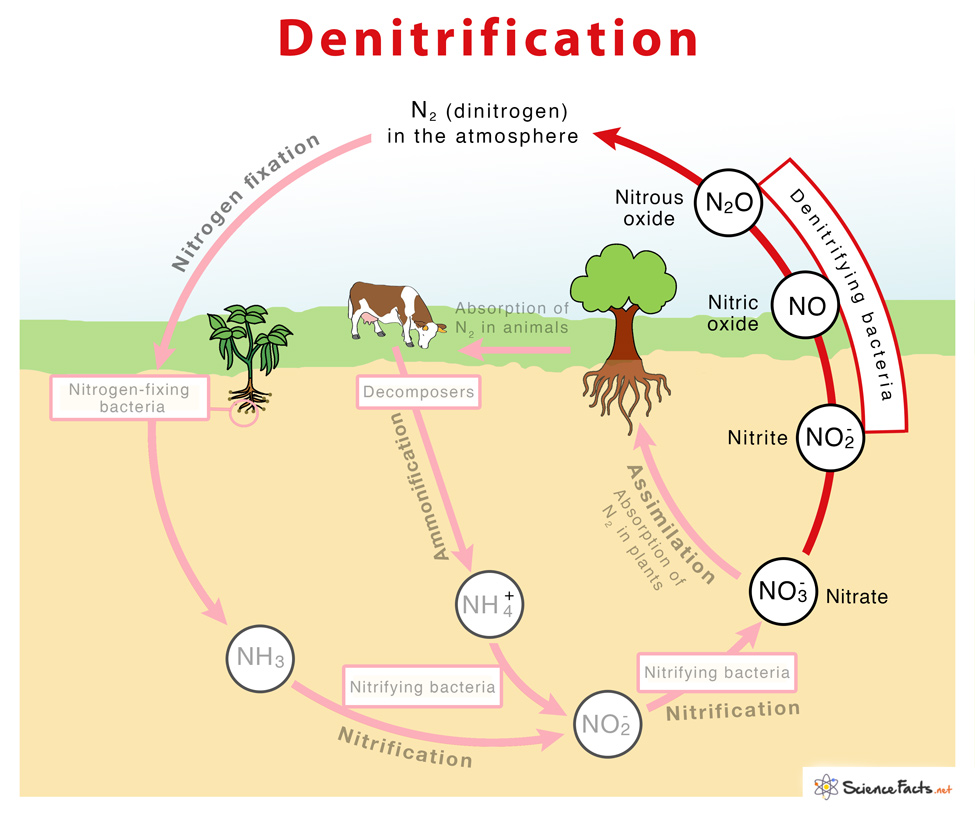
What is Denitrification
When Does it Occur
Where does It Occur
Importance of Denitrification
NO3− → NO2− → NO → N2O → N2 The different steps of denitrification are carried out by enzymes nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, nitric oxide reductase, and nitrous oxide reductase as shown below: Denitrification proceeds through a combination of the following half-reactions:
NO3− + 2 H+ + 2 e−→ NO₂− + H2O (by Nitrate reductase)NO₂− + 2 H+ + e− → NO + H2O (by Nitrite reductase)2 NO + 2 H+ + 2 e− → N₂O + H2O (by Nitric oxide reductase)N₂O + 2 H+ + 2 e− → N₂ + H2O (by Nitrous oxide reductase)
The complete balanced equation of the entire process is given below: 2 NO3− + 10 e− + 12 H+ → N2 + 6 H2O It is helpful in wastewater treatments. It helps remove unwanted nitrates from the wastewater effluents, reducing the chances that the water discharged from the treatment plants will cause undesirable consequences such as algal blooms (eutrophication). Denitrification is also essential in agriculture, where the loss of nitrates in fertilizer is detrimental and costly. In contrast, the byproducts of denitrification, such as NO and N2O, contribute to the formation of smog and greenhouse gas-based climate change.