It involves glycolysis but not the other two stages of aerobic respiration. Like glycolysis, fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ‘Ferment’ comes from the Latin word fervere, meaning ‘to boil’. The science of fermentation is called zymology. Some common fermented food beverages are wine, beer, cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, and pepperoni.
A Short History: Timeline
Why Does Fermentation Occur in the Cell
How does Fermentation Work, and What are its Types
What is the Purpose of Fermentation
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
The ETC being non-functional, the NADH made in glycolysis cannot transfer its electrons and revert to NAD+. However, the NADH must be oxidized to allow cells to continue making ATPs using glycolysis. In this condition, fermentation is necessary for the cell. How does Fermentation Allow Glycolysis to Continue In fermentation, pyruvate produced through glycolysis is reduced, and NADH is oxidized to NAD+. Regeneration and a steady supply of NAD+ allow glycolysis to continue, thus providing the cell with the energy necessary for all metabolic functions. How Many ATPs are produced in Fermentation Cells can make only 2 ATPs at most per fermentation as oxidative phosphorylation remains non-functional.
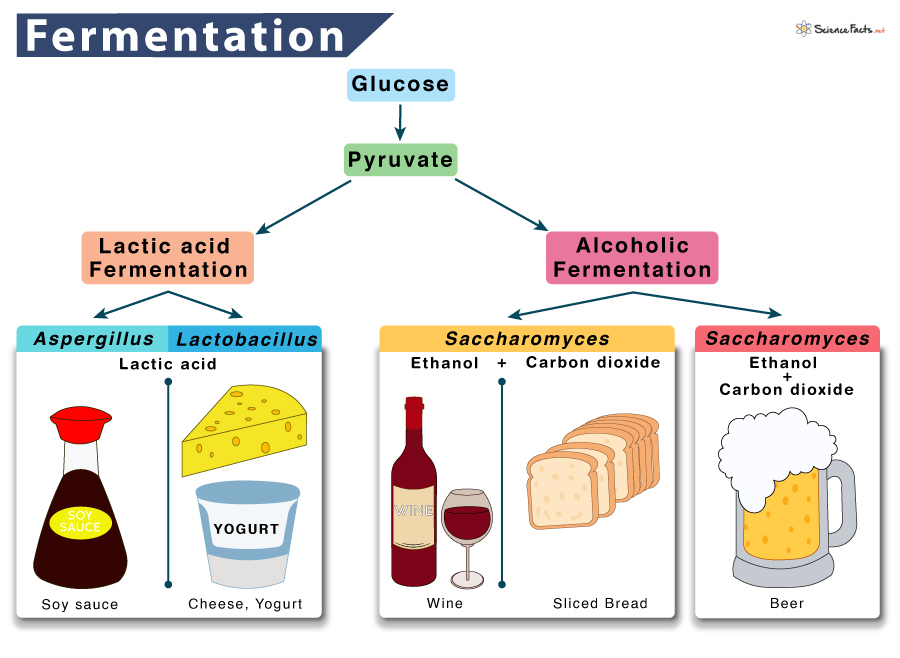
1. Lactic Acid Fermentation
The pyruvate produced through glycolysis is converted to lactate or lactic acid by the fungus Aspergillus. The enzyme that catalyzes this step is lactate dehydrogenase, lactic acid being the byproduct. Humans carry out lactic acid fermentation when the body needs much energy, such as during sprinting and workouts. Once the stored ATP in the cell is used up, our muscles start producing ATP through lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation also occurs in the bacteria Lactobacillus,which is used in making cheese and yogurt. Equation Glucose → 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH → 2 Lactic Acid + 2 NAD+
2. Alcoholic Fermentation
When yeasts such as Saccharomyces are kept without oxygen, they switch to alcoholic fermentation to generate usable energy from food. Similar to lactic acid and ethyl alcohol, the product of alcoholic fermentation is also a byproduct. It is a two-step process. Step 1: A carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide, producing a two-carbon molecule called acetaldehyde. Step 2: NADH passes its electrons to acetaldehyde, regenerating NAD+ and ethyl alcohol. It is the process that causes bread dough to rise. When yeast cells in the dough run out of oxygen, the dough begins to ferment, producing tiny bubbles of carbon dioxide as their waste products. These bubbles are the air spaces we see in a slice of bread. Alcoholic fermentation is also used in wine production. Equation Glucose → 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH →2 Ethanol + 2 NAD++ 2CO2
To produce fermented food and beverages. For example, wine, beer, cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, and pepperoni are high in nutritional value and can act as probiotics.To produce methane and hydrogen gasTo neutralize anti-nutrients like phytic acid in grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes, thus increasing their nutritional value
Likewise, sulfate-reducing bacteria and archaea reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide to regenerate NAD+ from NADH.