They are equivalent to undifferentiated human stem cells. Thus, cambium tissues can form any types of cell – from a fundamental structural cell to a complete organ.
Functions in Plant
Layers of Cambium
A cambial cell divides to form two identical daughter cells. One of them remains meristematic and keeps dividing, while the other becomes xylem or a phloem mother cell. The cambium cells produce secondary xylem cells toward the central axis of the stem and secondary phloem cells toward the outside. Some other functions of cambium are:
Increasing the girth of the plant by forming the bark of woody plantsTransporting water and nutrients and contribute to plant growthProtecting the plants from external injuriesRepairing and regenerating wounds
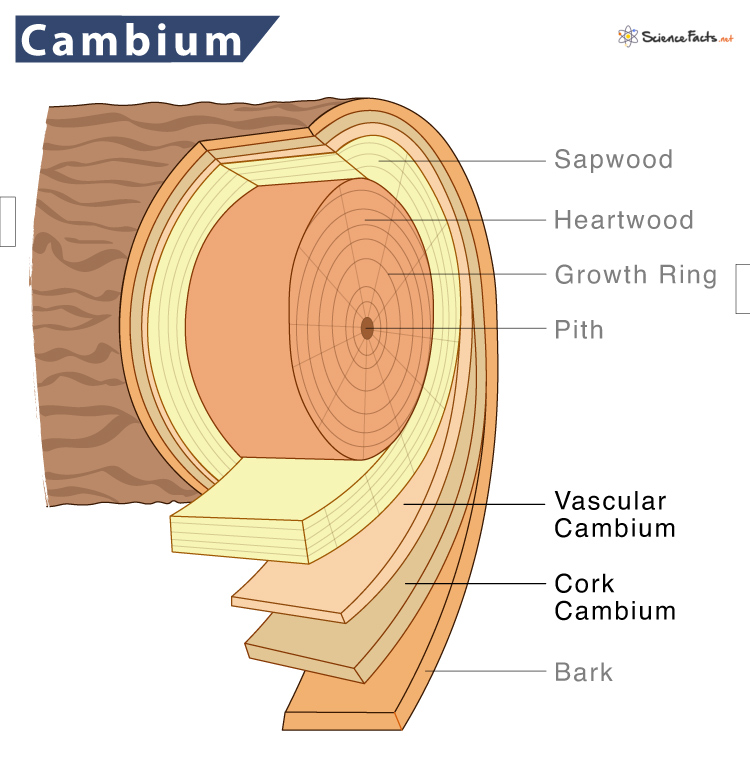
1. Cork Cambium
It is a meristematic tissue from which the plant grows. Cork cambium helps replace or repair the epidermis of roots in plants and forms the tree’s bark. Since it occurs where there is secondary growth, cork cambium is found in dicots (plants with two cotyledons) and gymnosperms (seed-forming plants) but are absent in monocots. To be precise, cork cambium is found in woody plants.
2. Unifacial Cambium
It is a cambium tissue that matures to form xylem but not phloem. The plants with unifacial cambium do not exhibit secondary growth and thus are shorter in height, not more than 50 meters. Unifacial cambium is thus found in smaller, less-complex plants such as lycophytes – mosses and warts.
3. Vascular Cambium
It is the primary growth tissue in stems and roots of vascular plants, especially in dicots such as oak trees and gymnosperms such as pine trees. Vascular Cambium gives rise to secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark. It occurs in the vascular bundles in herbaceous plants, arranged like beads on a necklace. While in woody plants, it is arranged in a cylindrical form as a continuous ring. Vascular cambium is also known as main cambium, wood cambium, or bifacial cambium.