It is the principal structural component of plant and algal cell walls. While animals do not produce them, many microorganisms, like bacteria, also make biofilms. Humans cannot digest cellulose as they lack the enzymes that can break down the β-acetal linkages of cellulose. Anselme Payen discovered cellulose from plant matter in 1838 and determined its chemical formula. It was first used to produce the first successful thermoplastic polymer, celluloid. Cotton is the purest natural form of cellulose, consisting of over 90% cellulose. In 1920, Hermann Staudinger discovered the chemical structure of this macromolecule. Cellulose plays a vital role in providing structure and strength to plants. It also finds great importance in the industry.
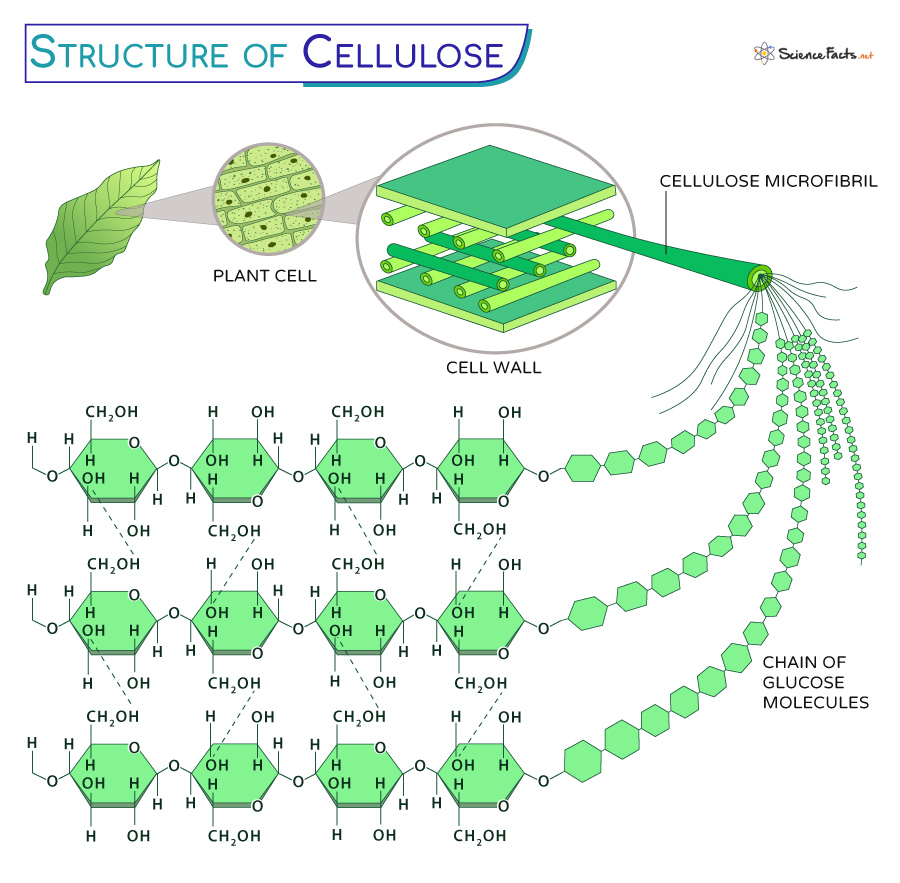
Structure and Properties of Cellulose
Types of Cellulose
Functions of Cellulose
Commercial Uses of Cellulose
Starch vs. Cellulose
Amylose vs. Cellulose
Glycogen vs. Cellulose
In contrast, cellulose II exists in regenerated cellulose fibers. The conversion of cellulose I to cellulose II is irreversible. Cellulose III is obtained by treatment of cellulose I or II with amines. Similarly, cellulose IV forms after treatment of cellulose III with glycerol at very high temperatures.
The most significant commercial application of cellulose is paper and paperboard production. Wood pulp, which contains a high percentage of cellulose, is processed to extract the cellulose fibers. These fibers are then converted into pulp to manufacture various paper products, including newspapers, books, packaging materials, and cardboard.Cellulose-based fibers are used in the textile industry to produce fabrics like rayon, modal, and lyocell. These fibers are derived from cellulose obtained from plant sources such as wood, bamboo, or cotton.Derivatives, such as cellulose acetate and methylcellulose, are used to produce biodegradable films and coatings, which are used to pack food items.Derivatives, like microcrystalline cellulose, are widely used as excipients in the pharmaceutical industry, serving as bulking agents in tablets and capsules.Cellulosic biomass, including agricultural residues, wood chips, and energy crops, is a potential feedstock for biofuel production.Many cellulose-derived polymers are biodegradable and serve as renewable resources. They tend to be non-toxic. Some common cellulose derivatives are celluloid, cellulose acetate, cellulose triacetate, nitrocellulose, methylcellulose, cellulose sulfate, and rayon.It is used in the construction industry to produce cellulose insulation.