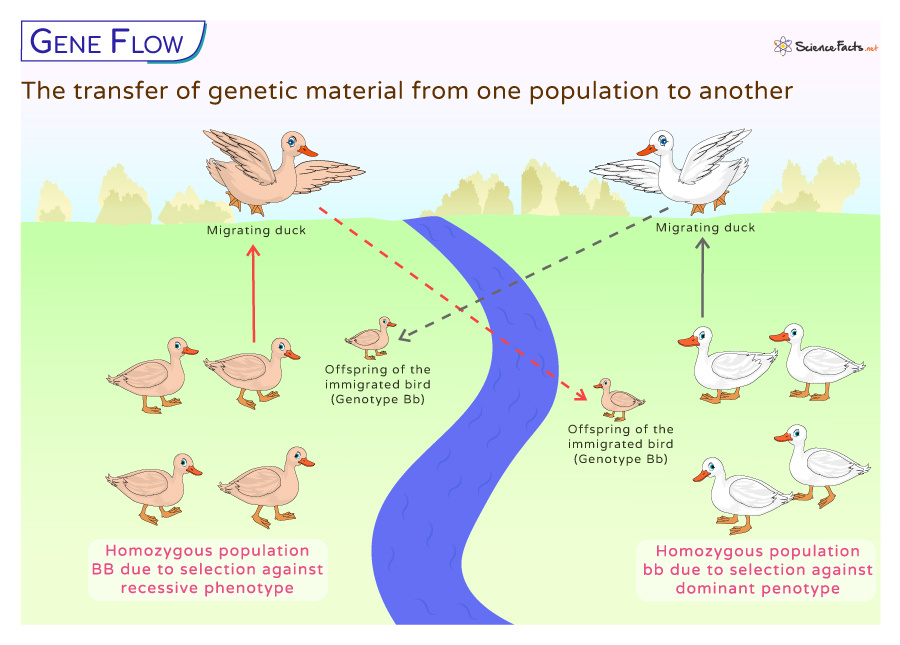
It changes the gene pool of the receiving population by changing the allele frequency. The gene flow thus plays a crucial role in shaping the genetic diversity or variation within and among populations of the same or different species.
When Causes Gene Flow
Factors Affecting Gene Flow
Examples of Gene Flow in Nature
Effect of Gene Flow on Population
Importance of Gene Flow in Nature
Gene Flow vs. Genetic Drift
Alternatively, it can occur between two species, from bacteria or viruses to higher organisms, through horizontal or lateral gene transfer (HGT or LGT).
Plant Pollination
In flowering plants, gene flow occurs through pollination. Bees, for instance, visit flowers to collect nectar, inadvertently transferring pollen between plants. This exchange of genetic material ensures the mixing of plant genes, contributing to the biodiversity of plant populations.
Insects and Wind Dispersal
Some butterfly species exhibit gene flow through wind dispersal during the larvae or pupae stage of their life cycle. This passive movement allows genetic material to be exchanged between geographically separated populations, influencing the genetic diversity within the species.
Migration in Birds
Arctic Terns are known for their annual migration from the Arctic to the Antarctic and back. They encounter individuals from different populations during these journeys, promoting gene flow. This movement helps maintain a degree of genetic homogeneity among widely dispersed populations.
Island Biogeography
Islands provide excellent examples of gene flow in action. Island populations often experience limited gene flow due to the surrounding water acting as a barrier. This isolation can lead to the development of unique species with distinct genetic traits. However, occasional migration events can introduce new genetic material, influencing the island’s biodiversity.
Human Populations
In human populations, migration patterns have shaped the genetic diversity observed today. For instance, the movement of humans out of Africa and their subsequent migration across the globe led to the development of diverse genetic traits in different populations. Modern transportation and globalization continue to influence gene flow among human populations.
Migration in Fishes
Salmon populations often migrate between freshwater and marine environments for breeding. Mixing individuals from different river systems during these migrations facilitates gene flow. This movement plays a crucial role in maintaining genetic diversity within salmon populations.
- Introduction of New Genes As individuals migrate and interbreed between populations, they bring new alleles that are absent or less frequent in the recipient population. It causes an increase in genetic variation within the population by expanding the pool of available alleles.
- Recombination and Mixing of Genes During interbreeding, the recombination of genetic material occurs, leading to the formation of new combinations of alleles in offspring.
- Maintenance of Variation Gene flow counteracts genetic drift and natural selection, which can reduce genetic diversity over time.
Creating Biodiversity in Population
The primary role of gene flow lies in its capacity to mold and maintain genetic diversity. As organisms migrate and interbreed, genetic material flows seamlessly. This constant mingling mitigates the effects of genetic drift and counteracts the selective pressures that could lead to uniformity. In essence, gene flow acts as a genetic bridge, connecting populations and fostering a shared genetic reservoir.
Mitigating Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, the random change of allele frequencies in a small population, can lead to the fixation or loss of specific alleles over time. Gene flow acts as a counterforce, infusing genetic material and preventing the fixation of alleles by introducing new variations. This continuous influx of diversity maintains the adaptive potential of populations, ensuring they remain resilient in the face of environmental challenges.
Improving Adaptation in Population
Gene flow is not merely a passive force. It actively contributes to the adaptive capabilities of populations. By introducing new genetic material, populations access a broader pool of traits. This influx of variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, enabling populations to adapt to changing environmental conditions.