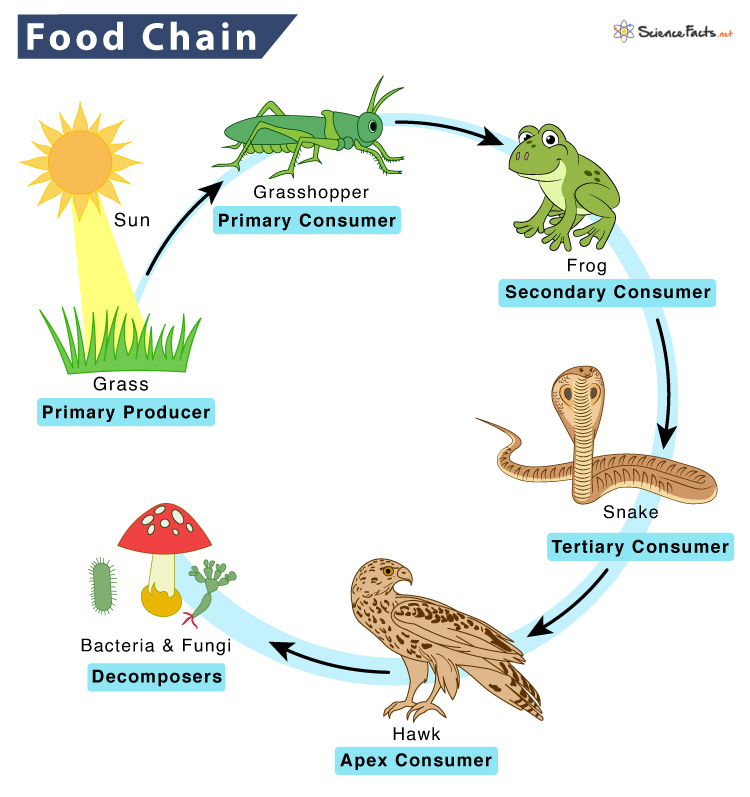
What is a Food Chain
Trophic Levels
Types of Food Chain
Many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. Even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. Thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. All interconnected to make a food web. The different trophic levels in a typical food chain are:
Primary Producers
They are the first biotic factor occupying the first tropic level or the bottom of the food chain. Primary producers mainly produce their own food by photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Plants, algae, and autotrophic bacteria are primary producers.
Consumers
They occupy the food chain’s second, third, and fourth trophic levels.
The organisms that depend on primary producers for food are primary consumers. Insects, flies, and some birds and animals are primary consumers. Primary consumers are grasshoppers, caterpillars, rabbits, hummingbirds, cows, sheep, deer, and goats. Animals that feed on grass and plants are called herbivores.The organisms that feed on the primary consumers are secondary consumers. They are primarily meat-eaters such as foxes, wolves, owls, hawks, and eagles are called carnivores. However, smaller animals like spiders, frogs, lizards, moles, and small birds like kingfisher are also part of this trophic level.Finally, the organisms that depend on the secondary consumers for their food are tertiary consumers. They can be carnivores (meat-eaters) or omnivores (plants and meat-eaters). Large animals like leopards, seals, sea lions and sharks are examples of tertiary consumers. Small reptiles like snakes are also a part of this trophic level. Tertiary consumers that do not have any natural predators sit at the top of the food chain.
Since secondary and tertiary consumers hunt their food, they are called predators. Some food chains contain additional trophic levels like quaternary consumers that feed on tertiary consumers. They are also called apex consumers or apex predators. These include lions, tigers, grizzly bears, polar bears, killer whales (orcas), giant snakes, golden eagles, and harpy eagles.
Decomposers
They are organisms that break down dead organic materials and wastes from other tropic levels. Decomposers include microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi that consume dead remains of plants or animals, including humans. Thus, the level of decomposers in the food chain runs parallel to primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers. Some decomposers are detritivores – debris eaters that are multicellular organisms such as earthworms, crabs, slugs, or vultures. They feed on dead organic matter, producing debris, and making it more available for bacterial or fungal decomposers. Decomposers complete the food chain and are essential to keeping the ecosystem healthy. When they break down dead material and wastes, they release nutrients to the soil for use by autotrophs, which can start a new food chain. The overall steps of a food chain in order are: Sun -> Primary Producers -> Primary Consumers -> Secondary Consumers -> Tertiary Consumers
- Grazing food chain starts with green plants, followed by herbivores and carnivores. Here, the energy in the lowest trophic level is obtained from photosynthesis. As autotrophs are at the base of all ecosystems on Earth, most ecosystems are of this kind. A typical example is phytoplanktons eaten by zooplankton, which small fishes eat, and then large fishes eat small fishes. A grazing food chain can be either predator or a parasitic type. In a predator grazing food chain, one animal consumes another animal. The animal that is eaten is known as the prey, and the animal that eats is called the predator. In contrast, plants and animals are infected by parasites in a parasitic grazing food chain.
- Detritus food chain begins with dead organic matter of plants and animals. Decomposers and detritivores such as fungi, bacteria, and protozoans feed on them. Then, the decomposers are eaten by smaller carnivores like maggots. Finally, the smaller carnivores are eaten by larger carnivores like frogs and snakes. Thus, the food chain study is essential as they show how an organism depends on another organism in an ecosystem for its survival. It also shows the path of energy flow inside an ecosystem.