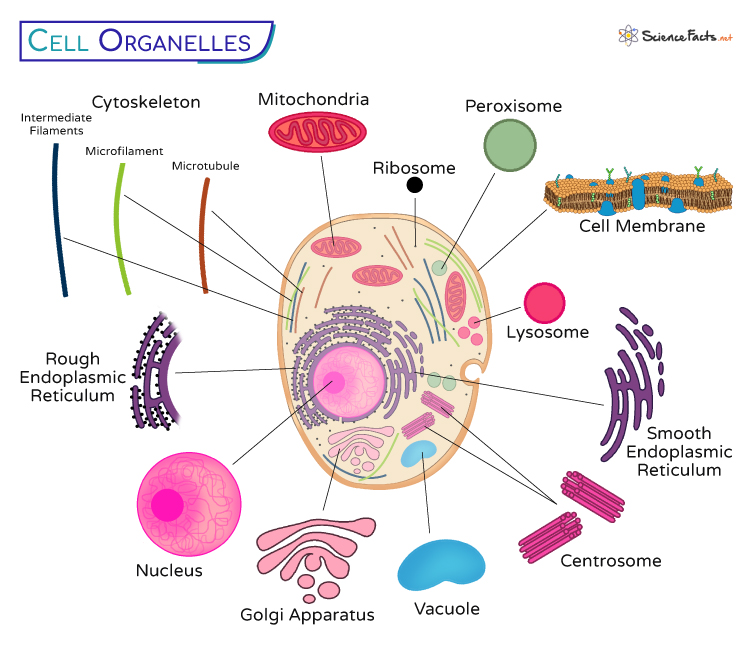
Membrane-bound organelles are essential as they allow proper segregation for their functioning in eukaryotic cells. All organelles in a cell are found embedded in a fluid-like material called cytoplasm. It is made of