The term ‘acid rain’ was used for the first time by Robert Angus Smith in 1852 while examining rainwater reaction from the U.K. and Scotland’s industrial sites.
Where does Acid Rain Occur?
What Causes Acid Rain and How is it Formed
How does Acid Rain Affect the Environment?
Solutions to Problems of Acid Rain
Advantages of Acid Rain
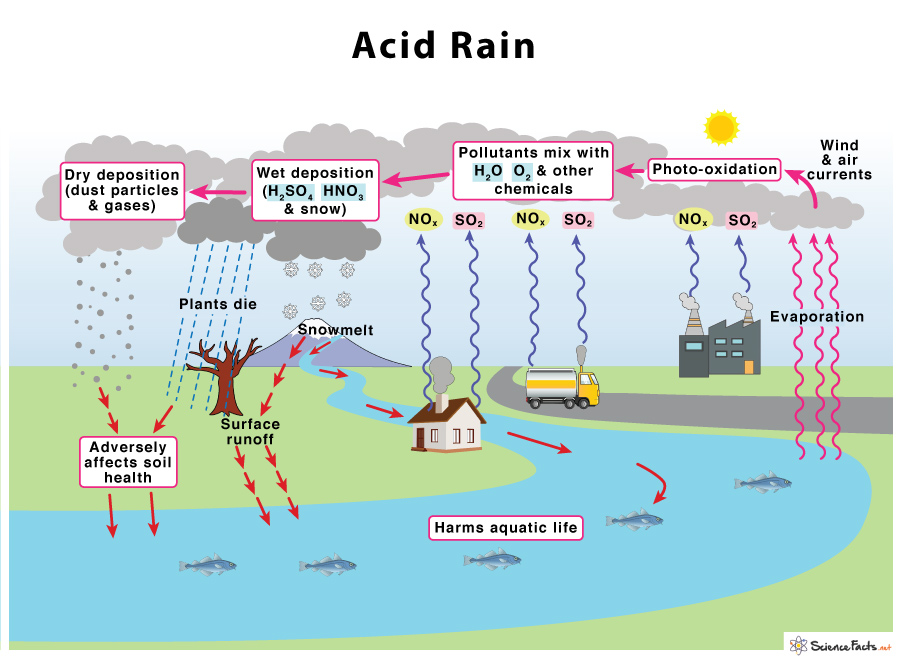
The process starts when SO2 and NOX are emitted into the atmosphere, undergo photooxidation in the presence of sunlight and oxygen, and react with water and other components present in the atmosphere. Wind and air currents spread these acidic substances over long distances. They eventually precipitate down in the form of wet deposits such as rain (sulfuric and nitric acids), fog, snow, and mist, or dry deposits as dust, gas, and smoke, adversely affecting soil heath and aquatic life.
How Acidic is Acid Rain?
Normal rain is slightly acidic, having a pH of 5.6. It forms when carbon dioxide reacts with water to form weak carbonic acid, which has no harmful effects. However, acid rain generally has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4. Here, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide undergo oxidation before reacting with water. The following equations show the formation of acid rain: Formation of Sulfuric Acid SO2 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq) H2SO3 (aq) + O2 (g) → 2H2SO4 (aq) Formation of Nitric Acid N2 (g) +O2 (g) → 2NO(g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g) 2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO3 (aq) + HNO2 (aq) Since nitrous acid is unstable, it eventually oxidizes to nitric acid. Thus, the overall reaction is: 2N2 (g) + 5O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) → 4HNO3 (aq)
- Effects on Soil: It robs the soil of its essential nutrients such as calcium, releasing aluminum that prevents water uptake in plants. It causes a change in soil composition, thus affecting crop production. Acid rain also affects forests, especially those at higher elevations.
- Effects on Plants: It weakens the trees by washing away the waxy, protective coating on leaves, thus damaging them. Acid rain washes away the essential nutrients and minerals from the soil, causing stunted growth in plants by affecting photosynthesis.
- Effects on Water Bodies: Acid rain makes lakes, streams, ponds, rivers, and other water bodies more acidic. It adversely affects aquatic life, such as freshwater shrimps, snails, and mussels. Most fish species cannot survive a pH of less than 5. When the pH becomes 4, the lake is dead, which means it becomes devoid of life. Again, the fall of acid rain causes aluminum absorption from the soil, which is carried into the water bodies. The combination of both makes water bodies more toxic for their survival. Some aquatic species can tolerate acidic pH better than others. Nevertheless, since all ecosystems are interconnected, organisms in one ecosystem depend on the other for their survival. For example, if a fish species disappear, the animals, including the birds that feed on them, will also become extinct.
- Effects on Building, Monument, and Statue: All structures, especially those made of limestone and sandstone, are mostly affected by the effect of acid rain. The calcium carbonate (limestone) present in the rocks or monuments reacts with sulfuric acid to form calcium sulfate, making them corrode. The soluble substances in the acidic deposition get dissolved in water and then washed away, known as chemical weathering. Corrosion in Taj Mahal is a real-life example. The chemical reaction causing their corrosion is given below: CaCO3 (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → CaSO4 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) Another instance is the Statue of Liberty, which is made of copper. It is also getting damaged by the cumulative action of acid rain and oxidation, thus becoming green.
- Other Impacts: It causes corrosion of water pipes, which results in the leaching of heavy metals such as lead, iron, and copper into drinking water. This effect can adversely affect humans. Dry precipitation is sometimes associated with heart and lung problems such as asthma and bronchitis.
Regulating their emission from coal-based and metal extracting industries by filtering the exhaust before releasing into the environmentReducing the dependence on non-renewable energy resources such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas. According to the EPA, this can be done by increasing renewable energy consumption from sunlight, wind, and water.Using eco-friendly vehicles instead of petrol or diesel-based ones. The use of catalytic converters filters the exhaust gases from the vehicles before releasing them into the environment. Planting more trees or afforestation helps to purify the atmosphere by reducing toxic gases.Restoring water-body damage by using powdered limestone that neutralizes the water, a process known as liming.
Makes holes in the limestone below ground resulting in caves and groundwater storage and providing habitat for some speciesSulfuric acid rain limits global warming by offsetting methane’s natural production by microbes in wetland areas, thereby limiting climate change.