The law is named after French physicist and Nobel laureate Pierre Curie, who formulated it in 1895, and it has since become a cornerstone of modern physics.
Equation
Where:
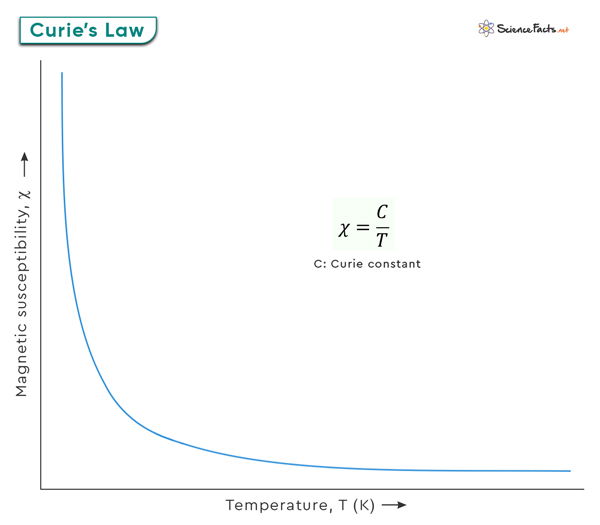
M represents the magnetization of the material.C is the Curie constant, a material-specific constant with the unit Aˑm-1ˑKˑT-1.B is the applied magnetic field.T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin (K).
The Curie constant (C) is unique to each material and reflects its inherent magnetic properties. Different materials have different Curie constants, which dictate how they respond to temperature. The magnetization is related to the applied magnetic field as follows: Where χ is the magnetic susceptibility. The Curie’s Law becomes