Earth’s surface and cause skin cancer and crop damage.Smog and Air Pollution: Automobile, industrial activities, and forest fires are significant sources of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere forming smog and other forms of air pollutions.Acidification of Water Bodies: The greenhouse gases in the air mix with rainwater and fall as acid rain, thus turning the Earth’s water bodies acidic. Also, rainwater drives the soil contaminants that ultimately fall into water bodies such as rivers, lakes, streams, and oceans, causing their acidification.
Scenario 1: This scenario arises when the planet’s temperature rises to the boiling point of water. At such a high temperature, all water from the water bodies changes to vapor, which traps more heat from the Sun, causing a further increase in the planet’s temperature. This evaporation enhances the greenhouse effect and is thus known as the ‘positive feedback loop.’ Scenario 2: At high temperatures, various chemical reactions start to happen. During one such reaction, carbon dioxide is released from rocks, which heats the planet and causes further disintegration, creating a ‘positive feedback loop.’