water, inorganic, and organic substances. In contrast to eukaryotes, prokaryotic cells like bacteria lack membrane-bound organelles. The organelles found in a generalized eukaryotic cell (plant and animals) are listed below:
1. Cell Membrane
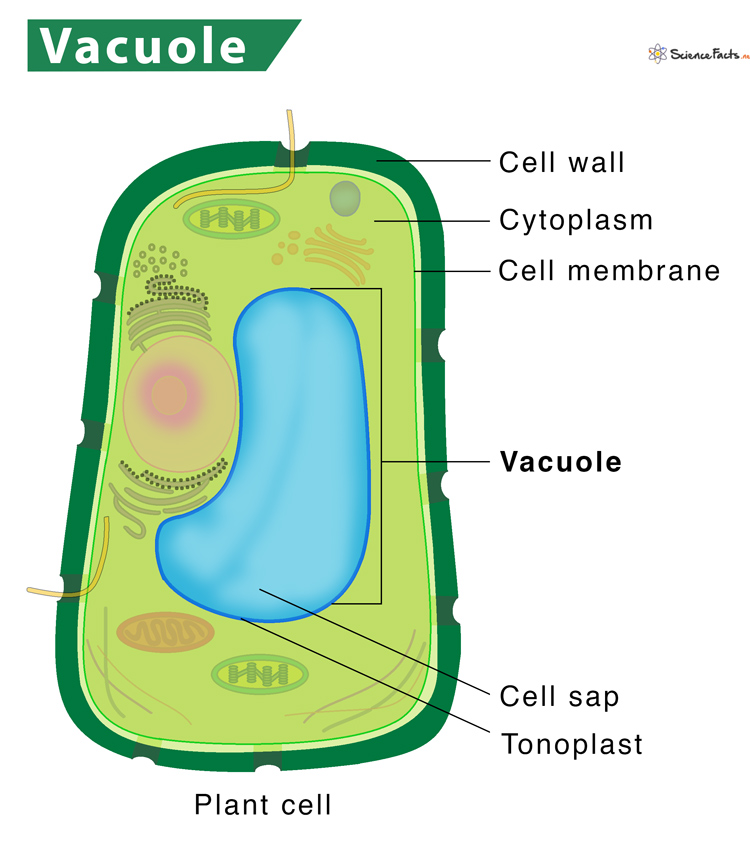
2. Vacuole
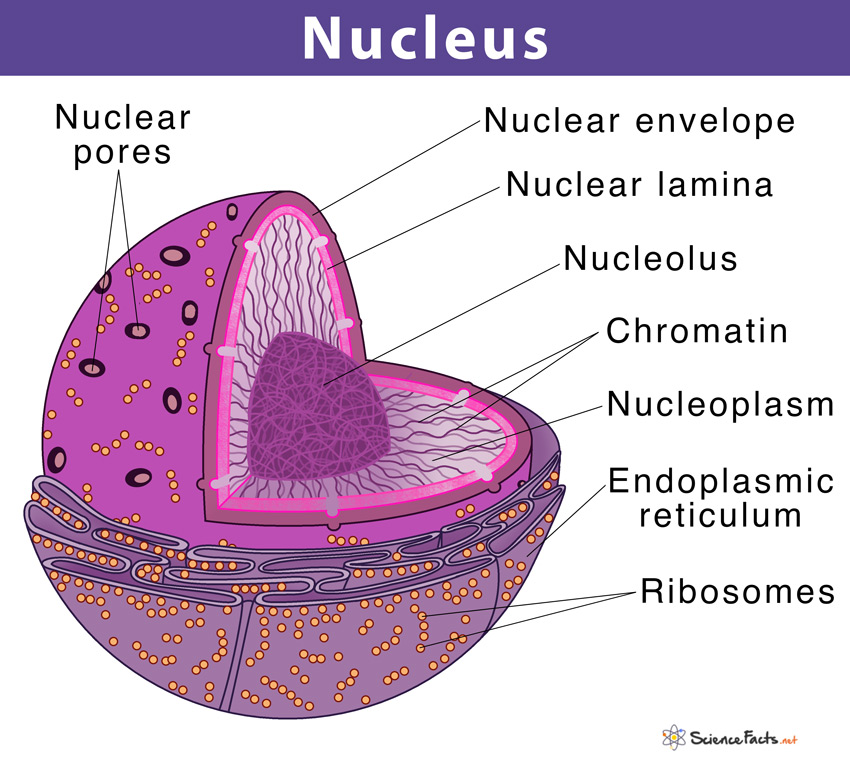
3. Nucleus
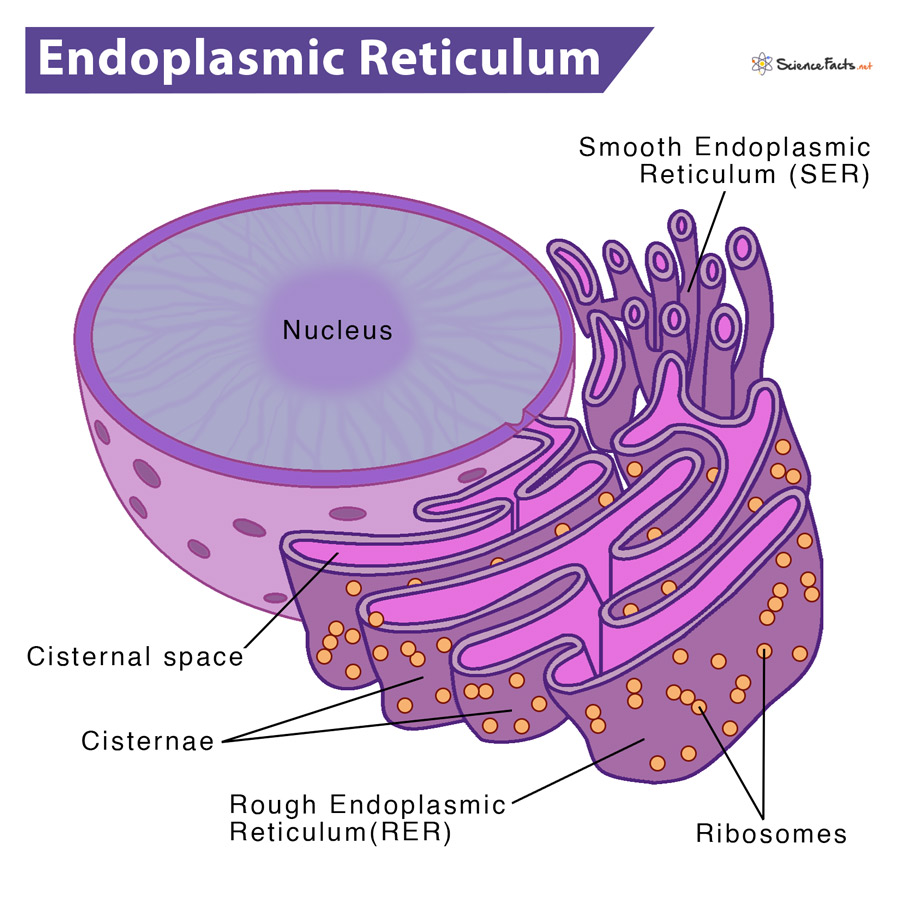
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
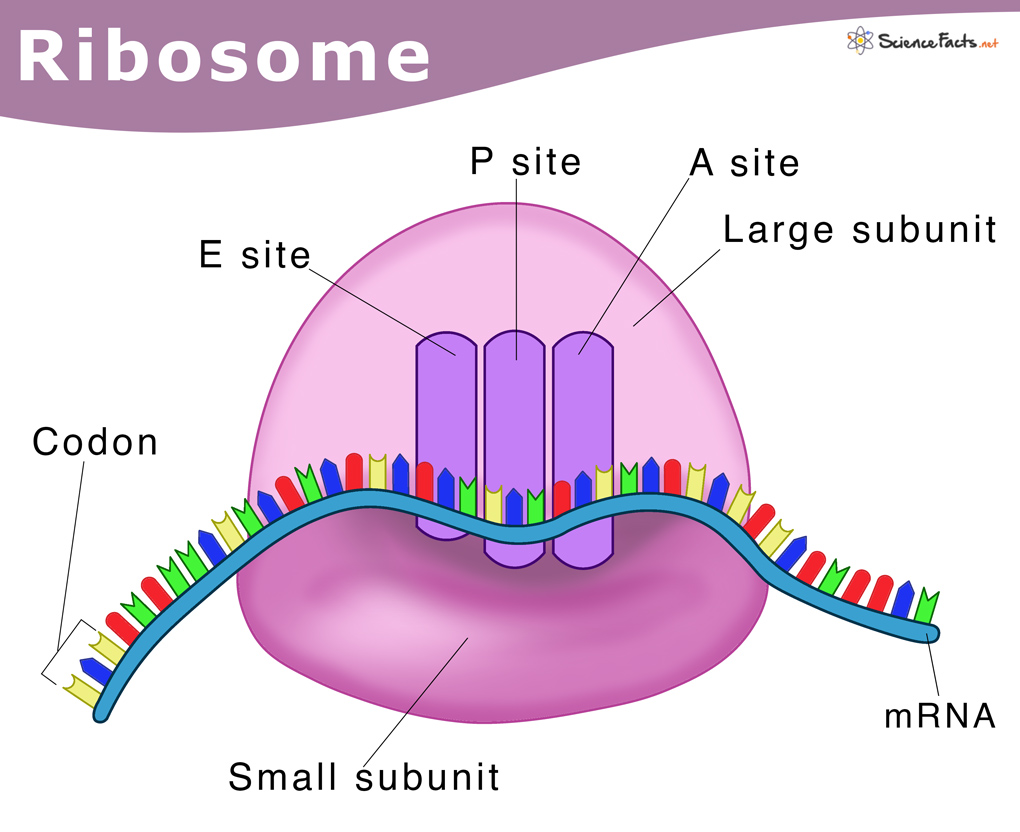
5. Ribosomes
