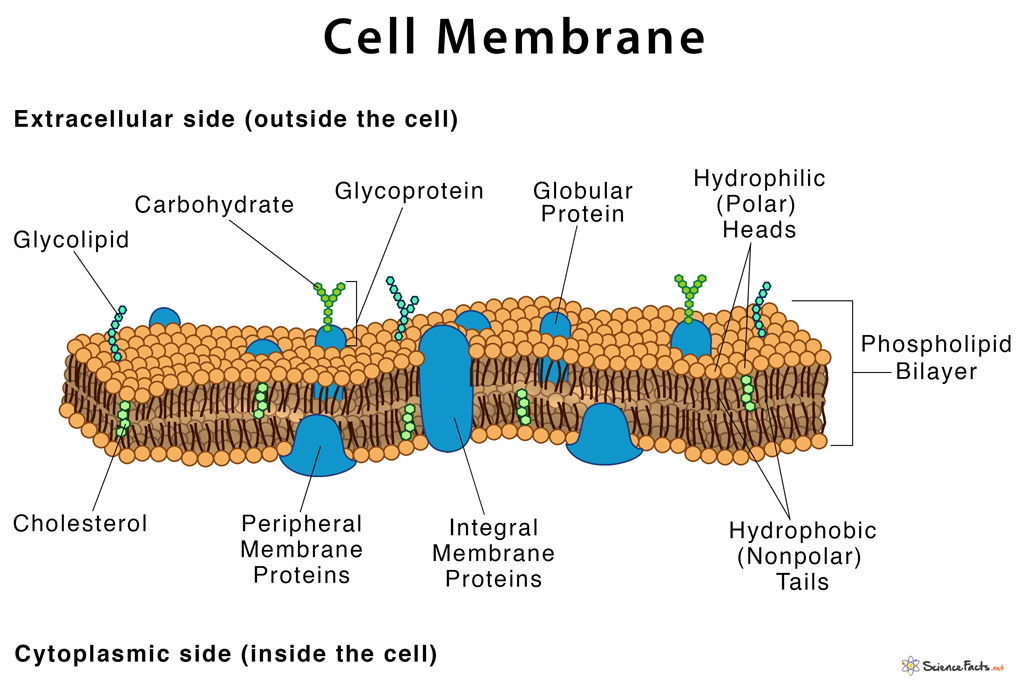
The most widely accepted model of the cell membrane was given by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson in 1972, popularly known as the fluid mosaic model. Described below are the three major parts along with their detailed make up:
1. Lipids
It is one of the main components of the cell membrane that makes up the cell’s structural framework. Membrane lipids are of the following types:
2. Proteins
It is the second major part of the cell membrane. The two main categories of membrane proteins are:
3. Carbohydrates
It is the least abundant component of the cell membrane. Carbohydrates are found on the outside surface of cells that exists in either of the following two forms:
Other Purposes
Protection and Cell Defense: Insulates the interior of the cell and provides mechanical support from outside shock and harmful agentsMaintaining Homeostasis: Determines the internal milieu of the cell, the physiological conditions such as temperature and osmotic pressure by maintaining the salt balanceMaintaining Concentration Gradient: Maintains the differences in concentration of substances inside and outside the cell thus helping in their transportSignal Transduction: Receives and processesthe extracellular signals by receptor molecules present in the cell membrane and relay them inside the cell for necessary actionsCatalysis of Chemical Reactions: Stimulates chemical reactions that help in the growth and metabolism of the cell using enzymesCell Communication: Allows exchange (receiving and sending) of messages between adjacent cellsthus helping them to function in a coordinated fashionAdaptation and Response: Helping to sense the extracellular environment and thus regulating the fluidity of the cell membranes by altering the lipid of the cellMaintaining Cell Shape and Morphology: Acting as the base of attachment for the cytoskeleton that helps in cell movement