The Role of Unit Cell in Crystal Structure
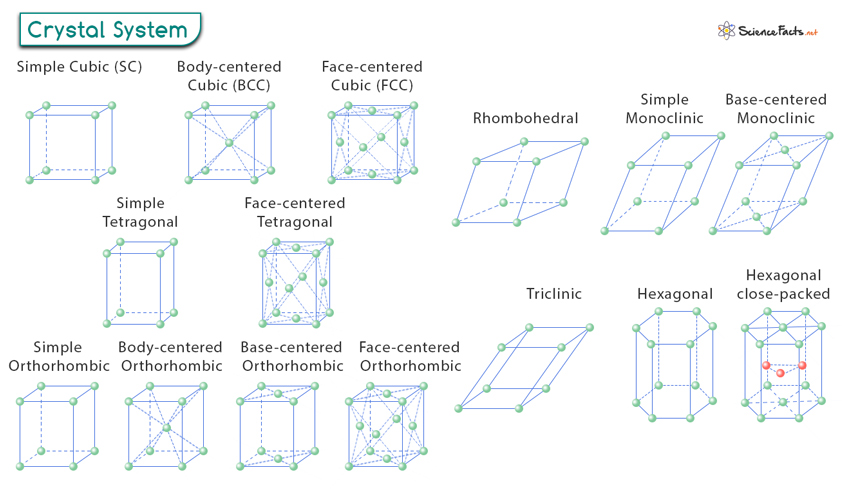
Crystal System
A crystal structure focuses on how the atoms are arranged inside the crystal. However, crystallographers are interested in the overall shape and size of the crystal as well as its external characteristics. To accomplish this, they need to know about the crystal system.
Example of Crystal Structure
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
The crystal structure of sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt, is a prime example of a cubic crystal lattice. In this arrangement, the sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl–) ions are positioned in an alternating pattern, forming a three-dimensional grid-like structure. The sodium chloride crystal lattice is characterized by the close packing of the positive sodium ions and negative chloride ions. Each sodium ion is surrounded by six chloride ions, and each chloride ion is surrounded by six sodium ions, creating a highly stable and symmetrical structure. This crystal structure is responsible for the unique physical and chemical properties of sodium chloride, including its high melting point, electrical conductivity, and ability to form ionic bonds easily.