What Causes Diamagnetism
Diamagnetic Materials
Applications
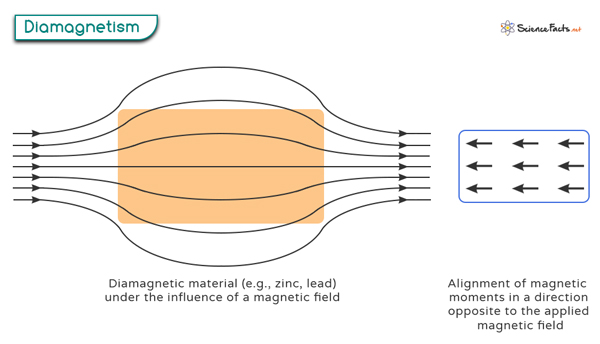
Diamagnetism occurs when all the electrons in an atom are paired up in the orbitals. When subjected to an applied magnetic field, the electrons realign their orbital motion so that their magnetic moments are opposed to the external field. As a result, a weak repulsive force between the diamagnetic atoms and the external magnetic field is generated. It is important to note that diamagnetism is inherent to all atoms. However, it becomes more noticeable when there are no unpaired electrons present.
Diamagnetic Elements
Diamagnetic Molecules
Materials Characterization
Another critical application of diamagnetic materials is in material characterization and quality control. Diamagnetic susceptibility measurements can be used to assess the purity and composition of substances. Scientists and engineers can gain insights into the material’s molecular structure and integrity by subjecting a sample to a known magnetic field and measuring its diamagnetic response. This technique finds utility in various industries, from pharmaceuticals and chemistry to mineral exploration and gemology.