It was discovered jointly by Walther Flemming in 1875 and Edouard Van Beneden in 1876 and later named and described in 1888 by Theodor Boveri.
Where is it Located
Structure
Functions
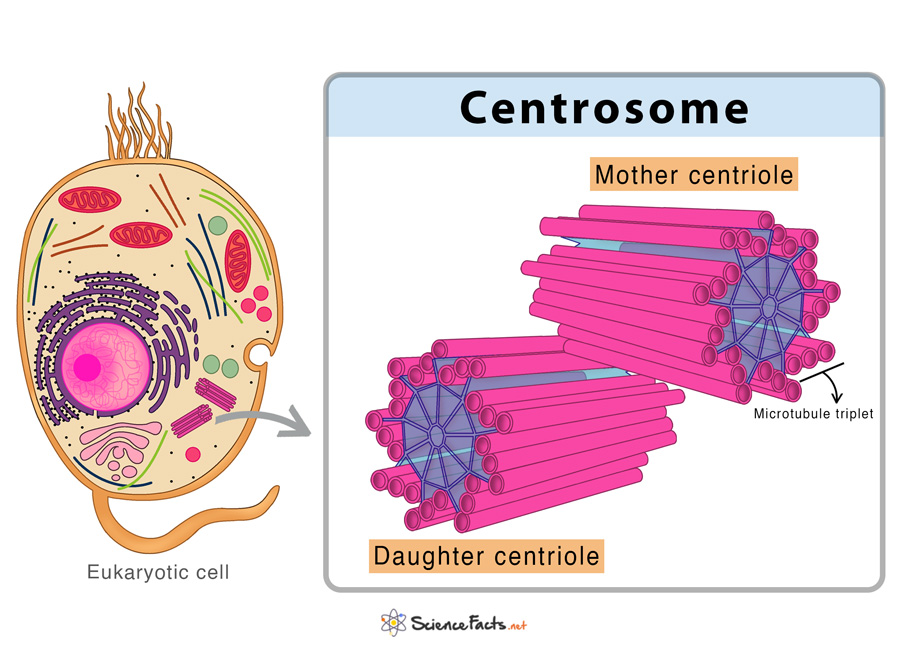
Each centriole of the centrosome consists of nine sets of short microtubule triplets (approximately 0.5 μm long and 0.2 μm wide) arranged in a cylinder with no central microtubules, called the 9 + 0 arrangement. A cilium replaces the centrosome during cellular differentiation in many cell types. However, once the cell starts dividing, the cilium is replaced again by the centrosome.
Main Purpose
It is the major microtubule-organizing center in animal cells. The centrosome thus helps protein dimers to assemble into microtubules, forming the mitotic spindle in dividing cells. The spindle fibers coordinate cellular processes such as cell motility, signaling, adhesion, developing cell polarity, and coordination of protein trafficking. The centrosome gets duplicated during the S phase of the cell cycle. Just prior to mitosis, the two centrosomes move apart until they reach the cell’s opposite poles. Microtubules arise from each centrosome, with their plus ends growing towards the metaphase plate, forming mitotic spindles. Centrosomes also play other critical roles during cell division and cell signaling, apart from their role in spindle formation.
Role in Cell Division
Changing the shape of the cell membrane, thus contracting the cell membrane and generating two cells by cytokinesisArranging the chromosomes in the metaphase plateEnsuring the equal distribution of chromosomes between the two newly formed daughter cells
The centrosome also has links to other cell organelles such as the nucleus, the Golgi, cell-cell junctions, and actomyosin cytoskeleton that helps in positioning the centrosome within the cell and shape the microtubule cytoskeleton, and forming cell polarity.
Role in Cell Cycle Progression
Activating cell signaling that allows cells to proceed to cytokinesis and the next round of the cycleSegregating signaling molecules such as mRNA so that they pass into one of the two daughter cells produced by mitosisDetermining the position at which the axon will grow out in some developing neurons