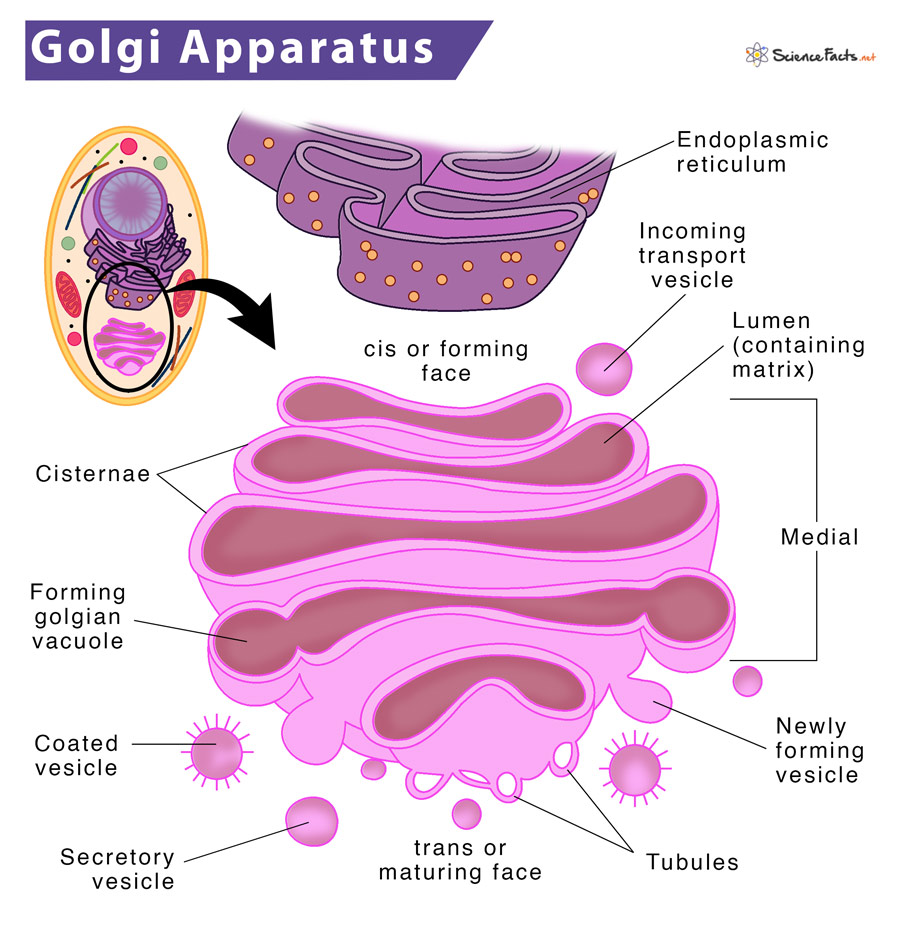
6. Golgi Apparatus
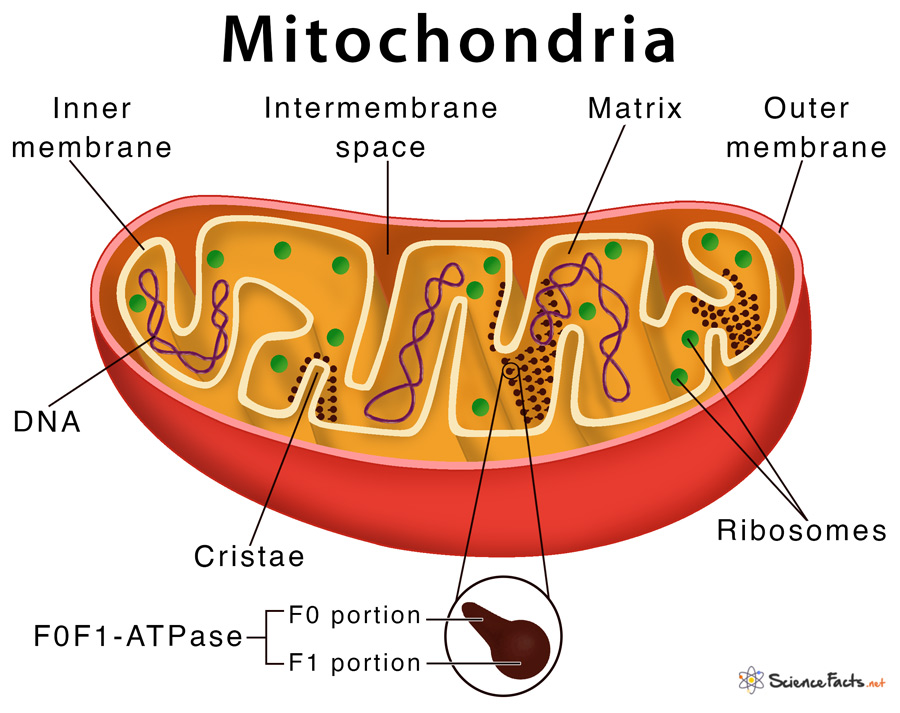
7. Mitochondria
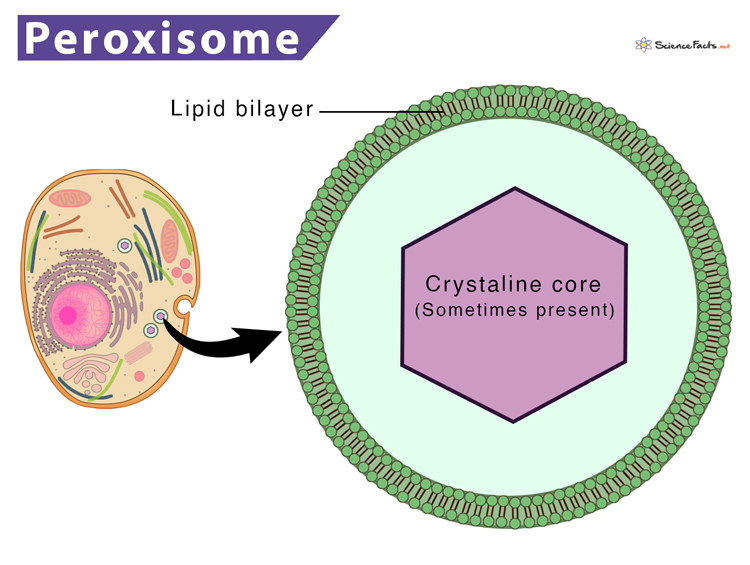
8. Peroxisomes
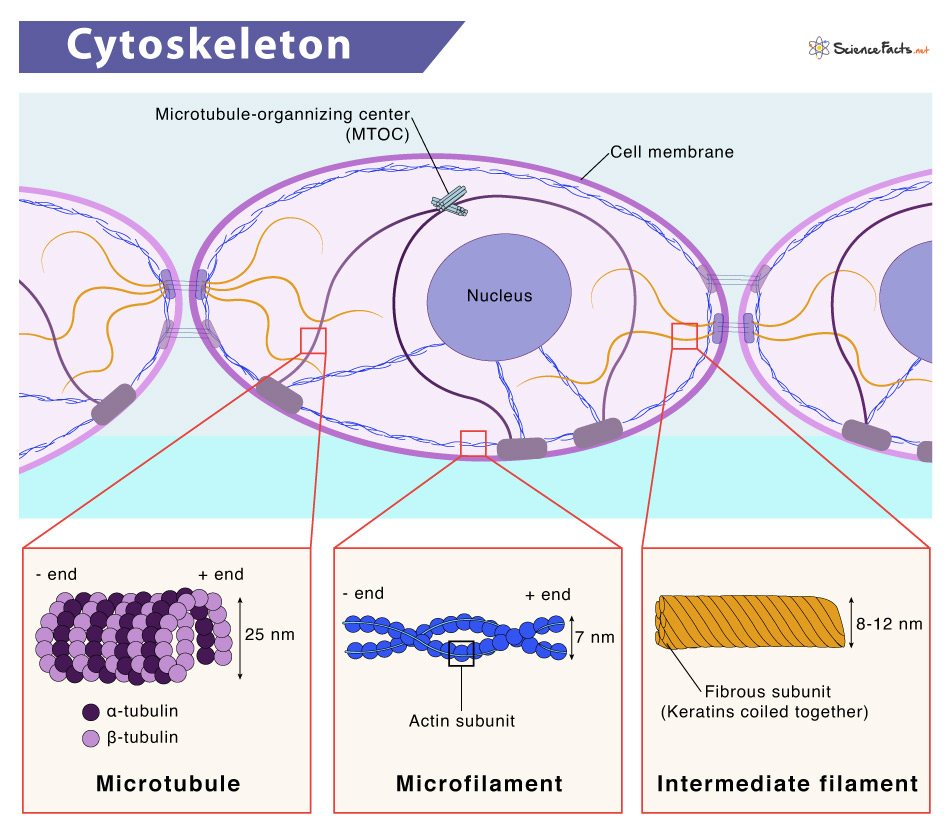
9. Cytoskeleton
Organelles Found Only in Plant Cells
