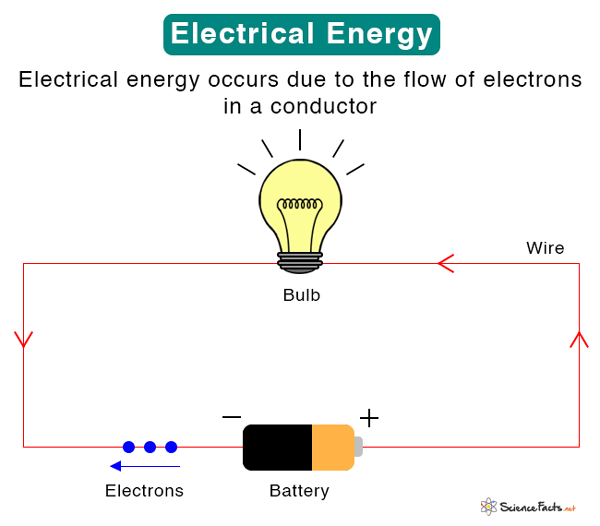
Electrical energy can be stored in small quantities using fuel cells, batteries, capacitors, or magnetic fields. Charges build up in a capacitor, which then stores electrical energy. Thus, electrical energy is also a type of potential energy.
Source of Electrical Energy
Electrical Energy Formula and Unit
Examples of Electrical Energy
Conversion of Other Energy Forms into Electrical Energy
Electrical cables transport electricity from one place to another through conduction. Conductors made from metal are used for this purpose. This method of transporting electrical energy for hundreds of miles is called an electrical grid. The electrical grid’s rate of energy transfer is called electrical power. Equation The equation for electrical energy is given by the following: E = P x t Where E : Energy transferred in kWh (1 kWh = 3.6 x 106 J) P : Power of the appliance in kW (1 kW = 1000 W) t : Amount of time in hours that the appliance operates ( 1 h = 3600 s) Example: If a 60-Watt lamp is turned on for two hours, how many joules of electrical energy are converted? Given P = 60 W, and t = 2 h = 2 x 3600 = 7200 s We have, E = P x t Or, E = 60 Js-1 x 7200 s Or, E = 432,000 J or 432 kJ
- Nuclear Power Plant In a nuclear power plant, nuclear energy is converted into electrical energy. A fission reaction generates heat that converts water into steam. The steam rotates turbine blades that drive a generator to make electricity.
- Hydroelectric Plant In a hydroelectric plant, water falling from a certain height rotates a set of turbines. The turbines power the generators that are connected to them and create electrical energy.
- Geothermal Power Plant In a geothermal power plant, water present in reservoirs beneath Earth’s surface produces steam through natural means. The steam rotates a turbine that activates a generator, producing electricity.
- Wind Turbine An example of a machine that converts mechanical into electrical energy is a wind turbine. The blowing wind turns the turbine blades. The mechanical motion of the blades fires up an electric generator, creating electrical energy.
- Solar Cells Solar energy is produced directly from the sun. The sun’s rays strike solar cells or photovoltaic cells and generate a small electric voltage. By connecting large numbers of individual cells, a large amount of electricity can be generated in a solar electric plant.
- Piezoelectricity Kinetic energy can be converted to electrical energy through piezoelectricity. When sound energy, a form of kinetic energy, is applied to a piezoelectric material, it creates strain in the crystal and produces an electric current. The current is then harvested into electricity.