Fertilization is similar in flowering plants (angiosperms) and seed-bearing plants (gymnosperms).
How does Plant Fertilization Occur
Types of Fertilization
What Happens After Fertilization
1. Pollination
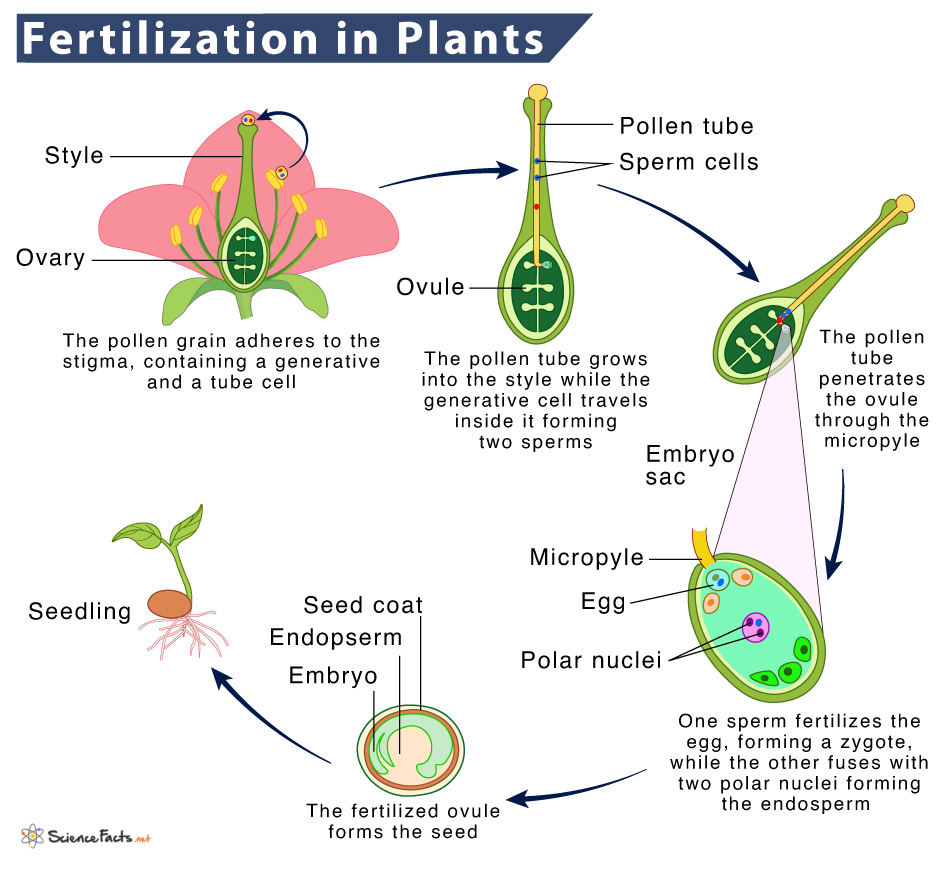
It is the first step of fertilization. Pollination is the act of transporting the pollen grain from the anther (male part) to the flower’s stigma (female part). Wind, water, insects, and animals are some common agents of pollination.
2. Germination
Mature pollen grains contain two cells: a generative cell and a pollen tube cell. When the pollen grain reaches the stigma, the tube cell forms a pollen tube through the style until it reaches the bottom of the ovary. The generative cell then migrates through the pollen tube to enter the ovary for fertilization. The germination of the pollen tube needs water, oxygen, and specific chemicals. As it moves through the style to reach the embryo sac, the pollen tube’s growth is supported by the tissues of the style. During this period, the generative cell divides to form two male gametes.
3. Penetration of the Ovule
The pollen tubes guided by the chemicals secreted by the synergid cells in the embryo sac enter the ovule through the micropyle.
4. Fertilization
Among the two sperm cells, one fertilizes the egg cell, forming a diploid zygote. The other cell fuses with the two polar nuclei, forming a triploid cell that develops into the endosperm. Since there are two fertilization events in angiosperms, it is called double fertilization. Immediately after fertilization, no other sperm can enter the ovule. The fertilized ovule forms the seed, while the ovary (enveloping the seed) becomes the fruit.
2. Chalazogamy
The pollen tube enters the ovule through the chalaza, opposite the micropyle. It is found in Casuarina species of plants
3. Mesogamy
In this process, the pollen tube makes its way into the ovule through its integument, the outermost layer(s). It is found in pumpkin, ridge gourds, bitter gourds, and other gourd plants.