Organelles Found Only in Animal Cells
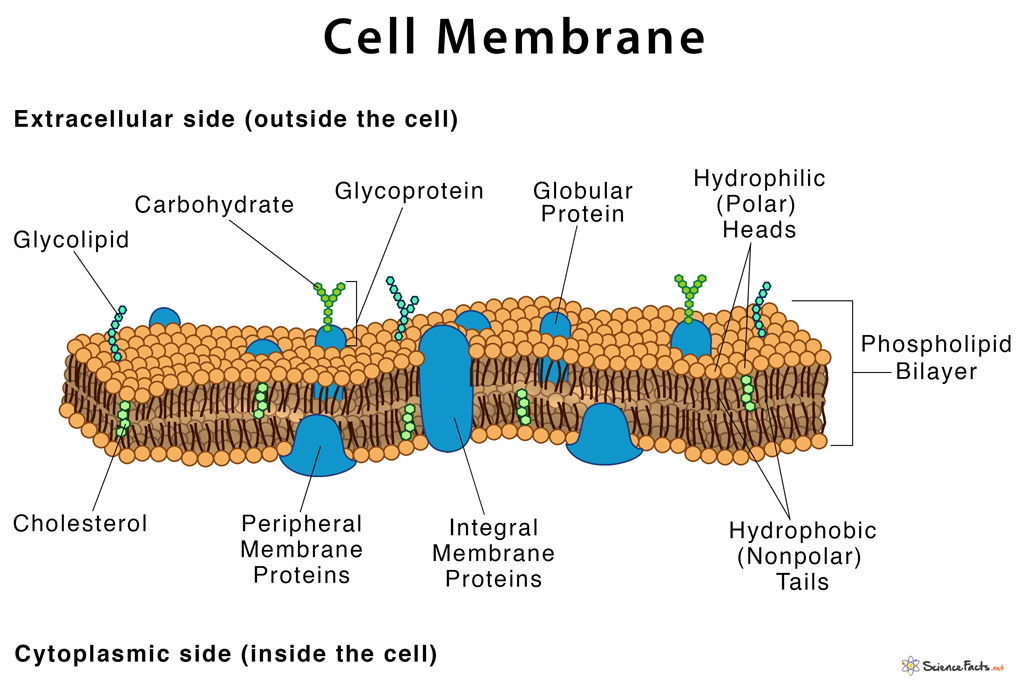
Cell membranes are made of phospholipid bilayers and are selectively permeable, allowing passage of certain substances while blocking others from entering the cell. The nucleus is thus called the control center of the cell. They are more active than all other organelles in causing apoptosis or programmed cell death. Apart from the above organelles found in both plant and animal cells, some are exclusively found in either of the two types.
