The process can be symmetrical, where the daughter cells get an equal share of the mother cell cytoplasm or asymmetrical when the cytoplasm is divided unequally. For example, the process of spermatogenesis in males is symmetrical, producing millions of sperms, all of the equal size. In contrast, oogenesis in females is asymmetrical, producing one large egg cell with mostly mother cell cytoplasm and three small cells called polar bodies. Cytokinesis in eukaryotes hugely resembles the prokaryotic process of binary fission in many ways. However, the exact mechanism differs due to their cell structure and functions.
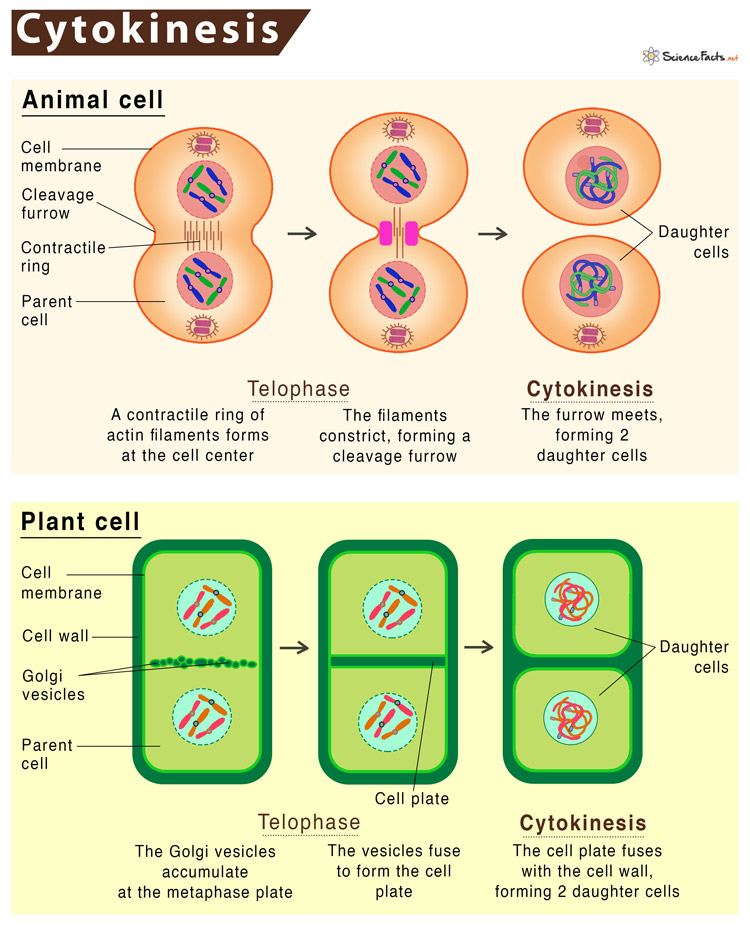
What Happens during Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells
Due to the lack of cell walls, cytokinesis in animal cells begins in anaphase and terminates in telophase. It follows the following stages: As the separation starts outside and moves towards the cell’s center, cytokinesis in animal cells is called centripetal cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
Since a plant cell contains a cell wall, cytokinesis starts during interphase and terminates in telophase. It follows the following stages: As the separation starts in the center and moves laterally to the outside, cytokinesis in animal cells is called centrifugal cytokinesis.