Who discovered the Carbon Cycle?
What are the Major Steps of the Carbon Cycle?
Why is the Carbon Cycle Important?
How do Humans Affect the Carbon Cycle?
What are the Effects of Combustion of Fossil Fuels on the Carbon Cycle?
How Does Deforestation Affect the Carbon Cycle?
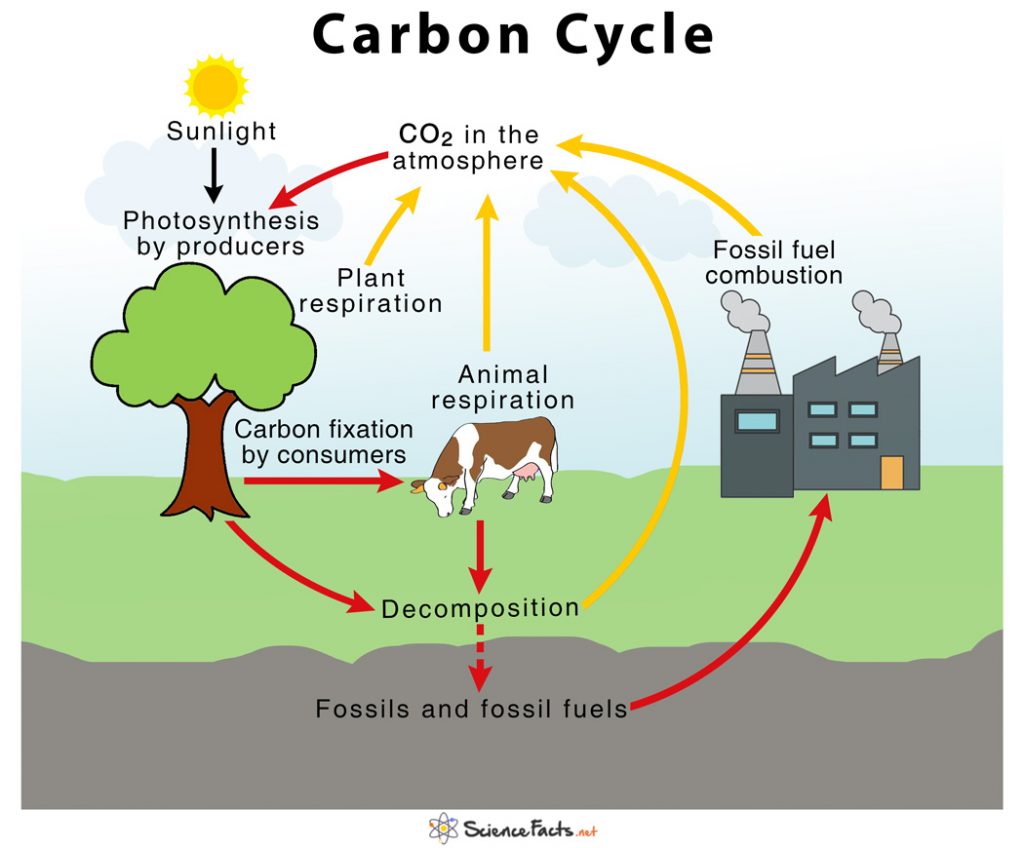
Carbon present in the air as carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants, the primary producers to produce food in the form of carbohydrates by a process called photosynthesis. This forms the foundation of the carbon cycle. Respiration by plants returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, thus once again contributing to the cycle in a different manner. 2. Role of Primary Consumers (Carbon Fixation and Cellular Respiration) The primary consumers such as cows and horses use plants as their food, and carbon gets accumulated and fixed into their bodies in the form of organic carbon, a process known as carbon fixation. Respiration by animals release carbon dioxide back to the atmosphere. 3. Role of Detritus Feeders (Decomposition) Once plants and animals die, the fixed organic carbon is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas through decomposition by the detritus feeders. 4. Role of Fossils and Fossil Fuels (Combustion) The carbon that is leftover in the body of the dead organisms after decay becomes fossil fuels over many years, which on combustion releases the carbon stored in them back to the atmosphere thus completing the cycle. Other Roles in Living Systems and the Environment:
Carbon forms an integral component of proteins, lipids, and DNA, the building blocks of all living thingsCarbon dioxide traps the long-wavelength radiations from the sun and prevents it from escaping into space, very much like the glass walls of a greenhouse, thus acting as a blanket over the planet and controlling the temperature of the earth
Combustion of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and natural gasesIndiscriminate cutting of trees or deforestation