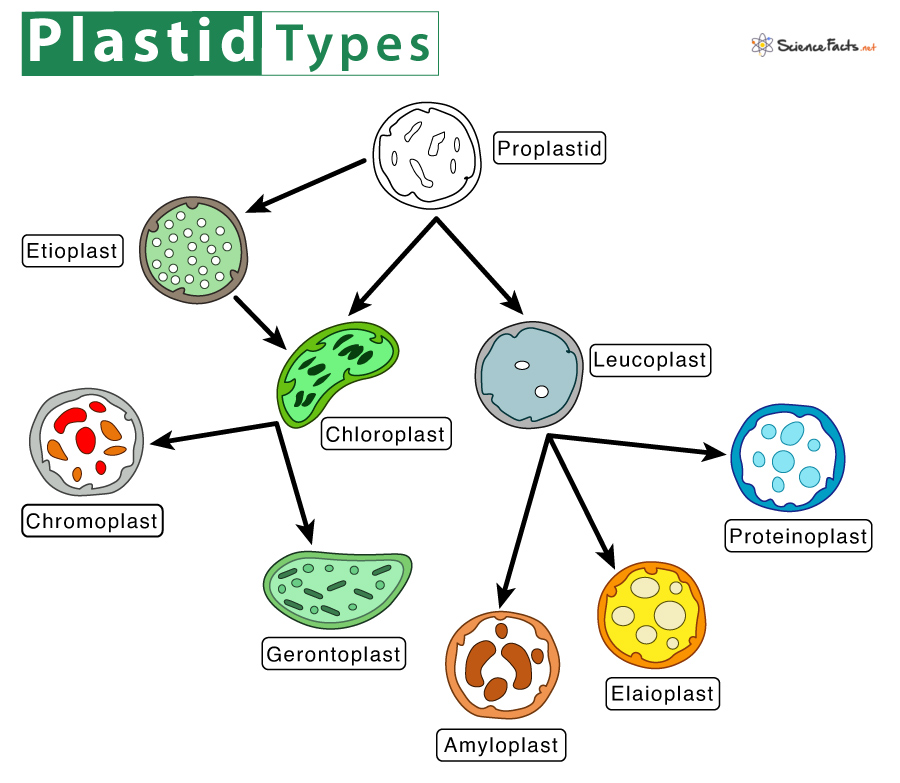
2. Plastids
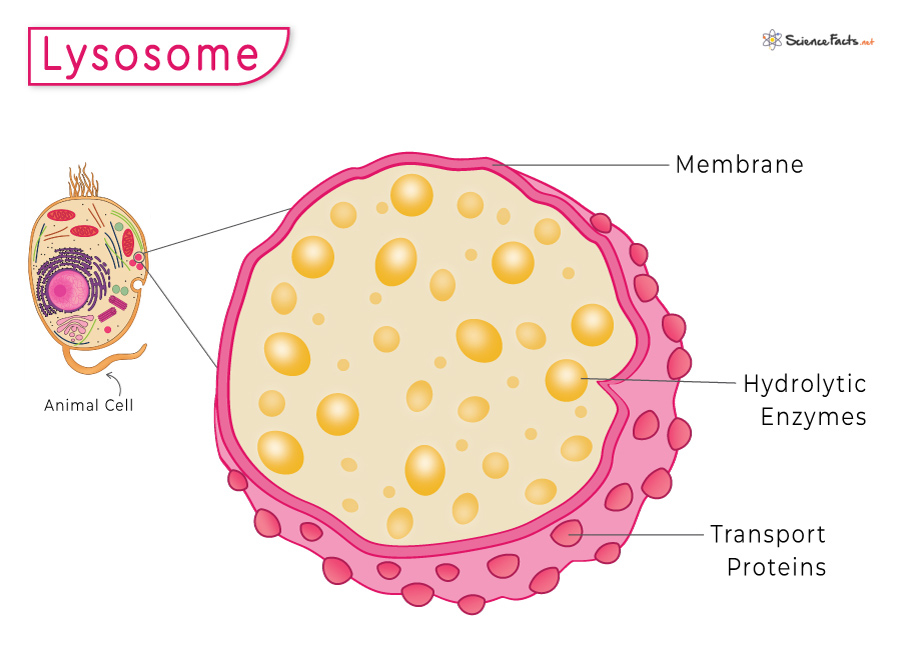
They are double membrane-bound organelles responsible for manufacturing or storing food in plants and algae. Chloroplast, chromoplast, and leucoplast are the types of plastids commonly found in them. Chloroplast harbors chlorophyll that helps plants to prepare their food through photosynthesis. In contrast, chromoplast is found in flowers and fruits that help pollinate, while leucoplast stores food. Lysosomes are rarely found in plant cells and are found to have no role in them.
