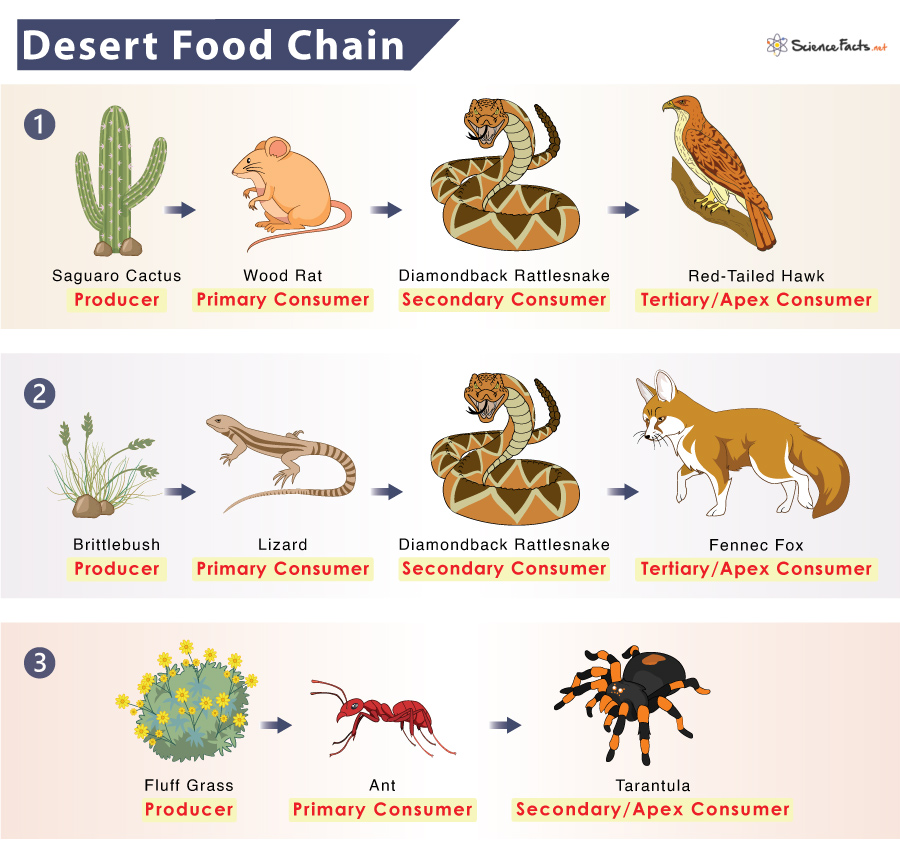
Producers are organisms that make their food. Usually, plants and microorganisms are producers. In contrast, consumers feed on producers for their livelihood. Based on their position in the food chain, consumers are divided into primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers or apex predators. A desert food chain is unique due to its harsh environment.
Desert Food Chain Examples
Decomposers
The Sahara Desert The Sonoran Desert The Gobi DesertThe Australian Desert Atacama DesertThe Arizona Desert
Like all ecosystems, organisms in deserts can be organized in different trophic levels:
Producers
Like other food chains, desert food chains also start with producers making their food. In deserts, date palms, cacti, acacia, sagebrush, desert milkweed, and desert willow are the producers. These plants store water in their bodies due to water scarcity in the environment. Plants like cacti are the keystone species of the desert biome. Without them, the whole food chain will collapse.
Primary Consumers (Herbivores)
Insects and small mammals like Kangaroo rats, desert tortoises, ground squirrels, Arabian camels, and some insects feed only on plants to survive. These groups of herbivorous animals are the primary consumers of the desert food chain.
Secondary Consumers (Omnivores)
Secondary consumers are mostly omnivores (plant and animal eaters), although a few may be carnivores (animal eaters). Animals like lizards, coyotes, rattlesnakes, mongooses, tarantulas, and scorpions are some examples of secondary consumers in the desert.
Tertiary and Apex Consumers (Carnivores)
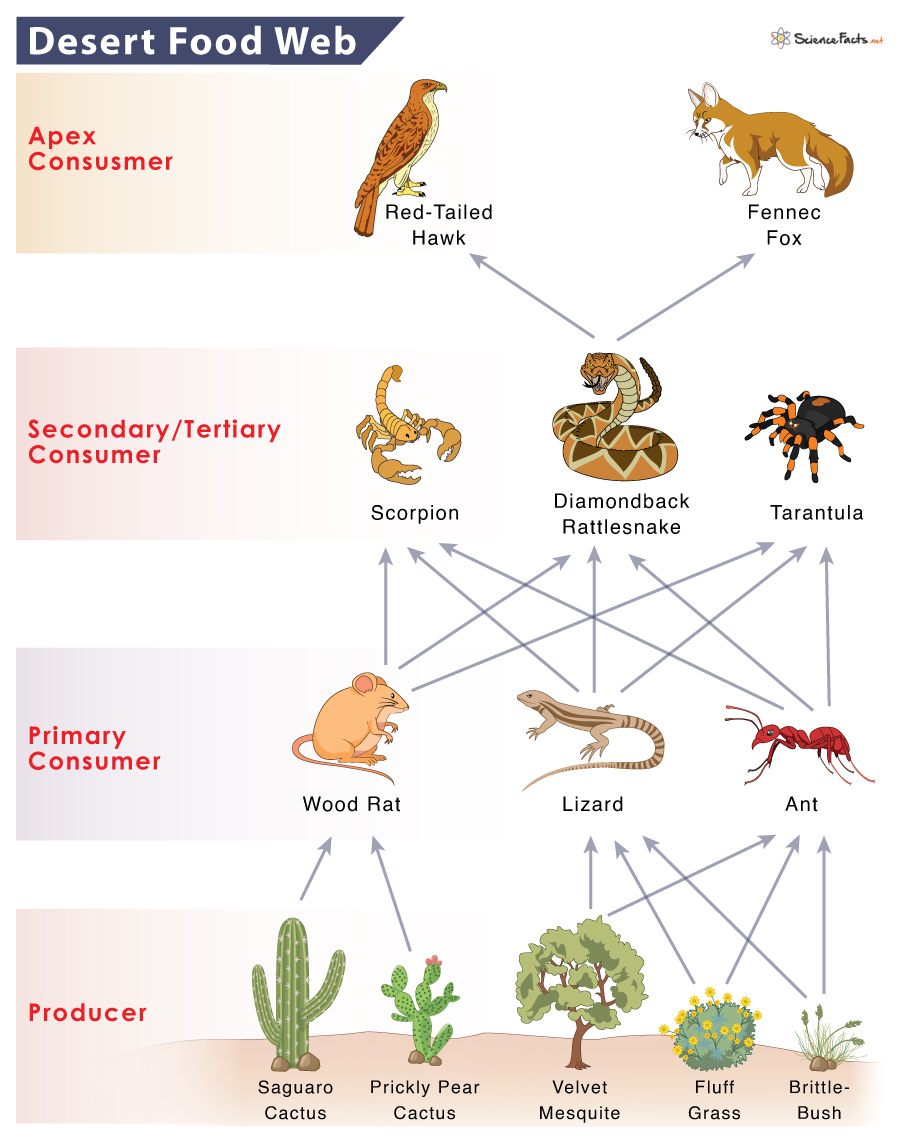
Tertiary and apex consumers are carnivorous animals that reside on the top two trophic levels of the food chain. The organisms in this group include predators like the striped hyena, sand cat, fox, hawks and eagle, and cheetah. They feed on primary and secondary consumers. Those organisms perform the role of a tertiary consumer or an apex predator based on their participation in the food chain. For example, the rattlesnake is the apex consumer in the food chain: Brittlebush -> Squirrel -> Rattlesnake. In contrast, the snake is the tertiary consumer in the food chain: Brittlebush -> Grasshopper -> Grasshopper mouse -> Rattlesnake -> Hawk. In the desert, humans are the ultimate predators. Other apex predators compete with humans for food and survival. When a group of overlapping and interconnecting desert food chains is represented, it forms a desert food web. A desert food web shows the nature of interdependence of the organisms in a desert over a wide area.