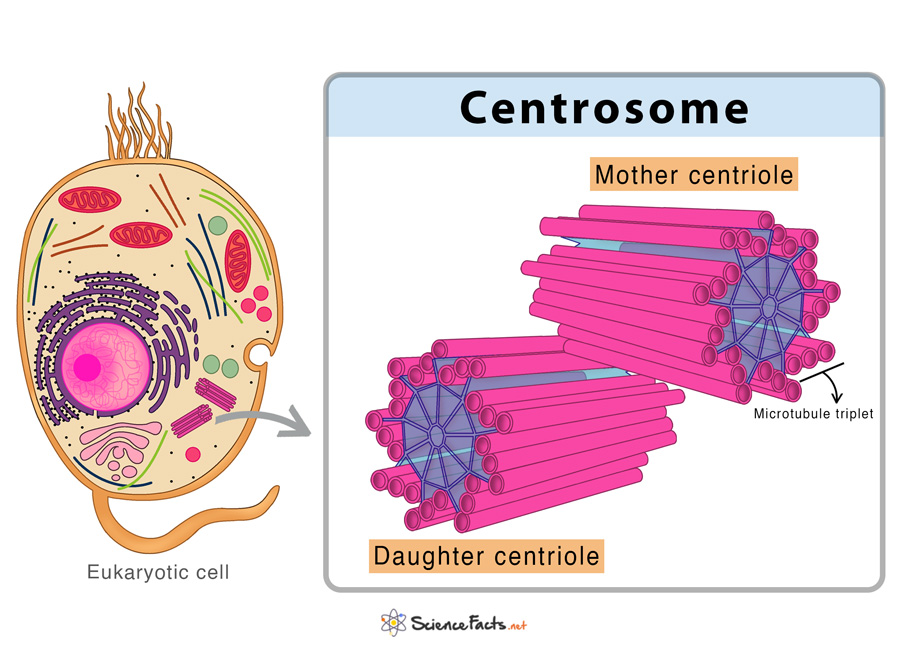
2. Centrosomes
They are specialized cell structures in animal cells participating in cell division. Centrosomes help separate the replicated chromosomes into the daughter cells equally. The collaborative functions of all these organelles within cells allow plants and animals to carry out essential functions, survive, and adapt to their environments.
Cell Organelles Chart
Here is a chart with the list of organelles found in a eukaryotic plant or animal cell for reference: